What is Interferon?
- Interferons (IFNs) are a group of antiviral and immune-modulating proteins produced naturally by cells in response to viral infections.
- They are used to treat viral infections, cancer, and immune disorders.
Types of Interferons
- Interferon-α (IFN-α) → Used for treating hepatitis B, hepatitis C, and leukemia.
- Interferon-β (IFN-β) → Used for treating multiple sclerosis.
- Interferon-γ (IFN-γ) → Used for treating chronic granulomatous disease and some cancers.
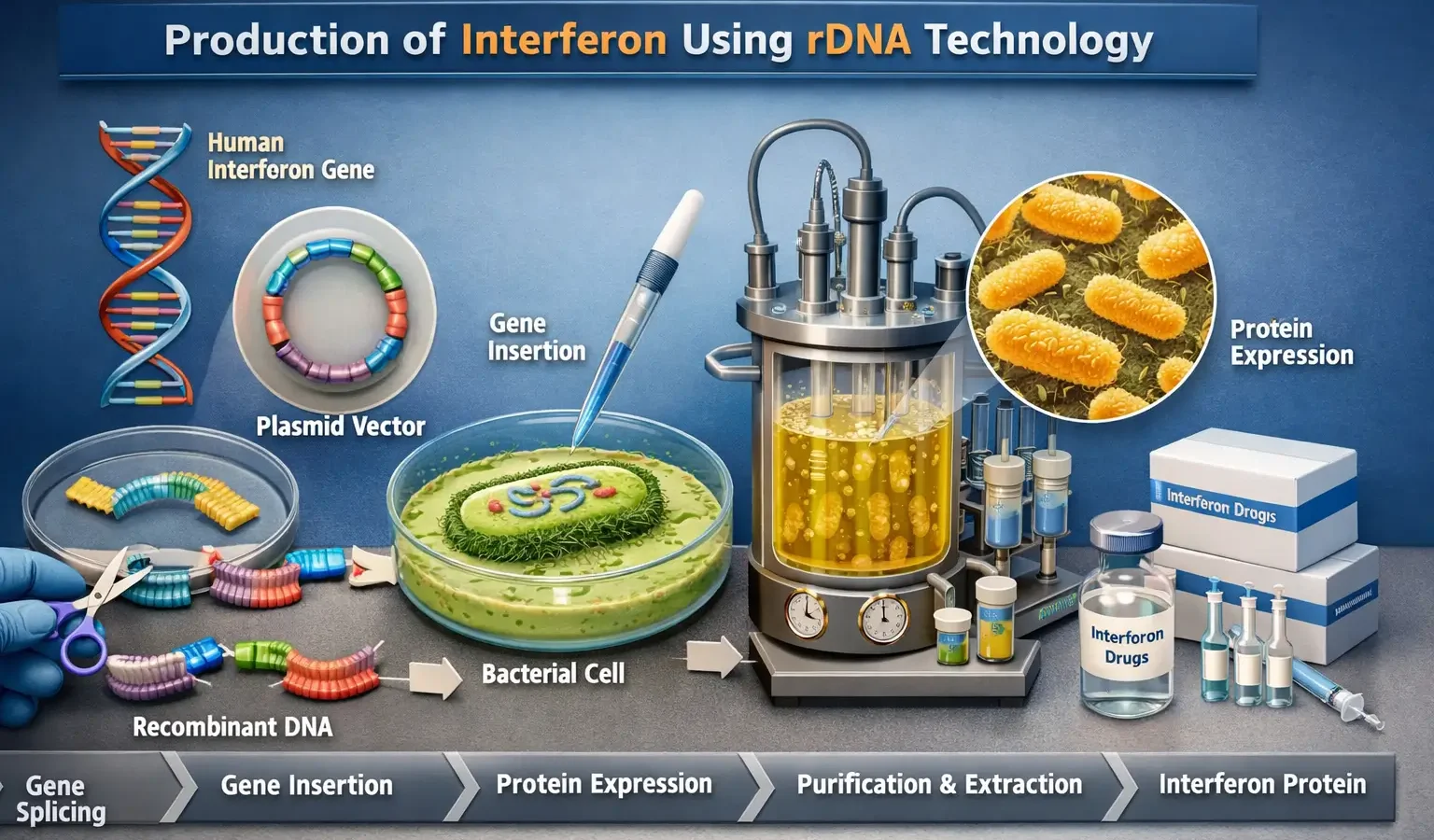
Production of Recombinant Interferon
- Isolation of the Gene – The gene encoding human interferon is isolated.
- Cloning into a Vector – The gene is inserted into a bacterial or mammalian expression vector.
- Host Cell Expression – The recombinant vector is introduced into host cells such as E. coli or Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells for protein production.
- Purification – The interferon protein is purified using chromatography to obtain a highly pure form.
Advertisements
Medical Applications
- Treatment of hepatitis B and C.
- Used in therapy for multiple sclerosis.
- Effective in treating certain cancers.
Commercial Production Example
- The first recombinant interferon, Roferon-A, was produced using E. coli.
- Interferon is used to treat viral infections (hepatitis, HPV), cancers (leukemia, melanoma), and immune disorders (multiple sclerosis).