Biopesticides/bioinsecticides are natural pest control agents derived from microbes and plants used for safe and sustainable farming.
Biopesticides and Bioinsecticides
- Biopesticides, also known as biological pesticides, are natural pest control agents derived from bacteria, fungi, viruses, plants, and other living organisms.
- They effectively manage insects, mites, and plant pathogens while being environmentally friendly and safer than conventional chemical pesticides.
- Bioinsecticides are a type of biopesticide specifically targeting insect pests.
- They are widely used in field crops, orchards, and greenhouses to control pests without harming non-target organisms.
Examples of Biopesticides/Bioinsecticides:
- Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) – A bacterium that produces insecticidal toxins.
- Neem Oil – A botanical pesticide effective against a range of insects.
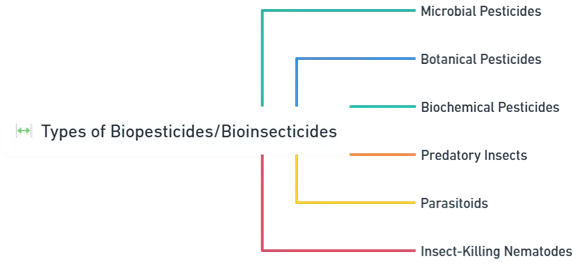
Types of Biopesticides/Bioinsecticides:
-
Microbial Pesticides:
- Made from bacteria, fungi, and viruses.
- Examples: Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt), Beauveria bassiana, Metarhizium anisopliae.
-
Botanical Pesticides:
- Derived from plant extracts and essential oils.
- Examples: Neem oil, pyrethrin, rotenone.
-
Biochemical Pesticides:
- Use naturally occurring substances like pheromones or plant growth regulators.
- Examples: Insect sex pheromones, azadirachtin (from neem).
-
Predatory Insects:
- Beneficial insects that prey on pests.
- Examples: Ladybugs, praying mantises.
-
Parasitoids:
- Insects that lay eggs inside pests, eventually killing them.
- Examples: Parasitic wasps, parasitic flies.
-
Insect-Killing Nematodes:
- Microscopic worms that attack soil-dwelling pests.
- Examples: Steinernema and Heterorhabditis species.
Click Here to Watch the Best Pharma Videos