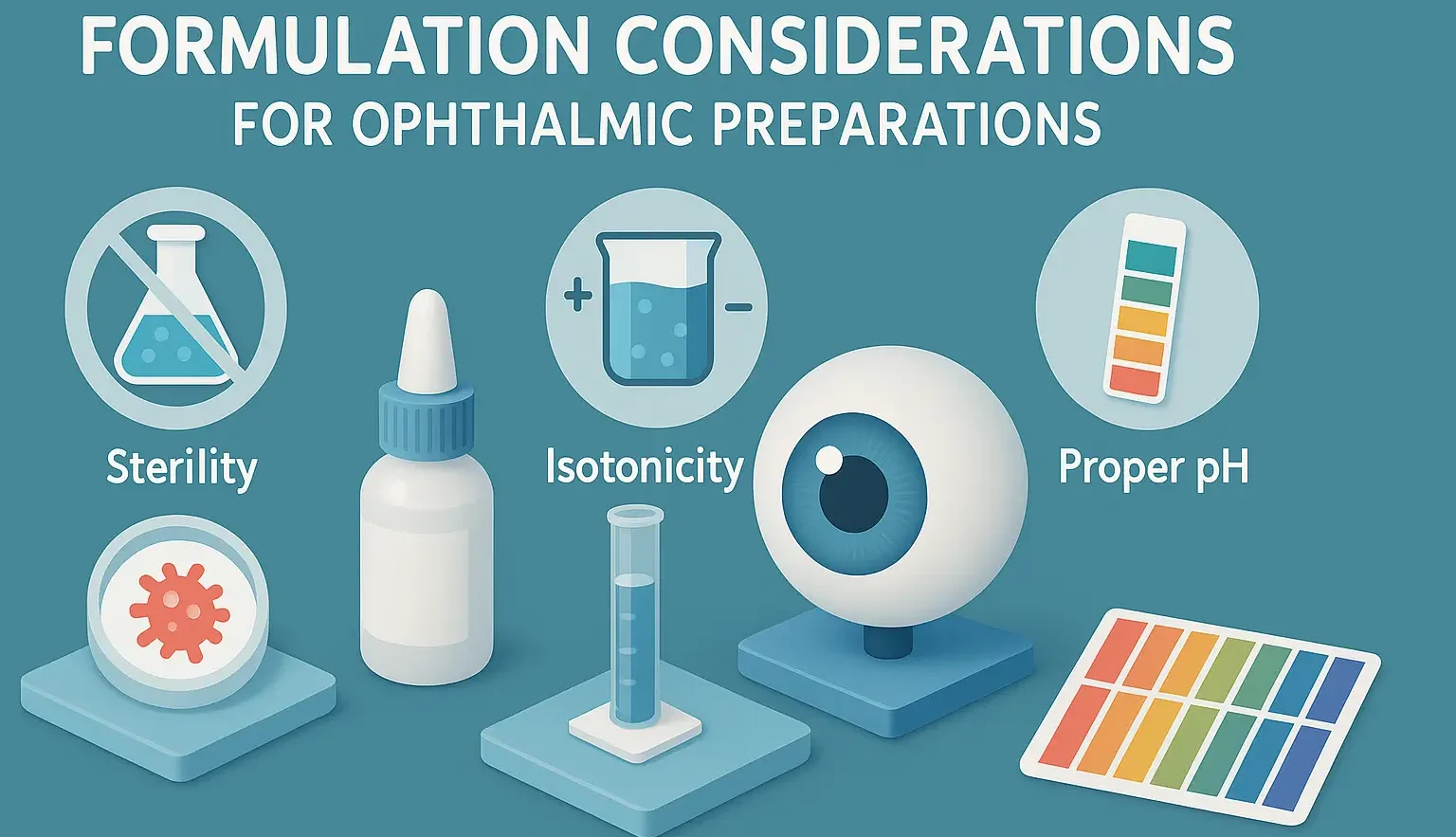
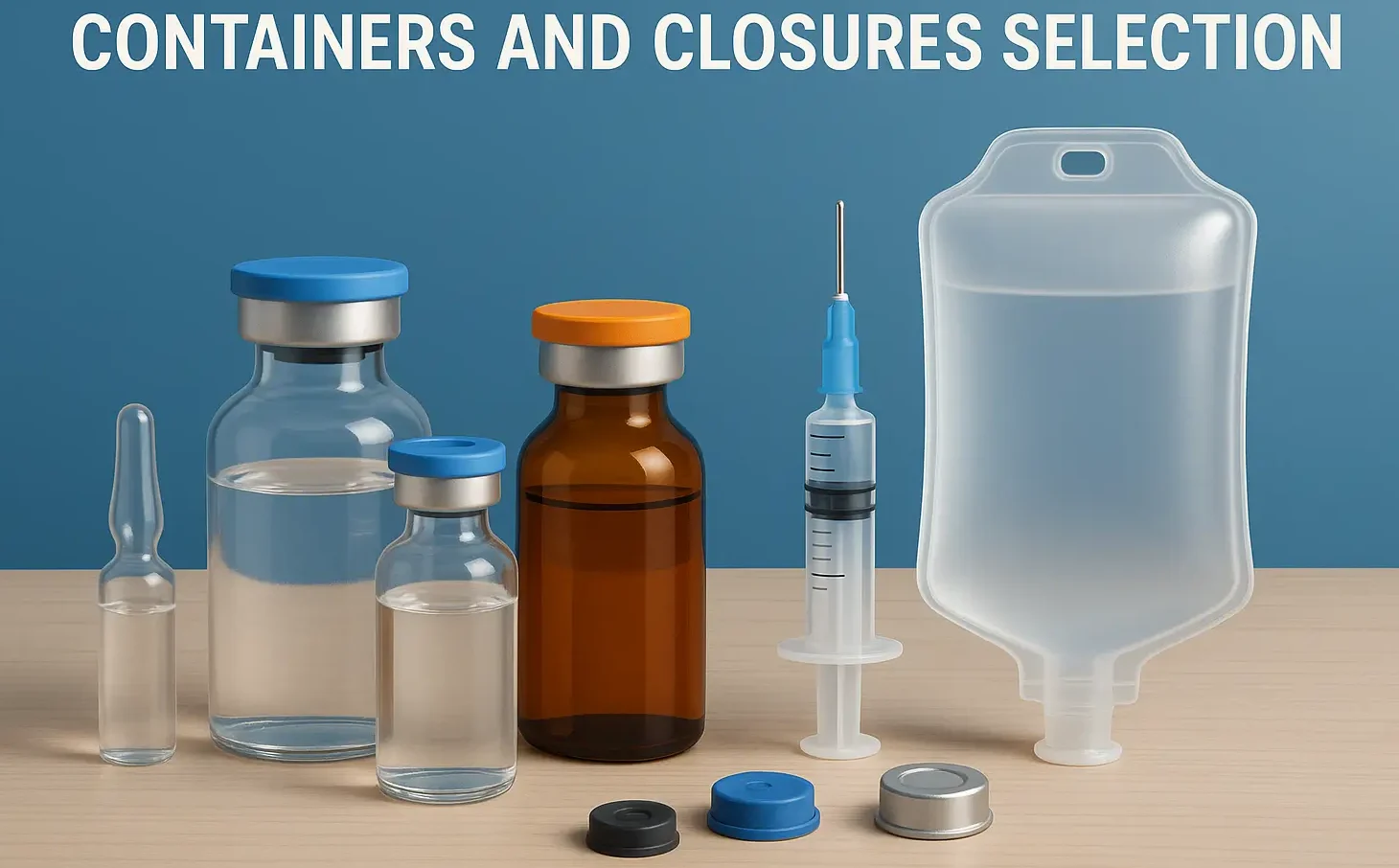
Preformulation Factors and Essential Requirements
Preformulation Factors and Essential Requirements are critical for developing stable, effective drug formulations. Preformulation Factors and Essential Requirements include physicochemical properties, solubility, stability, and compatibility, ensuring optimal dosage form design Preformulation Studies Preformulation involves the characterization of a drug’s physical and chemical properties to inform formulation development. Critical preformulation factors for parenteral products include: Solubility: Ensuring … Read more