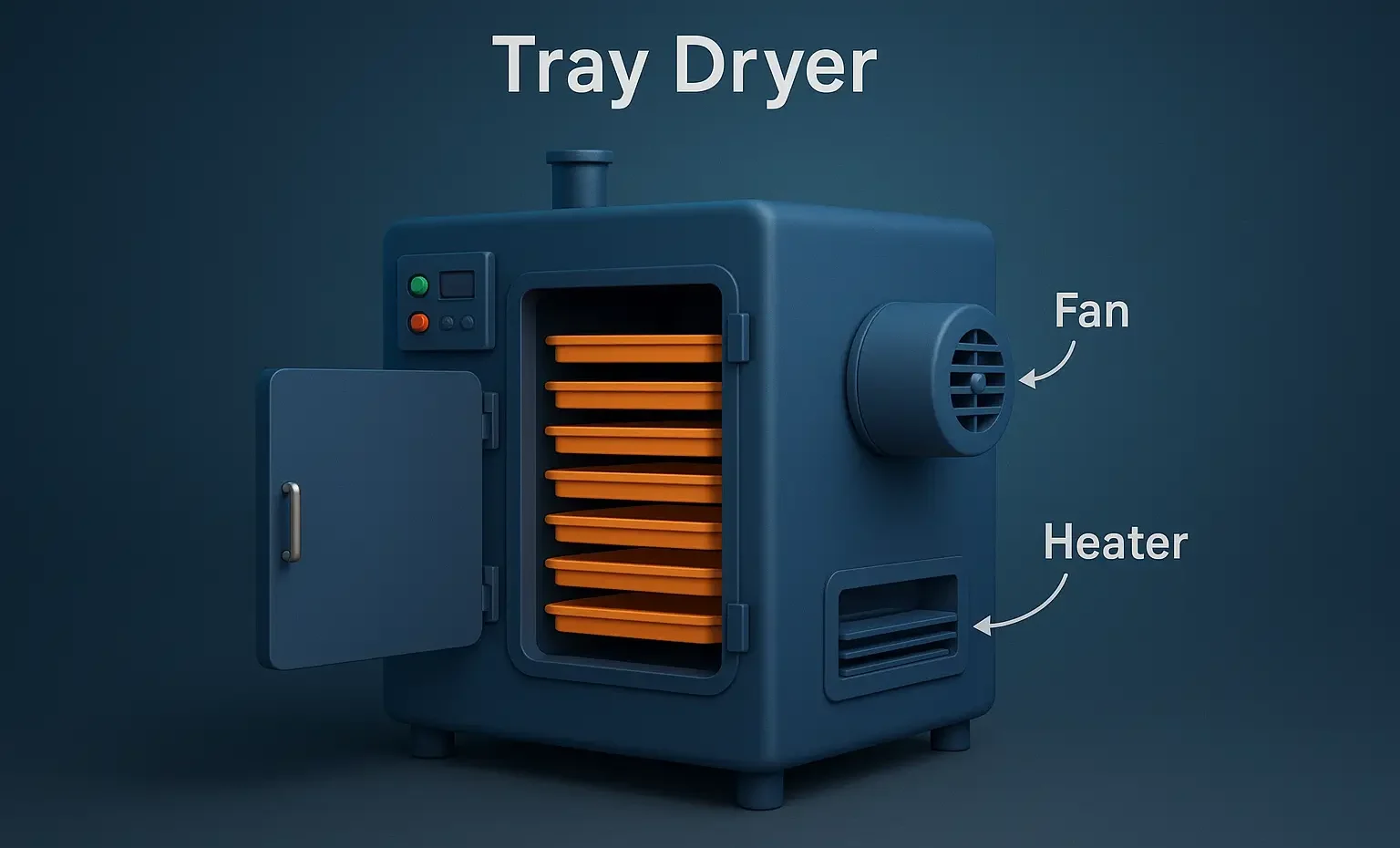
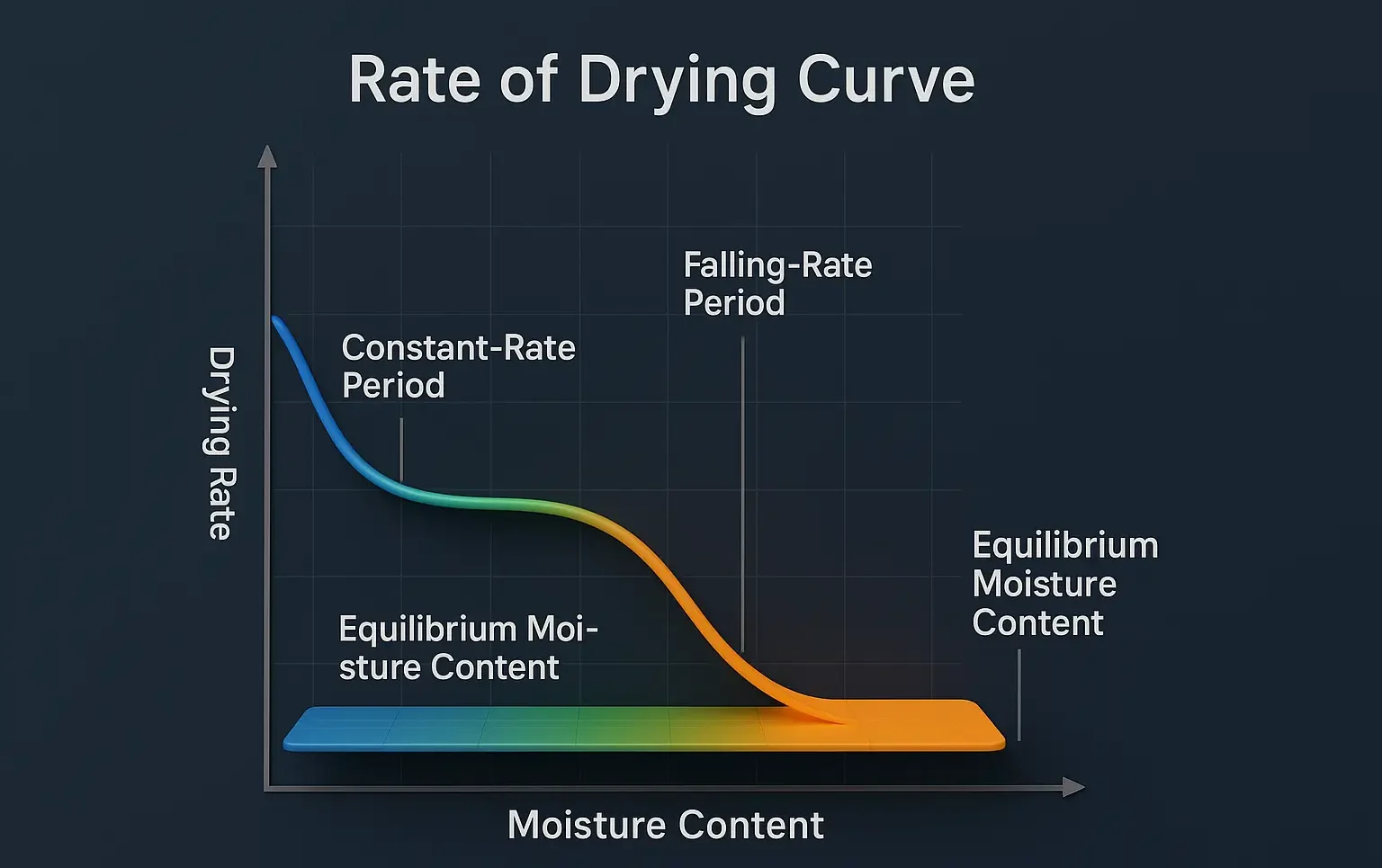
Filter aids & filter medias
Filter Aids Filter aids are materials added to the fluid to improve the filtration process. They can prevent clogging, improve flow rates, and enhance the clarity of the filtrate. Common filter aids include: Diatomaceous Earth: Made from fossilized remains of diatoms, used in fine filtration. Perlite: A volcanic glass material that expands and is used … Read more