- Structure and functions of cell: Cells are the basic structural and functional units of life.
- They can be classified into two main types: prokaryotic cells (found in bacteria and archaea) and eukaryotic cells (found in plants, animals, fungi, and protists).
- Both cell types share some basic structures and functions, but eukaryotic cells are generally larger and more complex than prokaryotic cells.
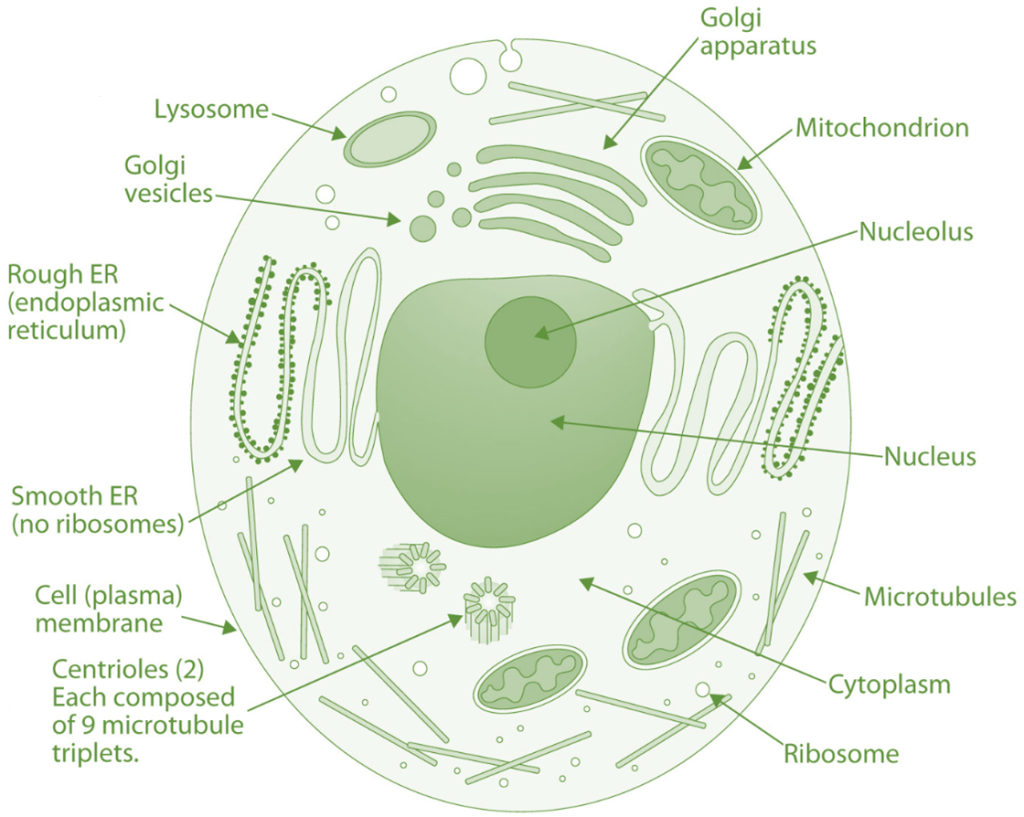
Here are the main structures (organelles) and functions of a typical eukaryotic cell

Cell membrane (plasma membrane)
- A selectively permeable barrier that surrounds the cell, controlling the passage of substances in and out of the cell.
- It is composed of a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins.
- Function:
- Controls the movement of substances in and out of the cell, maintaining a balance of ions, nutrients, and waste products.
- It also mediates cell-to-cell communication and recognition.
This is a sample ad placement!
Cytoplasm
- The gel-like substance within the cell membrane that contains organelles, enzymes, and other molecules required for the cell’s functions.
- It is the site of many cellular processes.
- Function:
- Provides a medium for cellular processes to occur, suspending organelles and facilitating the transport of molecules throughout the cell.
Nucleus
- The control center of the cell, which contains the cell’s DNA, organized into chromosomes.
- The nucleus is surrounded by a double-layered nuclear membrane and contains a nucleolus, which is involved in ribosome synthesis.
- Function:
- Contains genetic information (DNA) and regulates gene expression, controlling the synthesis of proteins required for cellular function, growth, and reproduction.
- It also houses the nucleolus, which produces ribosomes.
This is a sample ad placement!
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
- A network of membranous tubules and sacs that play a crucial role in protein and lipid synthesis.
- The ER can be classified into two types:
- smooth ER (involved in lipid synthesis and detoxification)
- rough ER (studded with ribosomes and involved in protein synthesis).
- Function:
- Involved in protein synthesis (rough ER) and lipid synthesis (smooth ER).
- The rough ER is studded with ribosomes and produces proteins destined for secretion or incorporation into the cell membrane.
- The smooth ER produces lipids and detoxifies harmful substances.
Ribosomes
- Small structures made of protein and RNA that are responsible for protein synthesis.
- They can be found free-floating in the cytoplasm or attached to the rough ER.
- Function:
- Small structures made of protein and RNA responsible for protein synthesis.
- They can be found free-floating in the cytoplasm or attached to the rough ER.
This is a sample ad placement!
Golgi apparatus
- A series of flattened, membrane-bound sacs that modify, package, and sort proteins and lipids for transport to their final destinations within or outside the cell.
- Function:
- Modifies, packages, and sorts of proteins and lipids for transport to their final destinations within or outside the cell.
Mitochondria
- The powerhouse of the cell, responsible for producing ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the cell’s primary energy source, through cellular respiration.
- Mitochondria have their own DNA and are believed to have originated from an endosymbiotic relationship with bacteria.
- Function:
- Produce ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the cell’s primary energy source, through cellular respiration.
Lysosomes
- Small, membrane-bound organelles containing hydrolytic enzymes that break down waste materials, cellular debris, and foreign substances.
- Function:
- Contain hydrolytic enzymes that break down waste materials, cellular debris, and foreign substances.
This is a sample ad placement!
Peroxisomes
- Organelles that contain enzymes involved in various metabolic reactions, including the breakdown of fatty acids and the detoxification of harmful substances.
- Function:
- Contain enzymes involved in various metabolic reactions, including the breakdown of fatty acids and the detoxification of harmful substances.
Cytoskeleton
- A network of protein filaments that provides structural support, maintains cell shape, and aids in cell movement and division.
- The cytoskeleton consists of microtubules, microfilaments, and intermediate filaments.
- Function:
- A network of protein filaments that provide structural support, maintain cell shape, and aid in cell movement and division.
- The cytoskeleton consists of microtubules, microfilaments, and intermediate filaments.
Thank you for reading from Firsthope's notes, don't forget to check YouTube videos!
This is a sample ad placement!
