Introduction to Pharmaceutical Biotechnology Notes [U-1]
Buy Premium
Get The High-Quality Pdf Notes on App
Advertisements
Introduction to Biotechnology in Pharmaceutical Sciences
- Introduction to Biotechnology in Pharmaceutical Sciences
- Enzyme Biotechnology – Methods of Enzyme Immobilization and Applications
- Biosensors: Working and Applications in the Pharmaceutical Industry
- Brief Introduction to Protein Engineering
- Use of Microbes in Industry
- Production of Enzymes — General Considerations and Examples
Production of Specific Enzymes
- Amylase
- Catalase
- Peroxidase
- Lipase
- Protease
- Penicillinase (Beta-lactamase)
- Basic Principles of Genetic Engineering
Advertisements
Other Units of Pharmaceutical Biotechnology
Pharmaceutical Biotechnology
Advertisements
Other Subjects of B Pharmacy 6th Semester
Topic wise notes of:
Biopharmaceutics and Pharmacokinetics
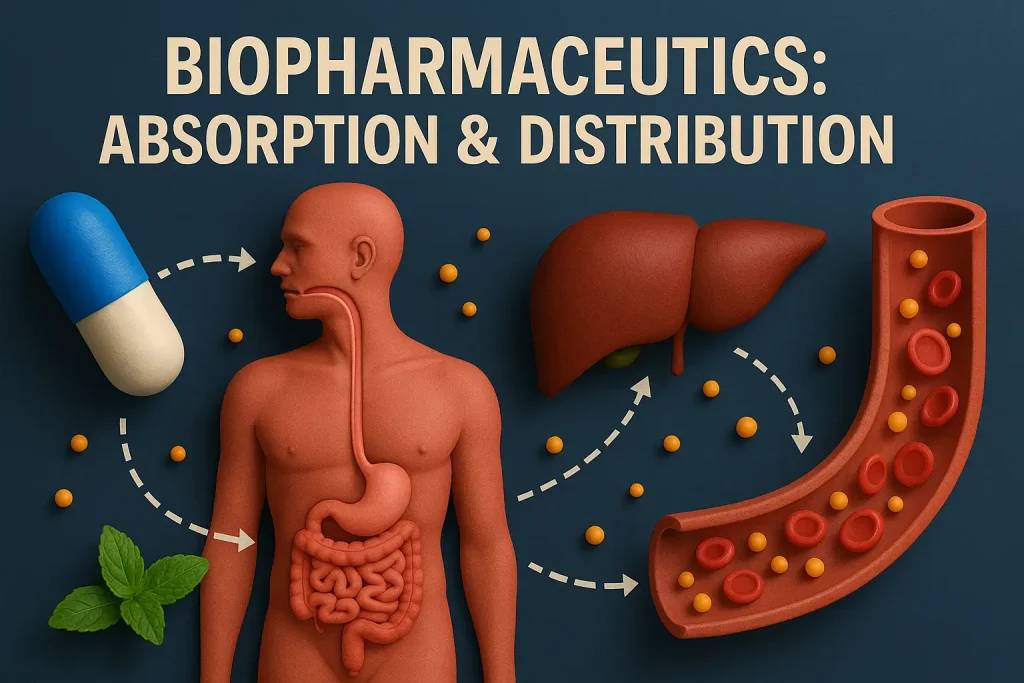
- Biopharmaceutics: Absorption & Distribution
- Drug Elimination, Bioavailability & Bioequivalence
- Pharmacokinetics Models, Dosing & Parameters
- Multicompartment models
- Nonlinear Pharmacokinetics
Advertisements
Topic wise notes of:
Medicinal Chemistry III
- Antibiotics & Aminoglycosides
- Antibiotics & Antimalarials: Structures & SAR
- Anti-TB, UTI & Antiviral Agents
- Antifungals, Antiprotozoals & Sulfonamides
- Intro to Drug Design & QSAR Approaches
Topic wise notes of:
Pharmaceutical Quality Assurance
- Quality Assurance, GMP, ICH, QbD & Quality System
- GMP: Personnel, Premises & Equipment Control
- Quality Control and Good Laboratory Practice
- Complaints & Document Management
- Calibration and Warehousing
Advertisements
Unit I: Introduction to Pharmaceutical Biotechnology Notes– Summary
Introduction to Biotechnology
Biotechnology uses living systems to create useful products. In pharmaceutical sciences, it helps make drugs, vaccines, and better treatments.
Enzyme Biotechnology
Enzymes speed up chemical reactions.
- Immobilization Methods: Adsorption, covalent bonding, entrapment, encapsulation, and cross-linking help reuse enzymes and keep them stable.
- Applications: Used in making antibiotics, vitamins, and other drugs.
Biosensors
Biosensors detect biological changes and convert them into signals.
- How They Work: They combine a biological part (like an enzyme) with a detector.
- Uses: Check glucose levels, monitor drug quality, and detect bacteria.
Microbes in Industry
Microbes help make many products.
- Used For: Fermentation and enzyme production.
- Examples of Enzymes:
- Amylase: breaks down starch
- Catalase and Peroxidase: break down harmful substances
- Lipase: breaks down fats
- Protease: breaks down proteins
- Penicillinase: breaks penicillin
Genetic Engineering
Changes genes to make better products.
At FirstHope, we provide BPharm notes that are topic-wise, easy to understand, and designed strictly as per the AKTU and Other Universities, hence designed according to PCI syllabus.
Advertisements