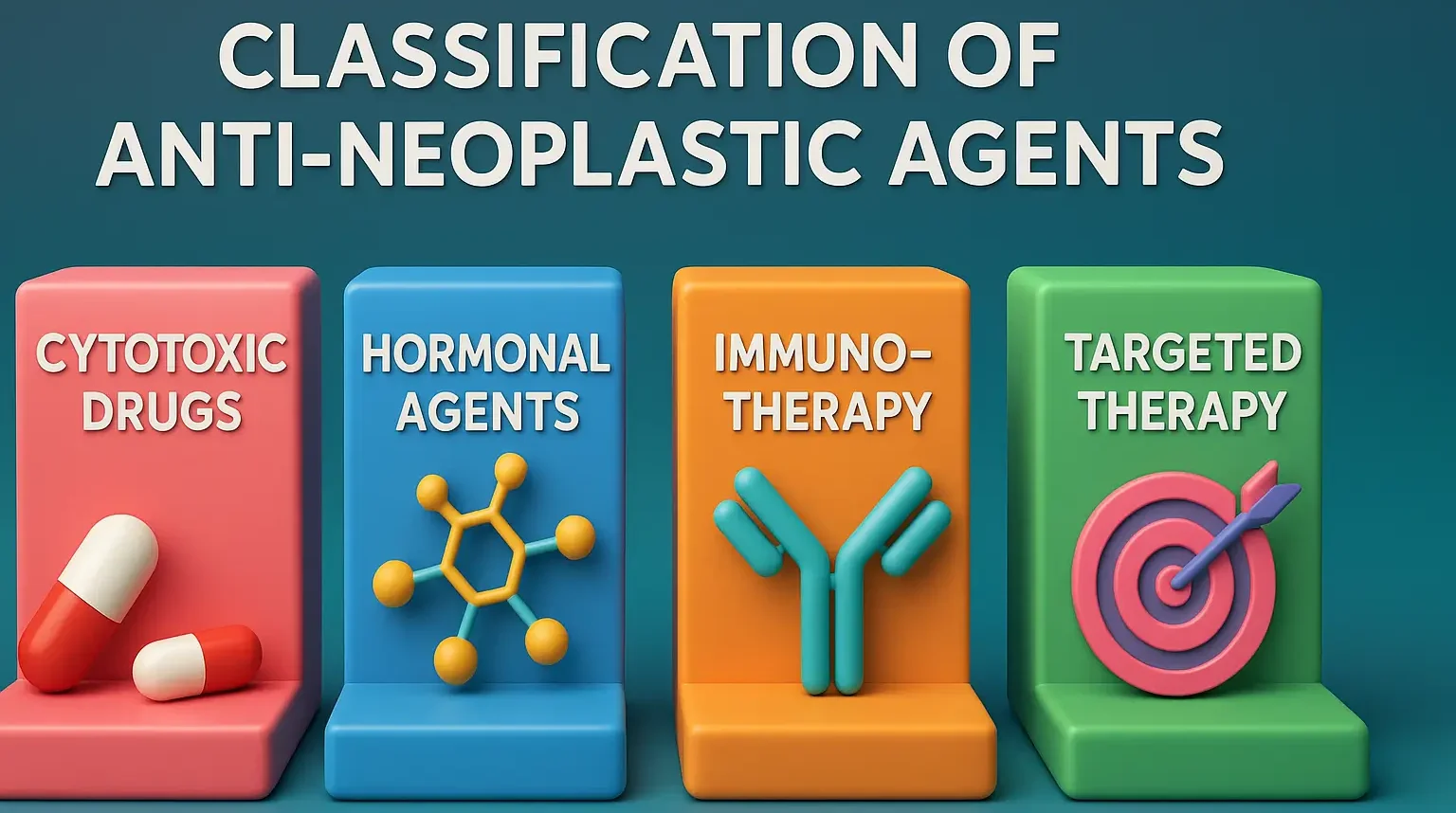
Classification of Anti-Neoplastic Agents
Classification of anti-neoplastic agents based on mechanism and origin, targeting cancer cells and aiding effective cancer therapy. Classification of Anti-Neoplastic Agents Anti-neoplastic agents are classified based on their mechanism of action and origin. The primary categories include: Alkylating Agents Mechanism: Add alkyl groups to DNA, causing cross-linking and preventing DNA replication and transcription. Examples: Mechlorethamine … Read more