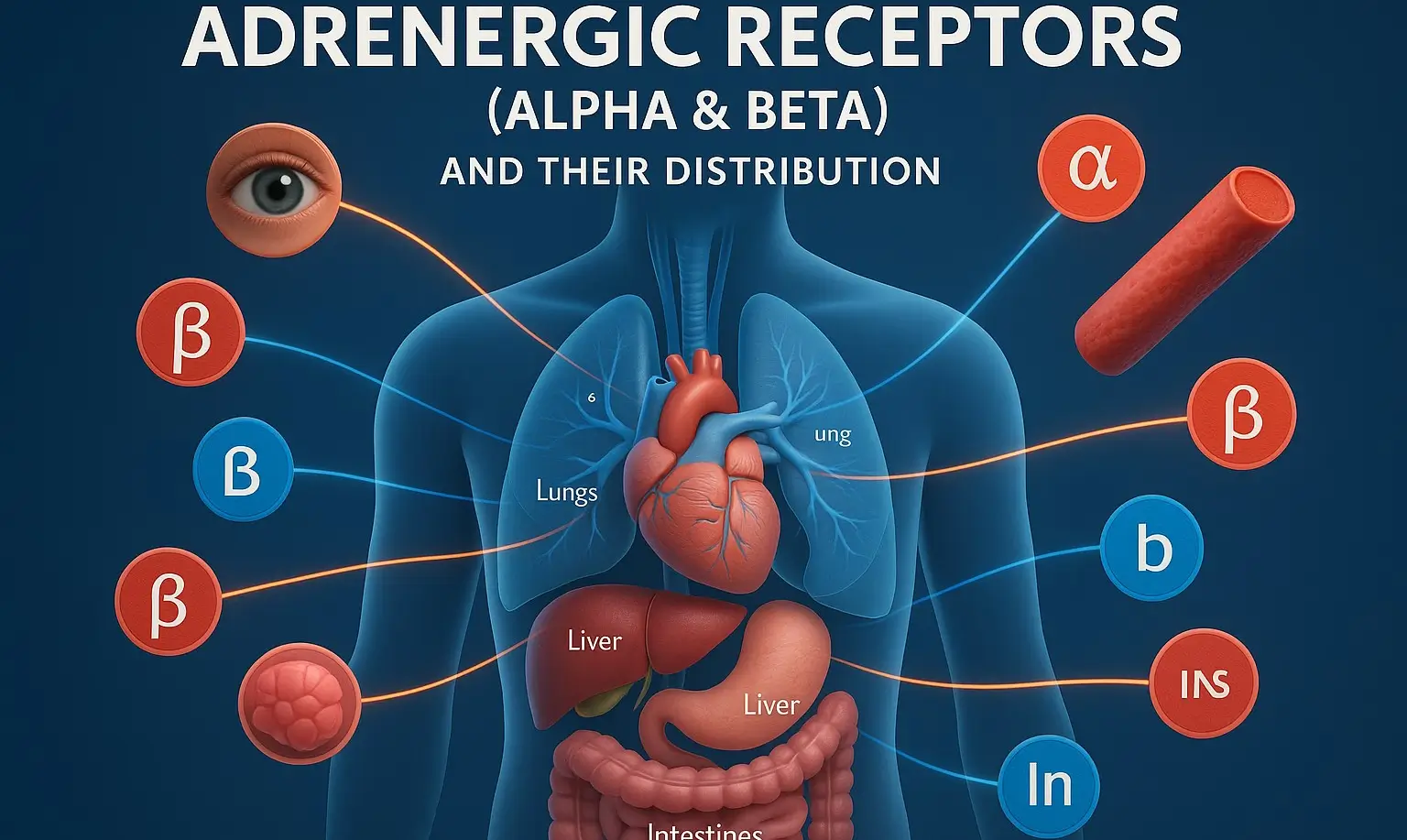
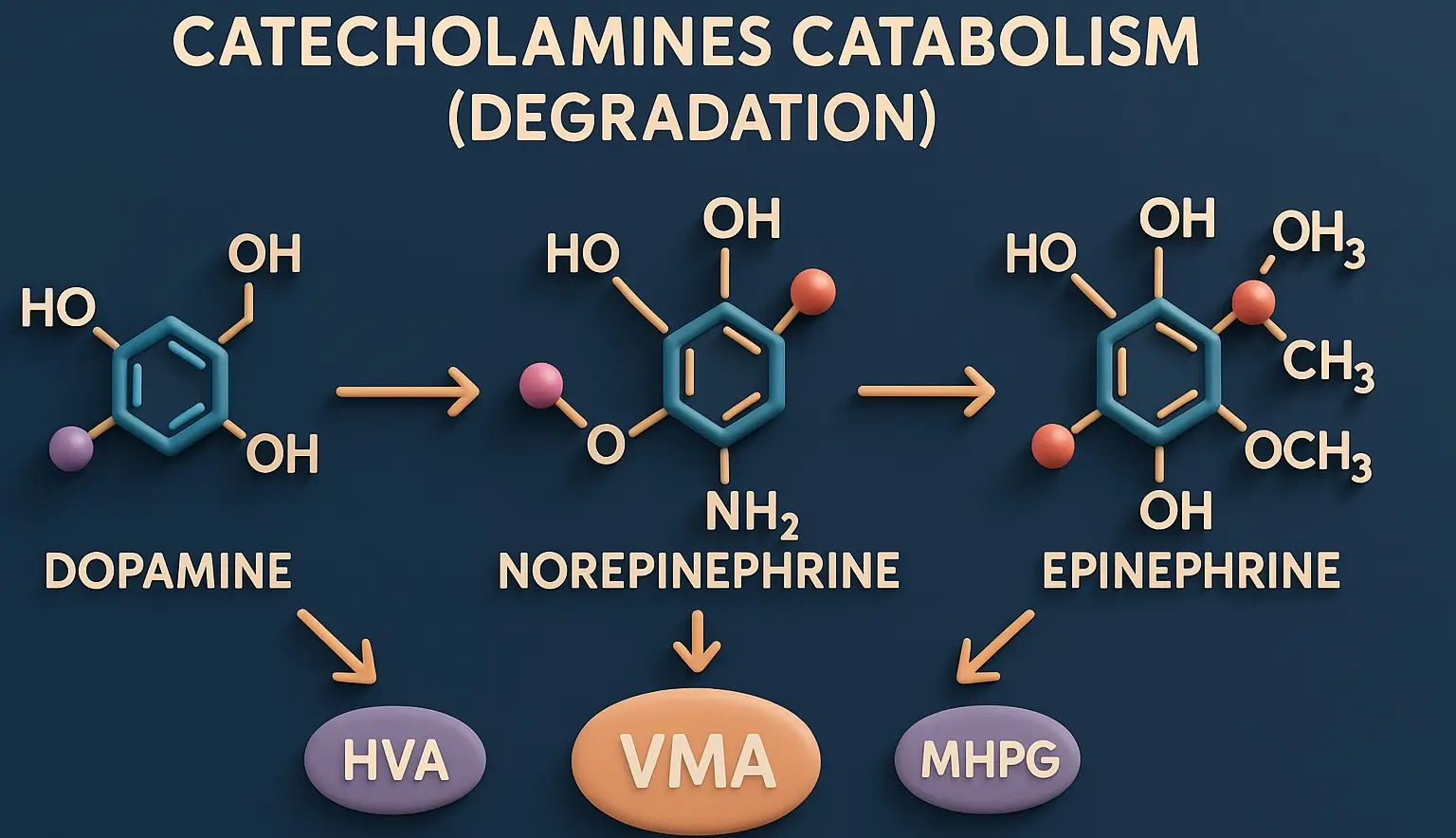
Adrenergic receptors (Alpha & Beta) and their distribution
Adrenergic receptors are G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) that mediate the effects of norepinephrine and epinephrine. Adrenergic receptors are classified into Alpha (α) and Beta (β) receptors, with further subtypes. Alpha-Adrenergic Receptors (α-Receptors) These receptors mainly mediate vasoconstriction and smooth muscle contraction. α1-Receptors (Gq-coupled) Mechanism: Activate phospholipase C (PLC) → Increase IP3 & DAG → Increase intracellular … Read more