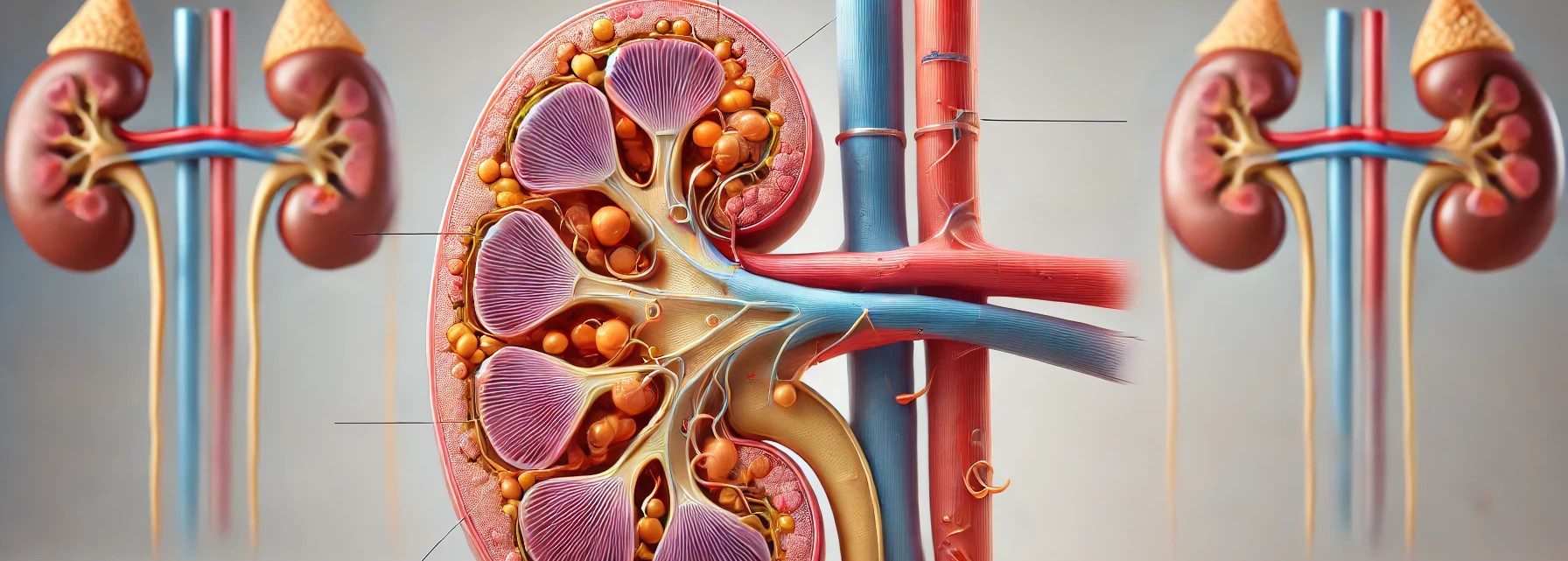
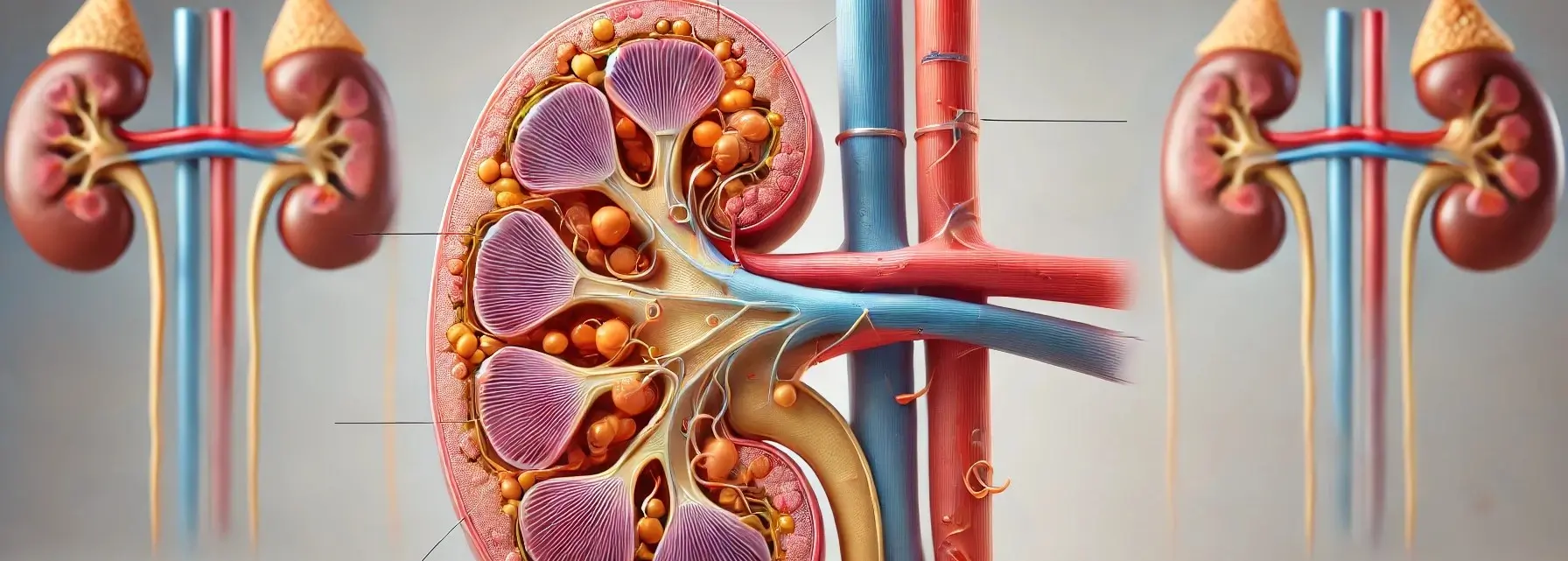
Adrenal glands
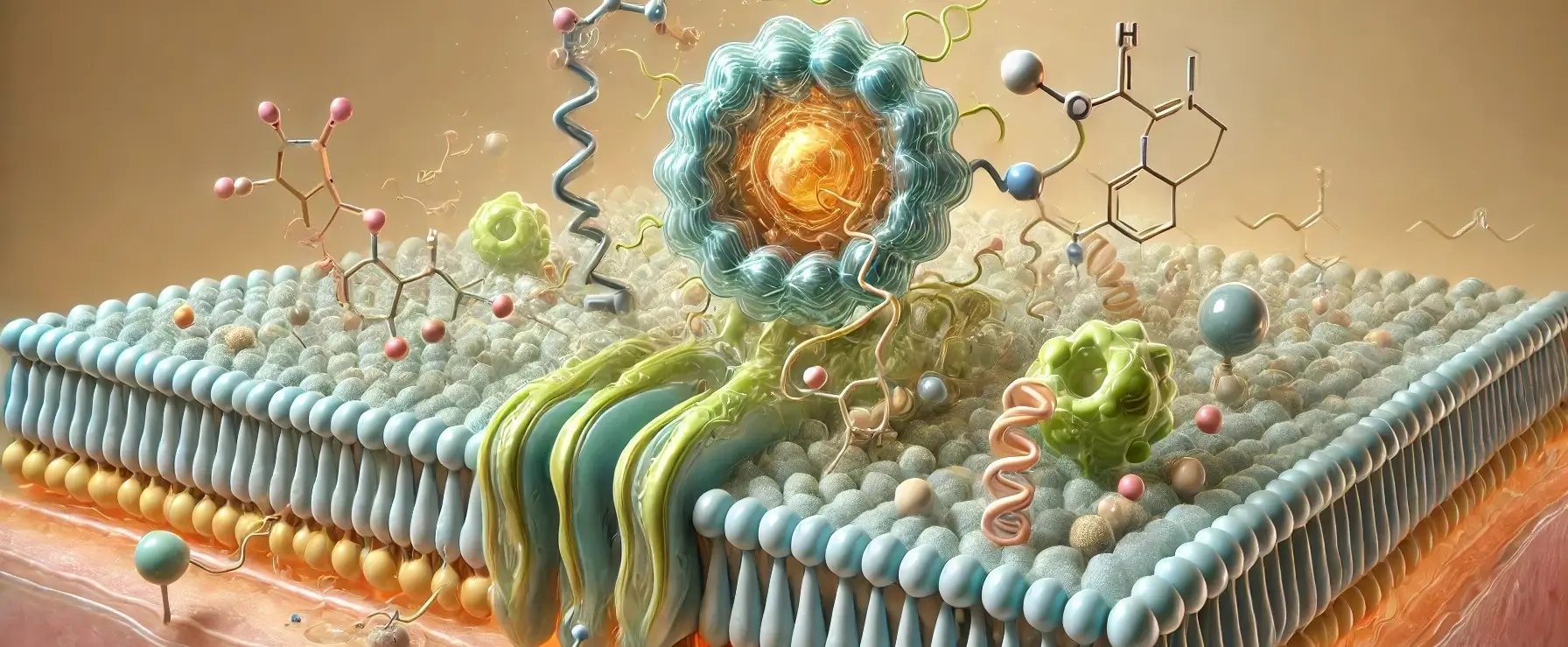
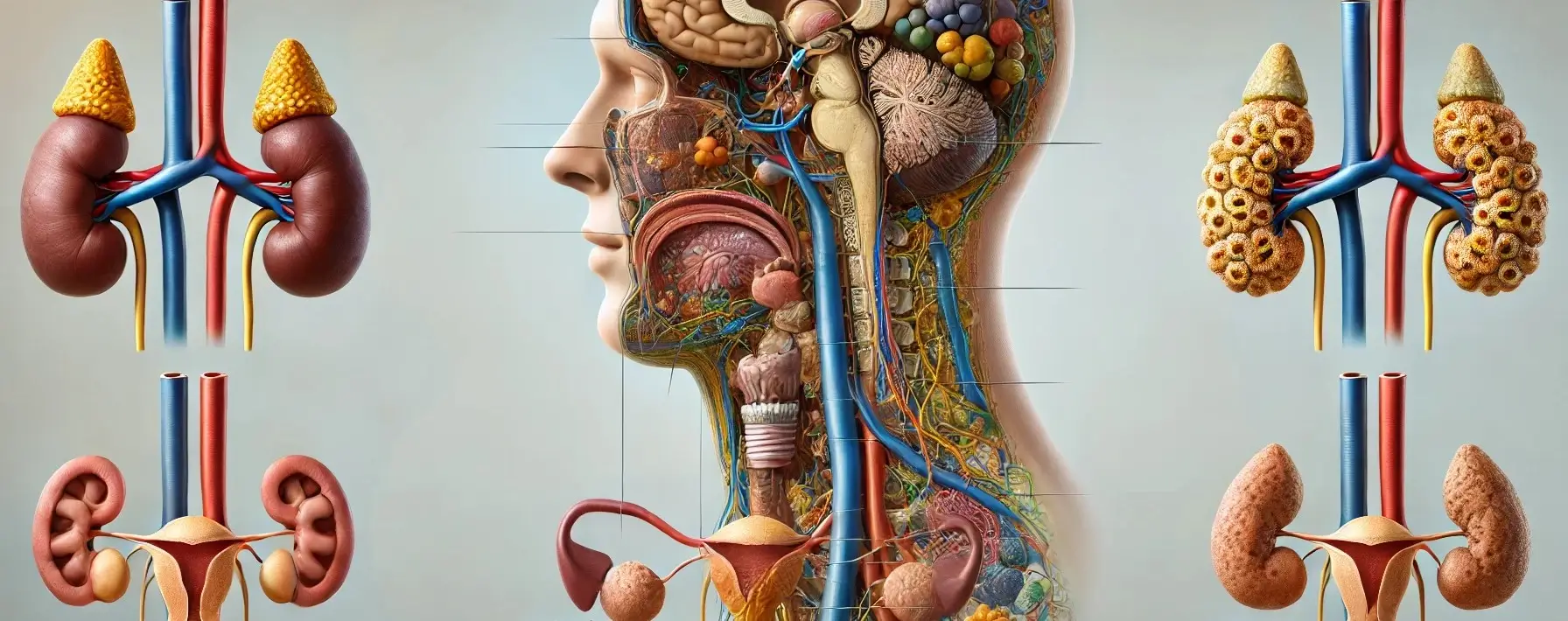
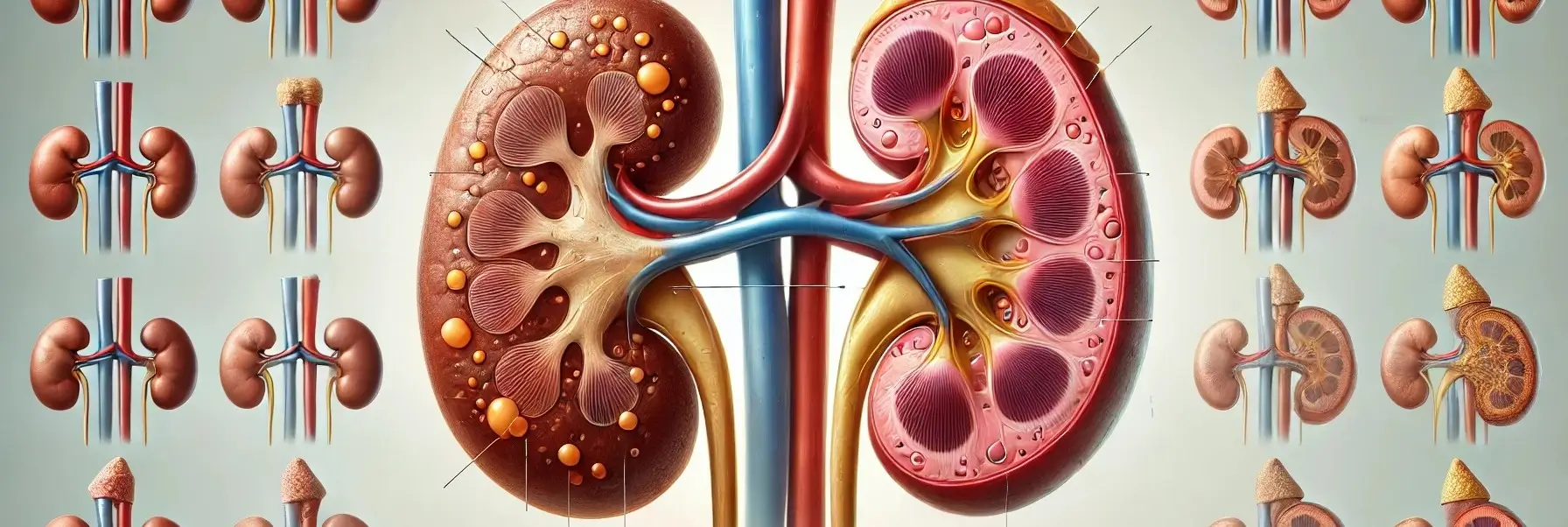
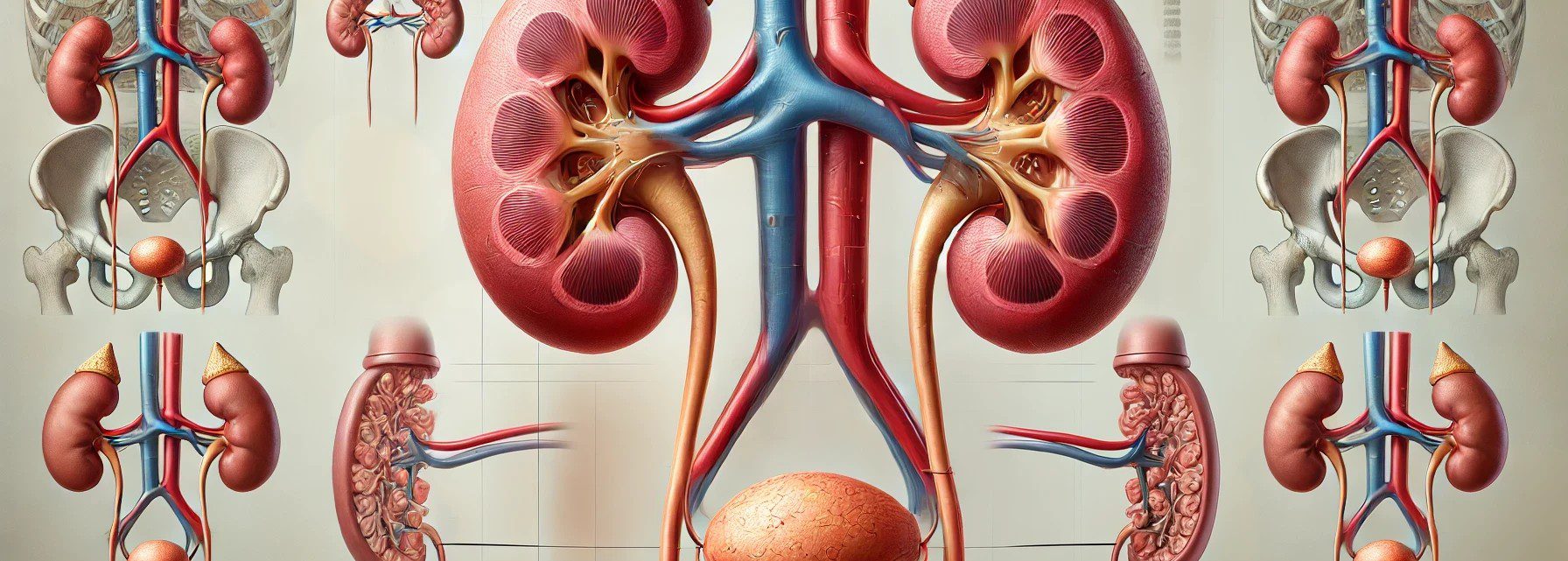
The adrenal glands are small, triangular-shaped glands located on top of both kidneys. They are part of the body’s endocrine system, producing hormones that are vital for life. Each adrenal gland is structurally and functionally divided into two main parts: the adrenal cortex and the adrenal medulla, each responsible for producing different sets of hormones. … Read more