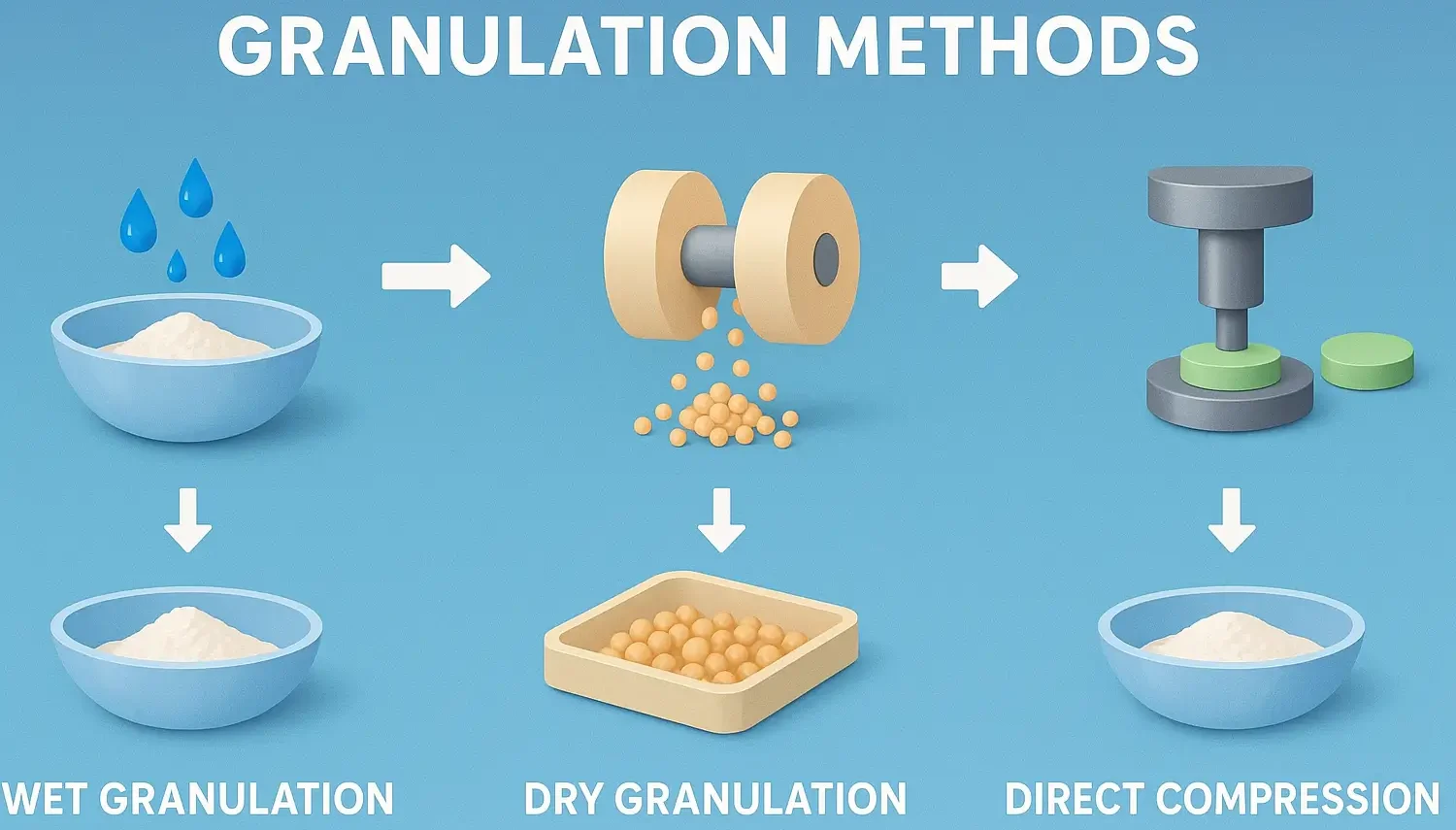
- Granulation Methods are the processes of particle size enlargement by forming agglomerates (granules) to improve flowability, compressibility, and uniformity of powders before tablet compression.
- It is classified into wet granulation, dry granulation, and direct compression.
1. Wet Granulation Methods:
Definition:
- Involves the use of a liquid binder to form granules by agglomerating the powder particles.
- Suitable for drugs that are not sensitive to moisture or heat.
Process:
-
Weighing and Mixing:
- API and excipients are blended uniformly.
-
Binder Addition:
- A liquid binder (e.g., starch paste) is added to form a wet mass.
-
Wet Sieving:
- Wet mass is passed through a sieve to form granules.
-
Drying:
- Granules are dried using an oven or fluid bed dryer.
-
Sieving (Sizing):
- Dried granules are resized to ensure uniformity.
-
Lubrication and Blending:
- Lubricants and glidants are added for compression.
Advertisements
Advantages:
-
- Improves flow and compressibility.
- Uniform drug distribution for low-dose drugs.
Disadvantages:
- Time-consuming and costly.
- Not suitable for moisture- or heat-sensitive drugs.
2. Dry Granulation Methods:
Definition:
- Granules are formed without using liquid binders.
- Suitable for moisture- or heat-sensitive drugs.
Process:
-
Weighing and Mixing:
- API and excipients are blended.
-
Slugging or Roller Compaction:
- Powders are compacted using high-pressure rollers (roller compactor) or slugging (tablet press) to form large sheets or slugs.
-
Milling and Sizing:
- Compact material is broken down into granules of desired size.
-
Lubrication and Blending:
- Lubricants are added before final compression.
Advantages:
-
- Suitable for moisture- and heat-sensitive drugs.
- Faster and cost-effective (no drying).
Advertisements
Disadvantages:
- High-pressure equipment needed.
- Poor binding properties and dust generation.
3. Direct Compression Methods:
Definition:
-
- Tablets are made by directly compressing powdered materials without prior granulation.
- Suitable for drugs with excellent flowability and compressibility.
Process:
-
Weighing and Mixing:
- API and excipients are blended.
-
Lubrication:
- Lubricants and glidants are added.
-
Compression:
- Direct compression into tablets using a tablet press.
Advertisements
Advantages:
- Simple, fast, and economical.
- Ideal for heat- and moisture-sensitive drugs.
Disadvantages:
- Requires excellent flowability and compressibility.
- Not suitable for low-dose drugs due to segregation.
- compressibility requirements.
- Lack of uniformity for low-dose drugs.
Comparison Table of Granulation Methods
| Aspect | Wet Granulation | Dry Granulation | Direct Compression |
| Process Complexity | Complex, multiple steps. | Moderate, fewer steps. | Simplest, no granulation. |
| Cost | High (equipment, time). | Moderate (no drying). | Low (minimal processing). |
| Suitability | Not for heat/moisture-sensitive drugs. | Suitable for sensitive drugs. | Ideal for free-flowing powders. |
| Tablet Strength | Strong and uniform. | Moderate strength. | Depends on powder properties. |