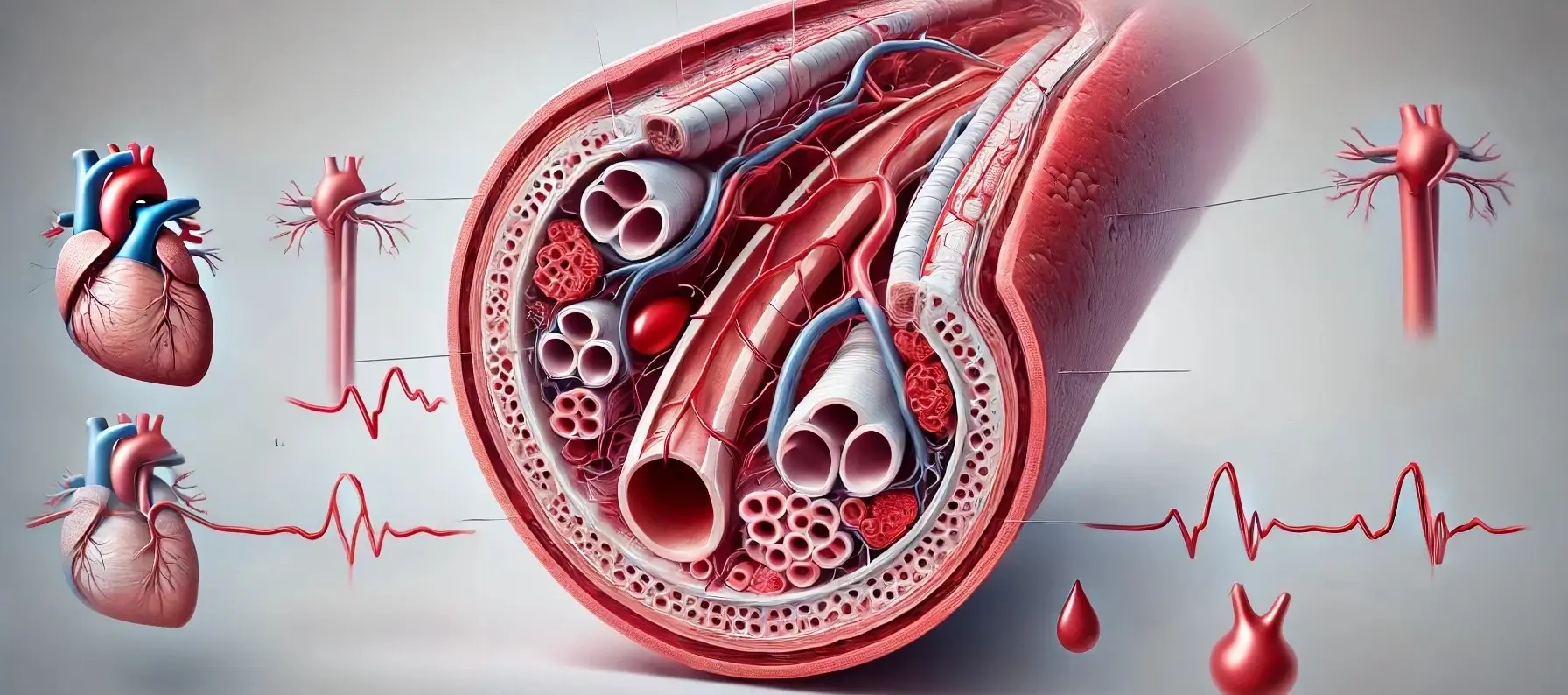
Atherosclerosis
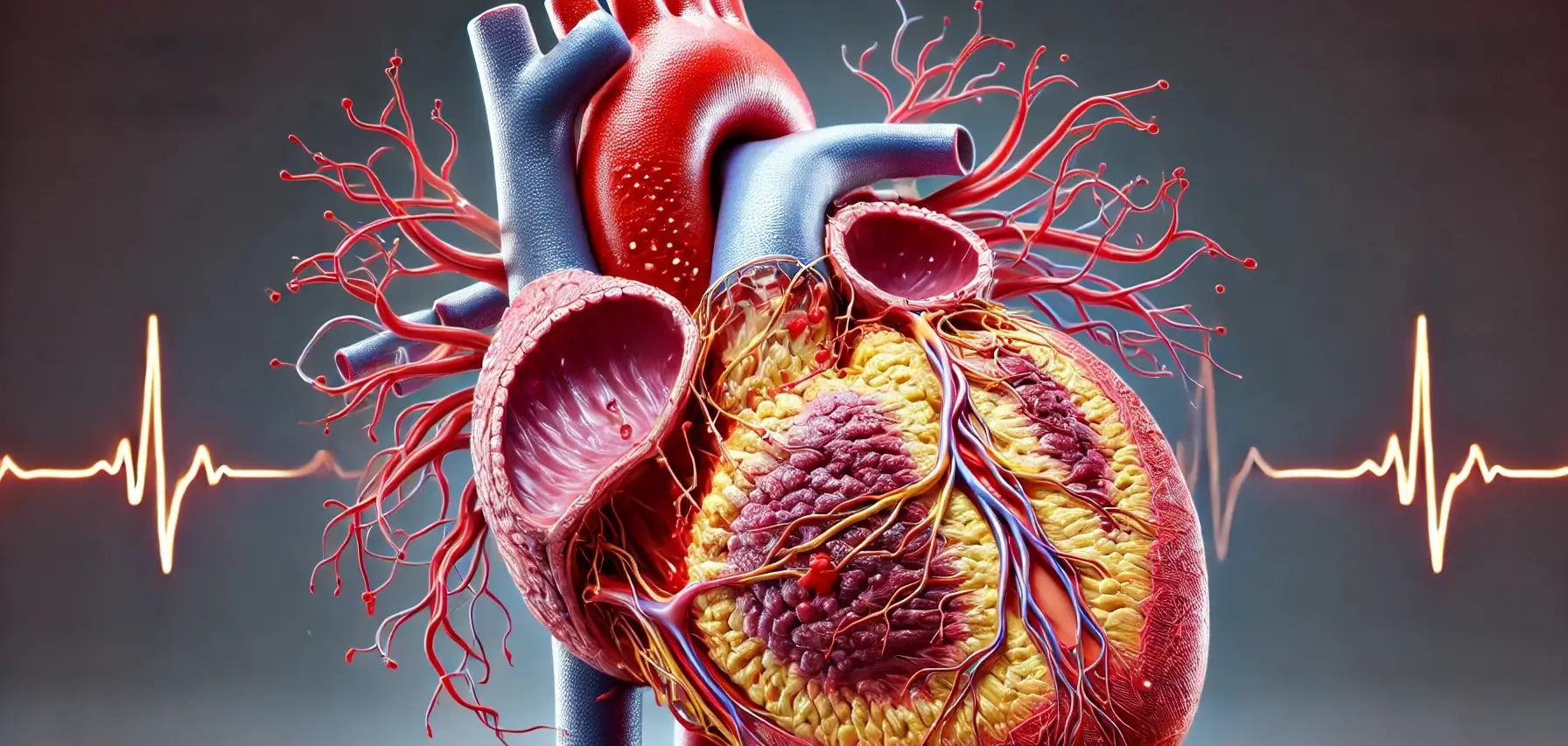
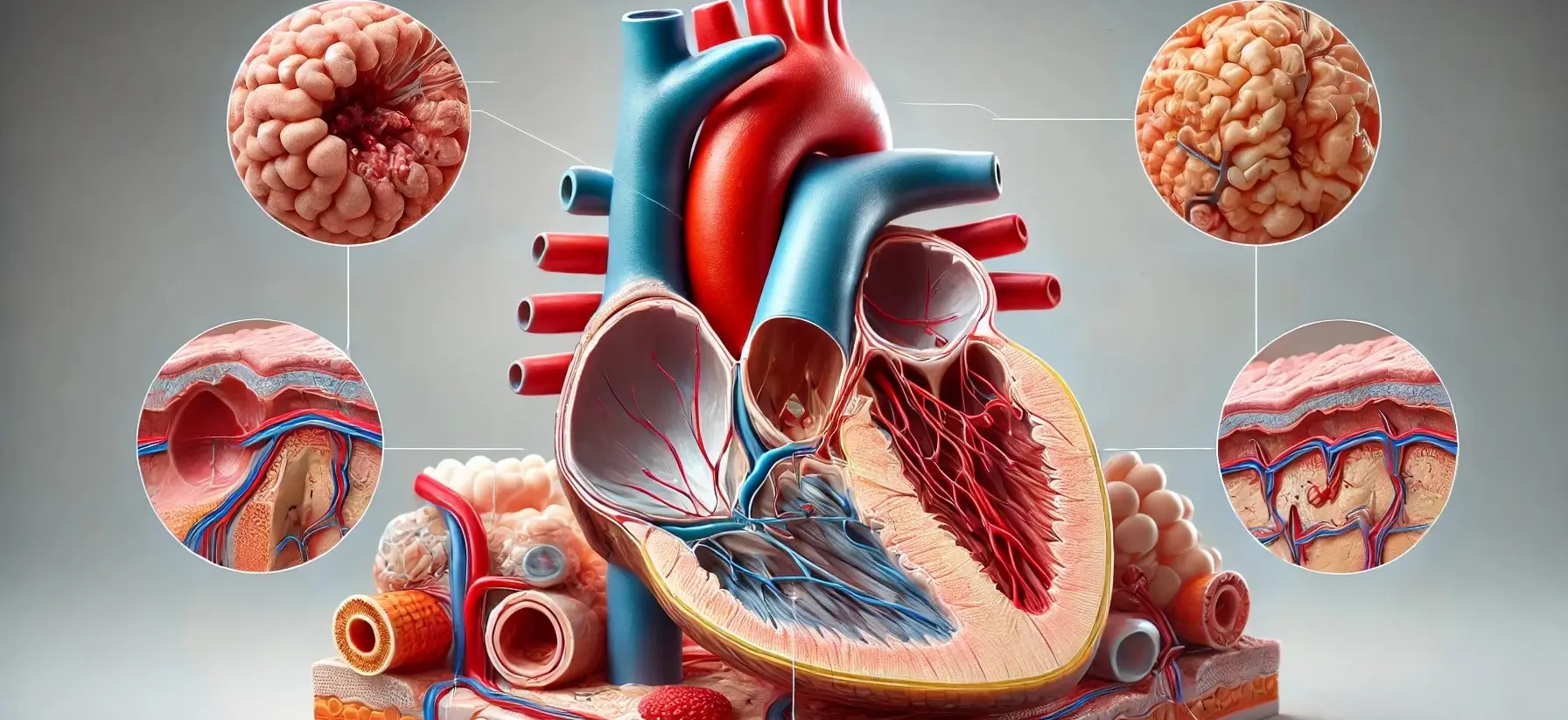
Introduction of Atherosclerosis Atherosclerosis is a condition characterized by the buildup of plaques made of fat, cholesterol, and other substances in the arteries, leading to narrowed and hardened arteries. Types Coronary Artery Disease (CAD): Affects the arteries supplying blood to the heart. Carotid Artery Disease: Affects the arteries supplying blood to the brain. Peripheral Artery … Read more