Introduction to Metabolic Pathways in Higher Plants and Their Determination
- Metabolic Pathways in Higher Plants and Their Determination involve complex biochemical reactions essential for growth and survival.
- Metabolic Pathways in Higher Plants and Their Determination are studied using isotopic labeling, chromatography, and spectrometry tools.
Metabolites and Their Types:
What Are Metabolites?
- Metabolites are small molecules involved in metabolism, essential for energy production, growth, repair, and various cellular functions.
- They are intermediates or end products of metabolic pathways.
Types of Metabolites
-
Primary Metabolites
- Involved in basic processes like growth and energy production.
- Examples: Glucose, amino acids, ATP, fatty acids.
-
Secondary Metabolites
- Non-essential for growth but important for defense, signaling, and adaptation.
- Examples: Alkaloids (nicotine), terpenoids (menthol), flavonoids, antibiotics (erythromycin).
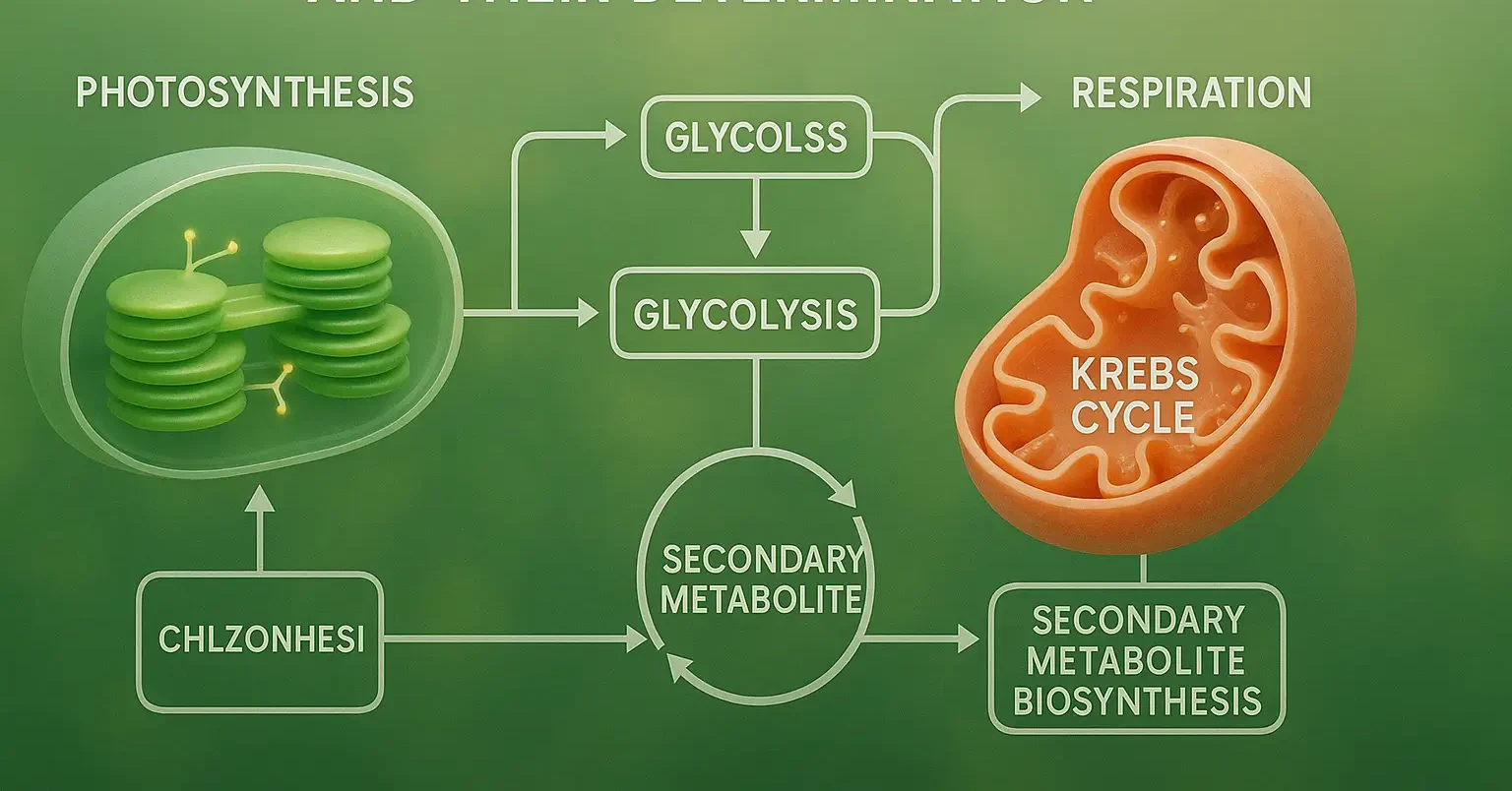
Primary Metabolism
- Primary metabolism involves pathways essential for life, such as photosynthesis, respiration, and the biosynthesis of carbohydrates, amino acids, and lipids.
Key Processes:
-
Photosynthesis:
- Converts light energy into chemical energy, forming sugars from carbon dioxide and water.
-
Respiration:
- Breaks down sugars to release energy for cellular processes.
-
Biosynthetic Routes:
- Carbohydrate Synthesis: Produces sugars via the Calvin Cycle.
- Amino Acid Metabolism: Forms the building blocks for proteins.
- Lipid Synthesis: Builds cell membranes and energy-storing molecules.
Secondary Metabolism
- Secondary metabolites are derived from primary metabolic pathways and include diverse classes of compounds such as alkaloids, terpenoids, and phenolics.
Biosynthetic Origins:
- Phenylpropanoids: Derived from the amino acid phenylalanine.
- Terpenoids: Derived from isoprene units originating in carbohydrate metabolism.
- Alkaloids: Derived from amino acids and other primary metabolic intermediates.
Determination of Metabolic Pathways:
- Understanding metabolic pathways requires experimental techniques that map out the biosynthesis and function of metabolites:
Key Techniques:
-
Biochemical Techniques:
- Enzyme isolation, in vitro assays, and substrate feeding experiments to identify enzymatic steps in pathways.
-
Radioisotope Labeling:
- Introducing radioactive isotopes (e.g., 14C or 3H) into precursors to track the movement of atoms through metabolic routes.
-
Analytical Methods:
- Techniques like chromatography, mass spectrometry, and NMR are used to identify and quantify metabolites.
-
Molecular Biology Tools:
- Genetic manipulation, gene expression profiling, and mutant analysis to study enzyme roles and regulatory networks.