Neuroglia
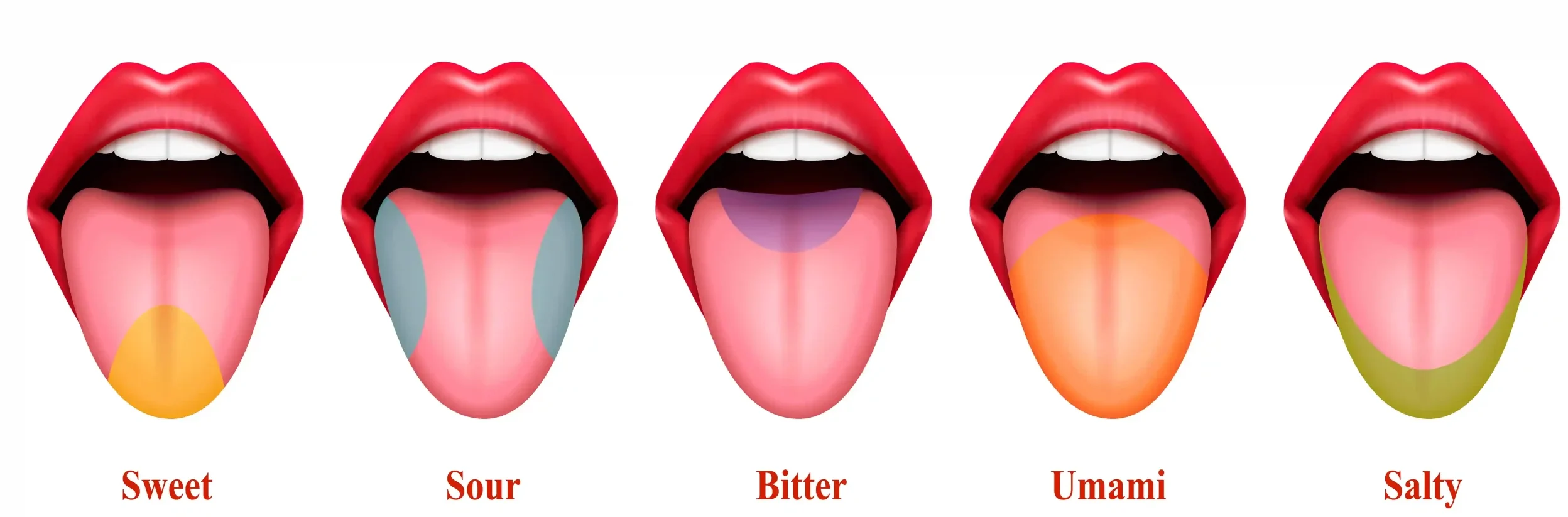
Neuroglia, or glial cells, are non-neuronal cells in the nervous system that support, protect, and maintain the proper functioning of neurons. They play vital roles in providing structural support, modulating synaptic transmission, and maintaining the extracellular environment. There are several types of glial cells, each with specific functions The classification of neuroglia cells can be … Read more