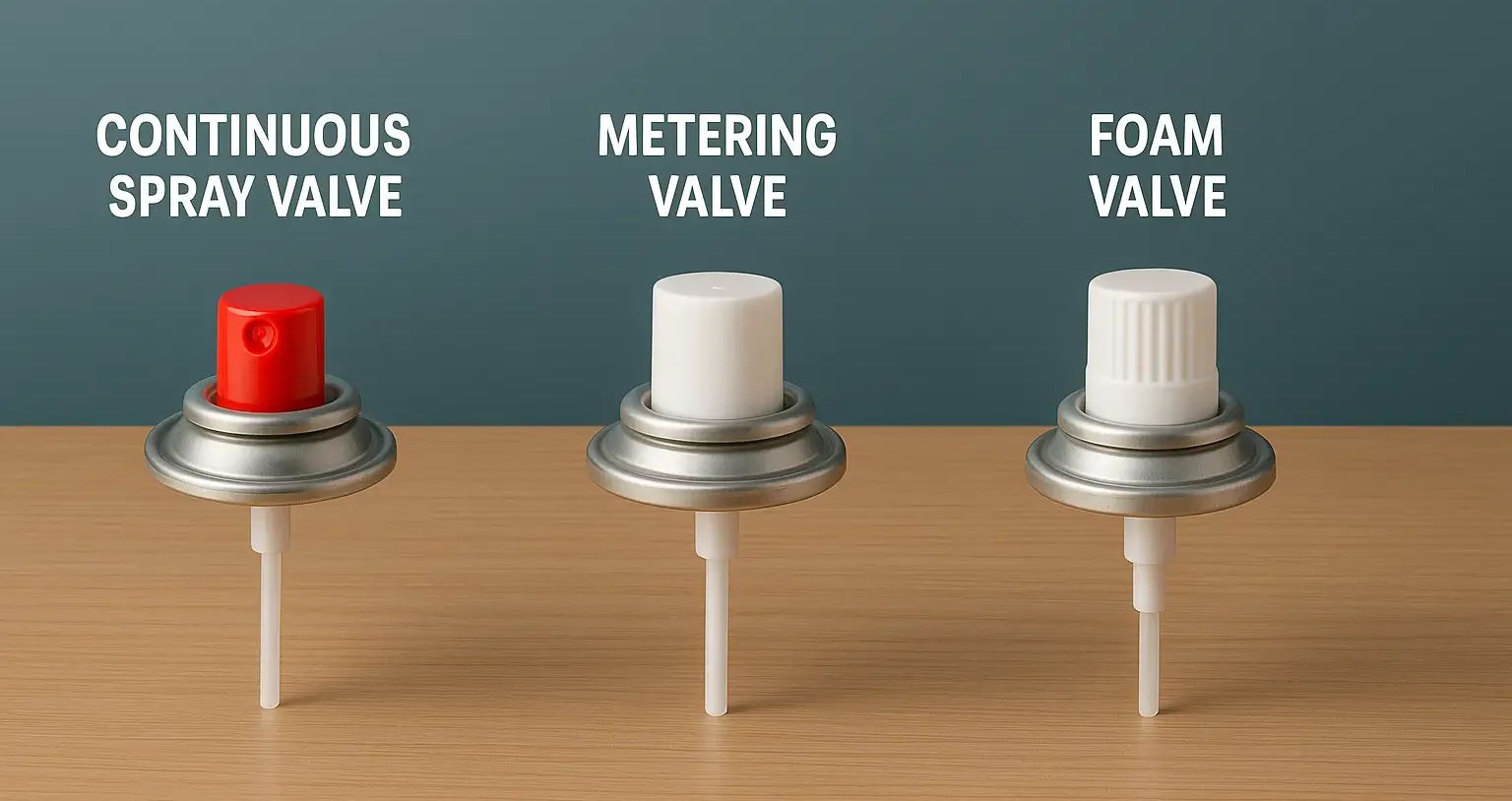
Types of Aerosol Systems
Types of Aerosol Systems vary by formulation, such as solution, suspension, or emulsion-based delivery mechanisms. Pharmaceutical aerosol systems vary based on formulation type, application route, and dose delivery mechanism. Types of Aerosol Systems: Liquefied Gas Systems Propellants: Hydrocarbons or nitrous oxide. Mechanism: Propellant evaporates to expel product. Uses: Hairsprays, deodorants. Compressed Gas Systems Propellants: Nitrogen, … Read more