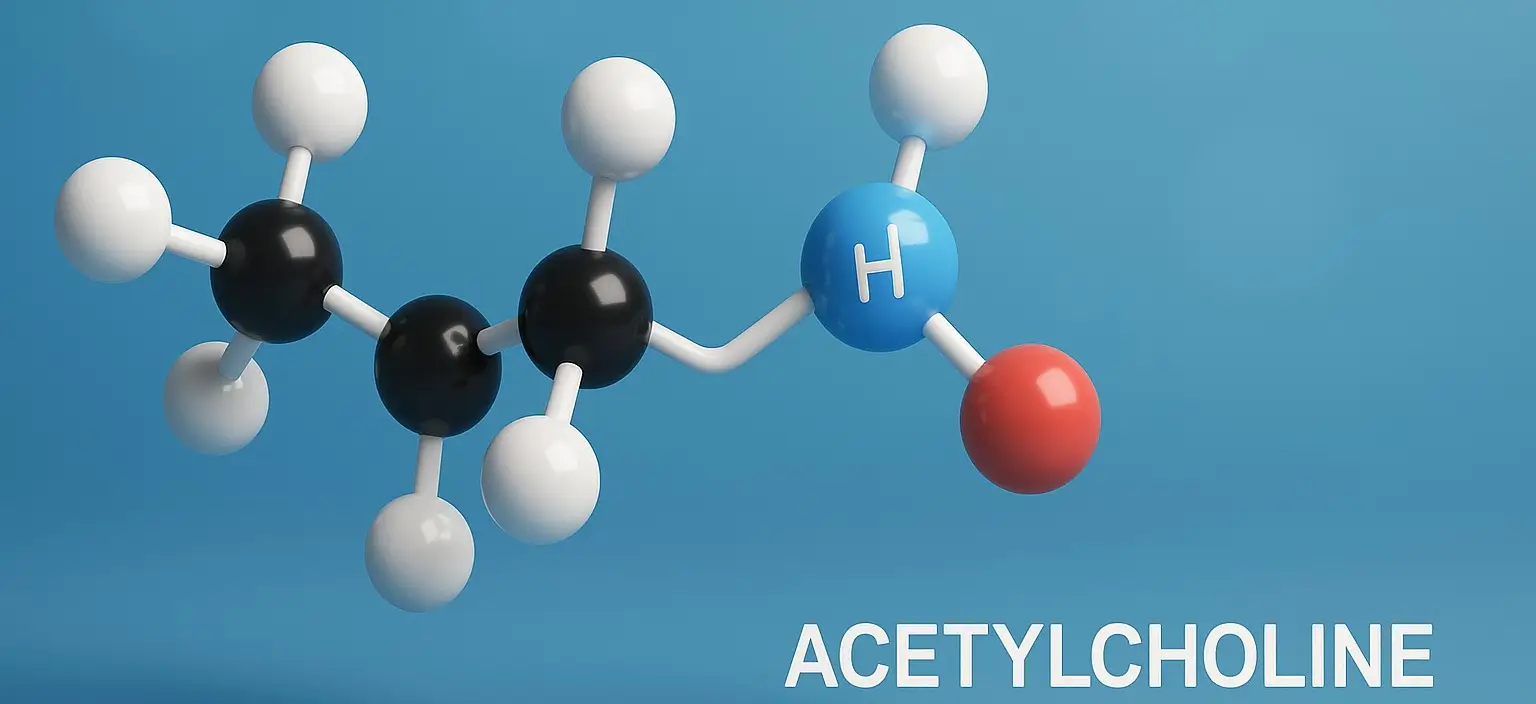
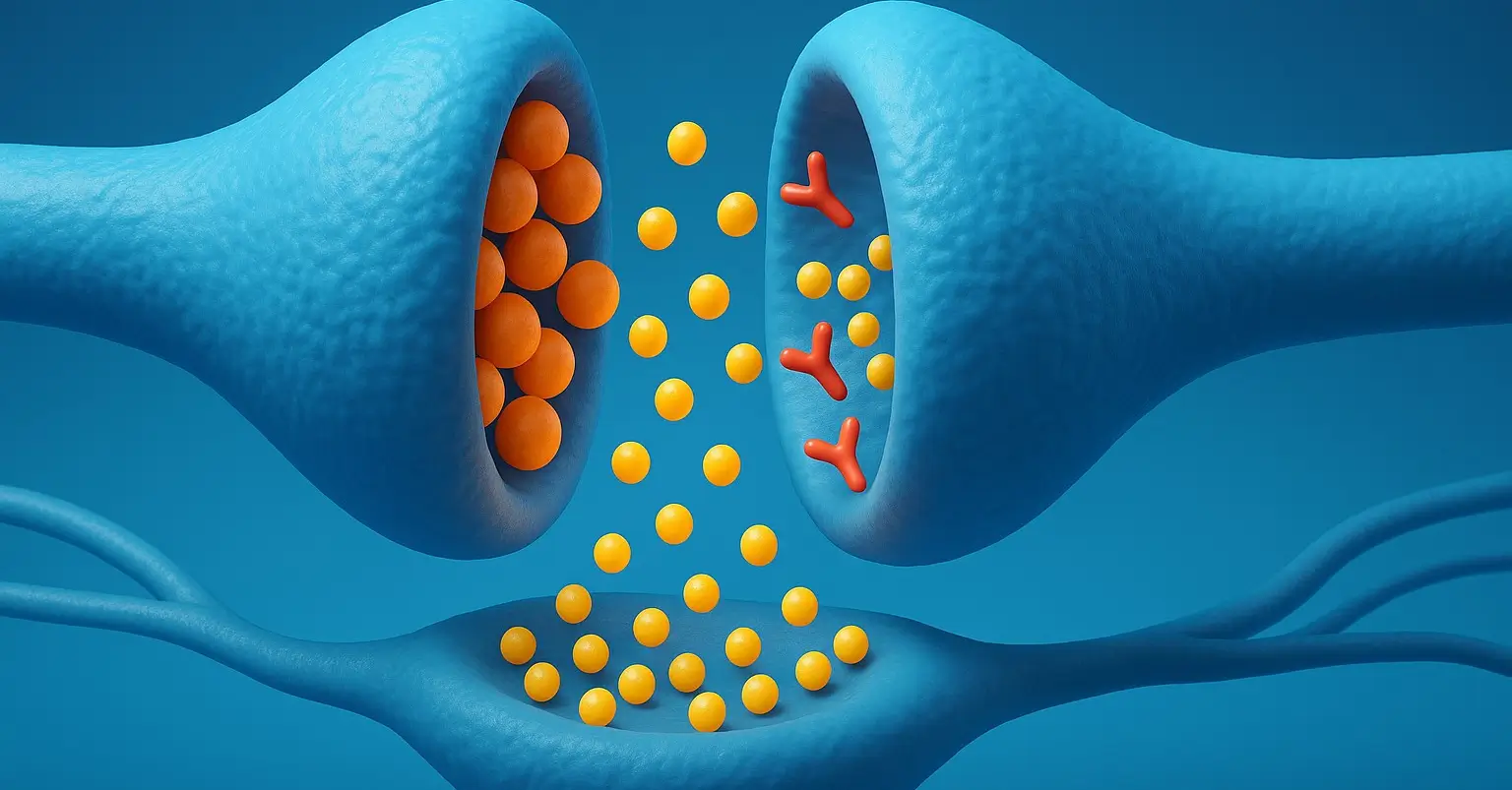
Acetylcholine
Acetylcholine (ACh) is a neurotransmitter a chemical messenger that plays a crucial role in transmitting signals in both the central and peripheral nervous systems. Biosynthesis of acetylcholine Location Synthesized in the cytoplasm of cholinergic neurons, particularly at nerve terminals. Precursors Choline: Obtained from diet and recycled ACh. Acetyl-CoA: Formed in mitochondria from pyruvate (product of … Read more