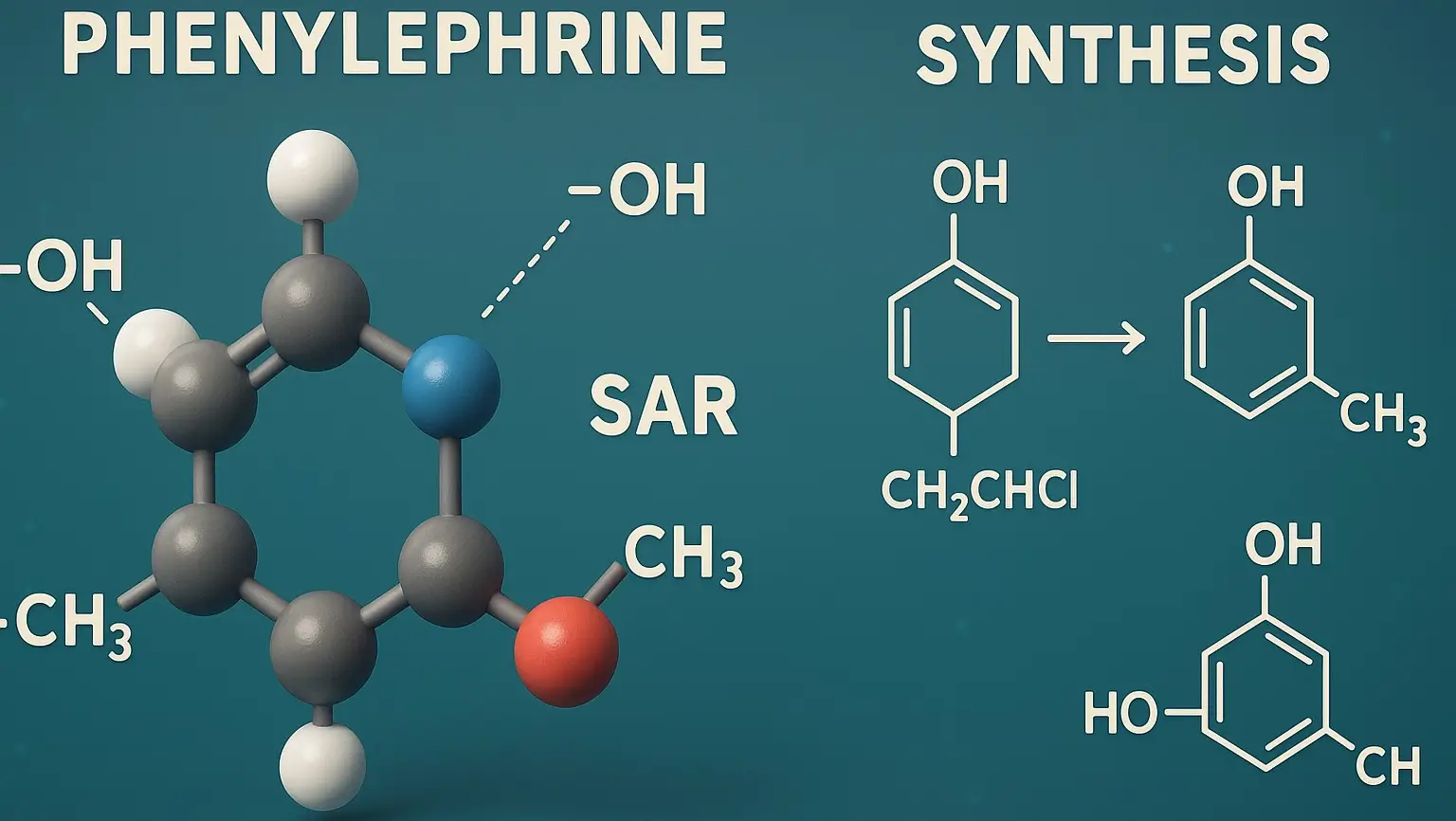
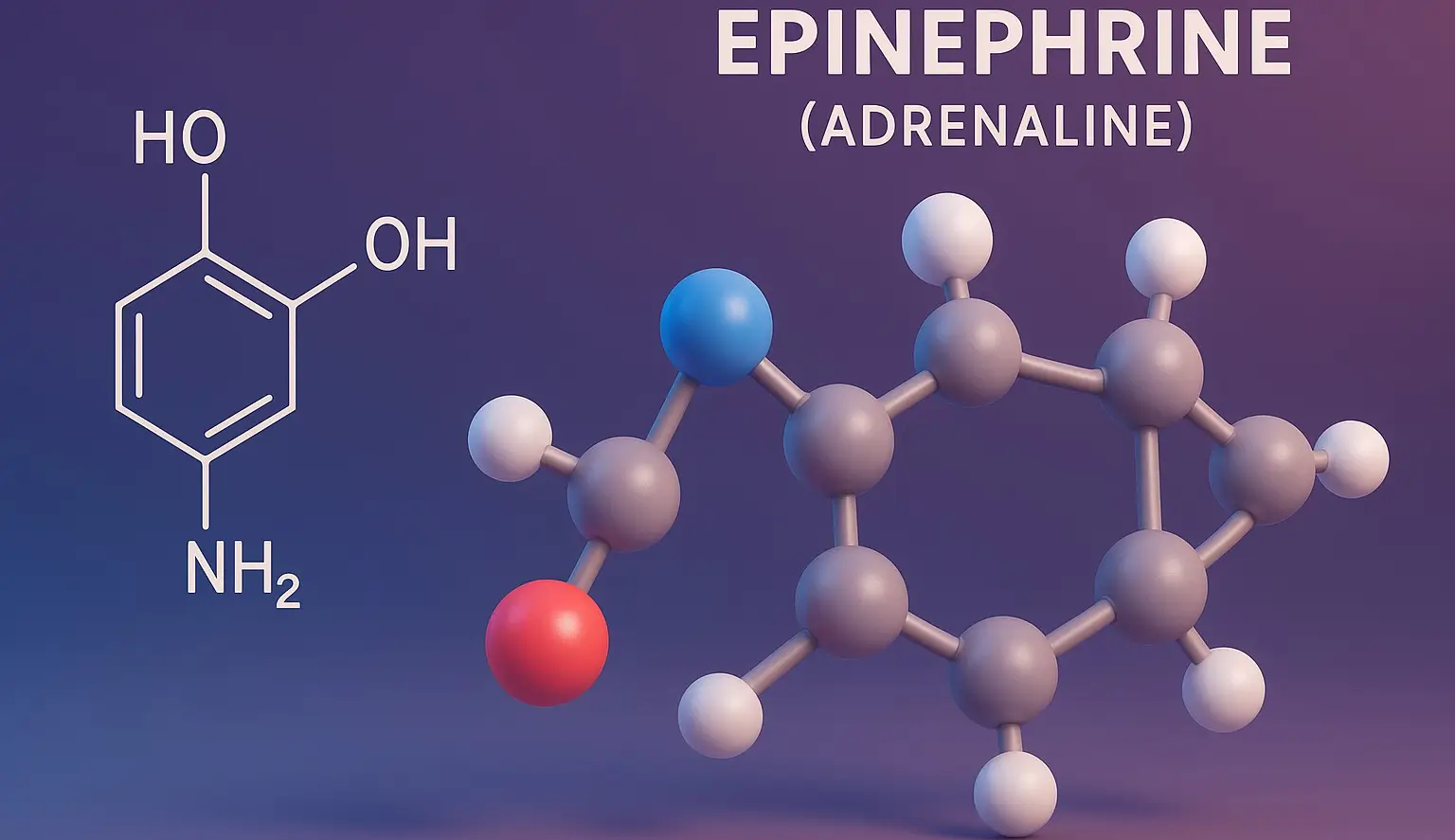
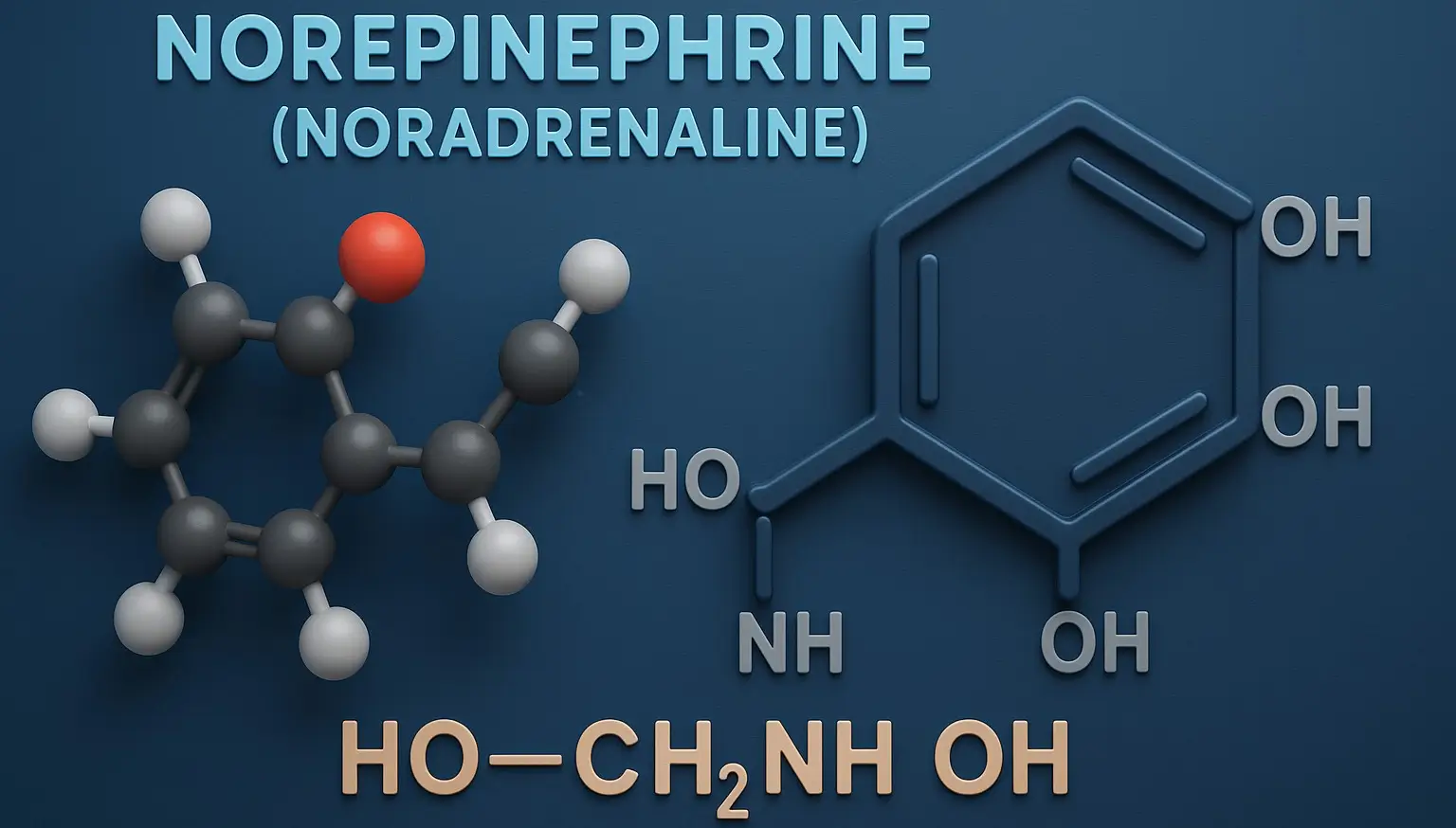
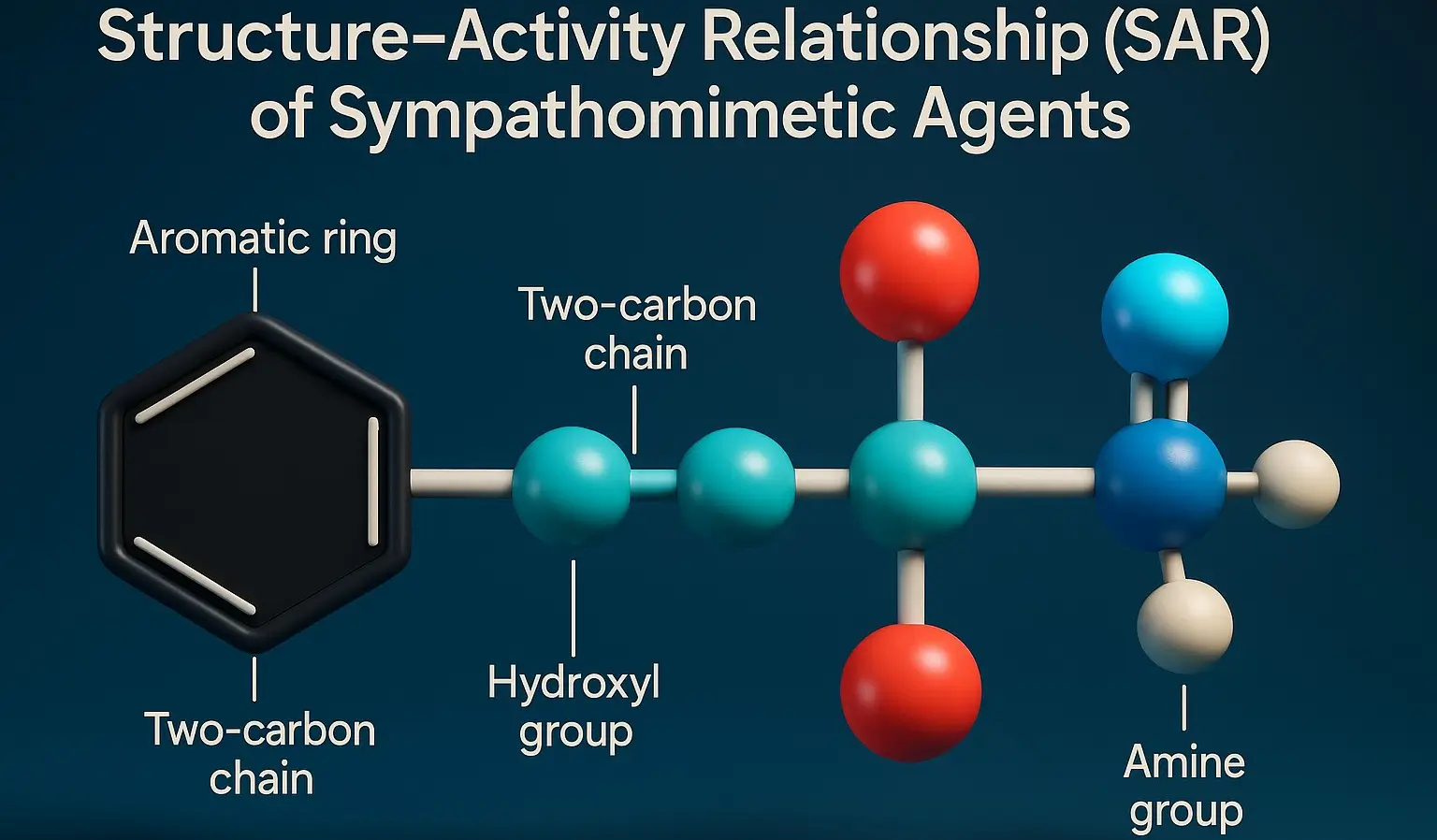
Toothpastes
Definition of Toothpastes: Toothpastes are complex formulations designed to clean and polish teeth, protect against cavities, and freshen breath. The primary mechanisms include mild abrasive action, chemical plaque removal, and beneficial active ingredients like fluoride. Formulation Goals: Cleaning: Mechanical removal of plaque and food debris. Mild Abrasivity: Effective yet gentle on tooth enamel. Foaming: Aid … Read more