Reactions of Benzene
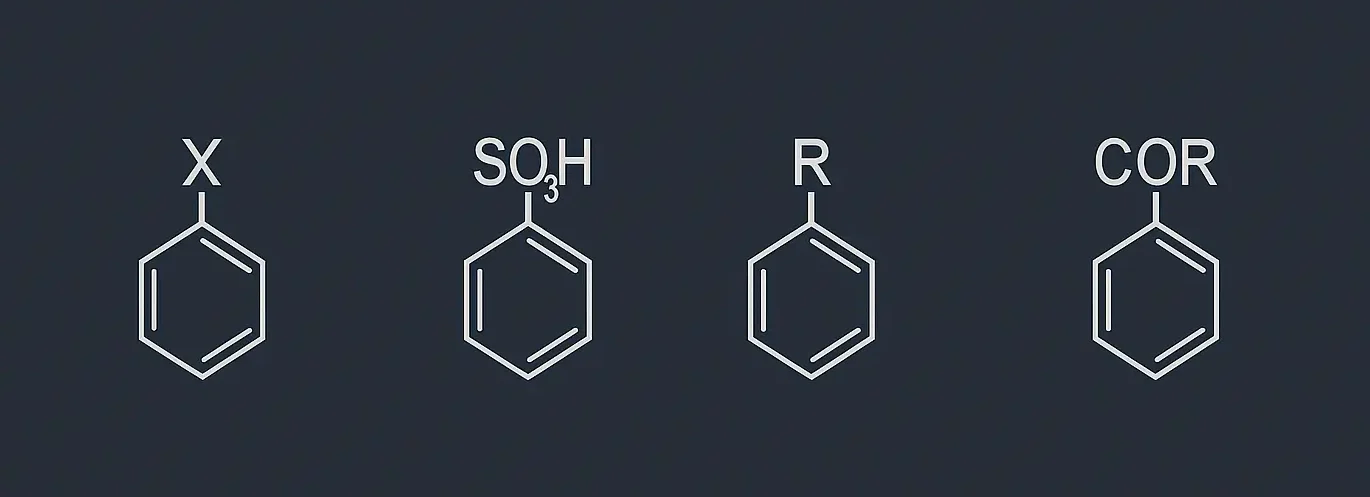
Reactions of Benzene: Benzene (C₆H₆) is a highly stable aromatic hydrocarbon due to its conjugated π-electron system. This stability makes benzene a prime candidate for electrophilic substitution reactions, where an electrophile replaces one of the hydrogen atoms on the benzene ring. Here are the key electrophilic substitution reactions of benzene: nitration, sulphonation, halogenation, Friedel-Crafts alkylation, … Read more