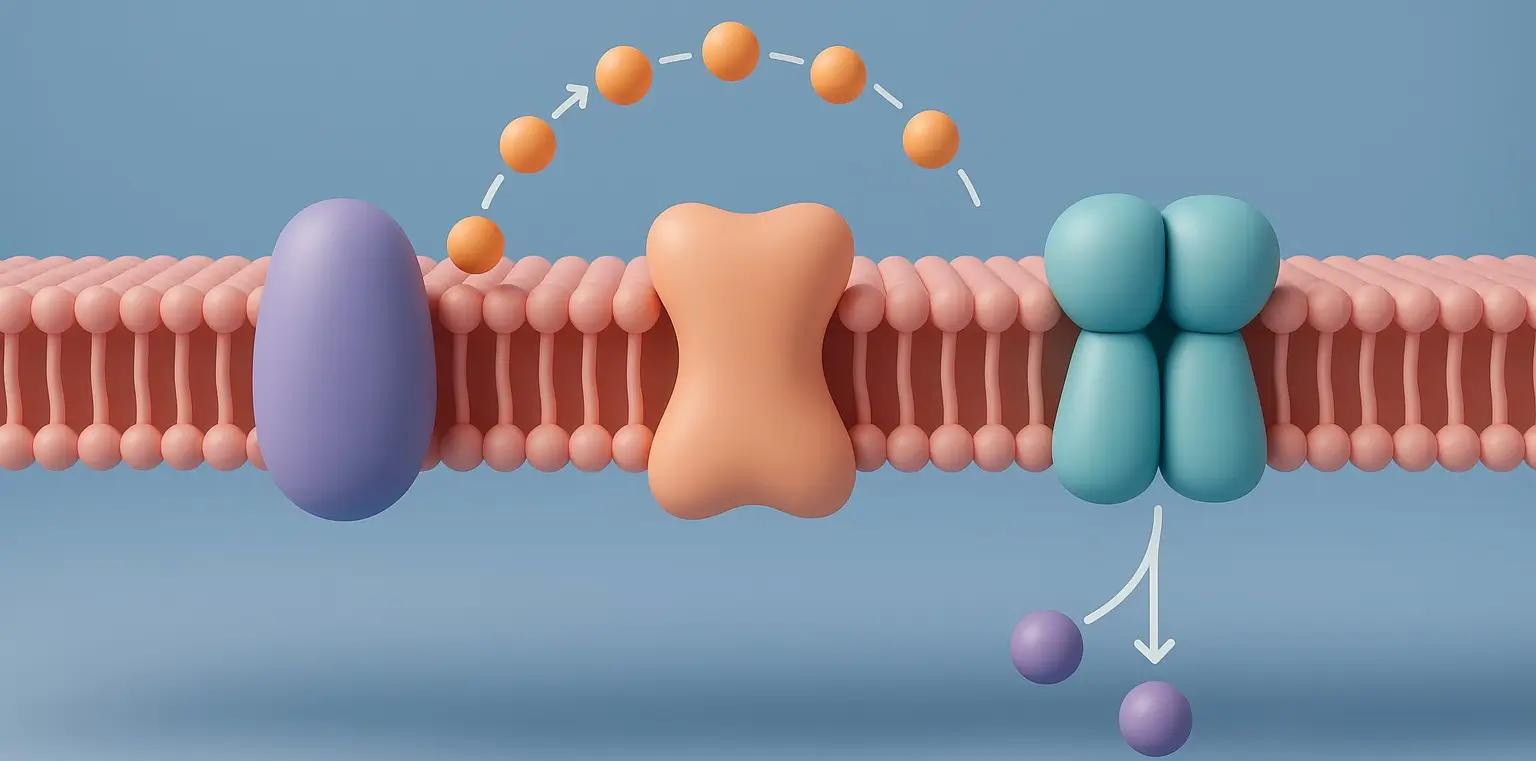
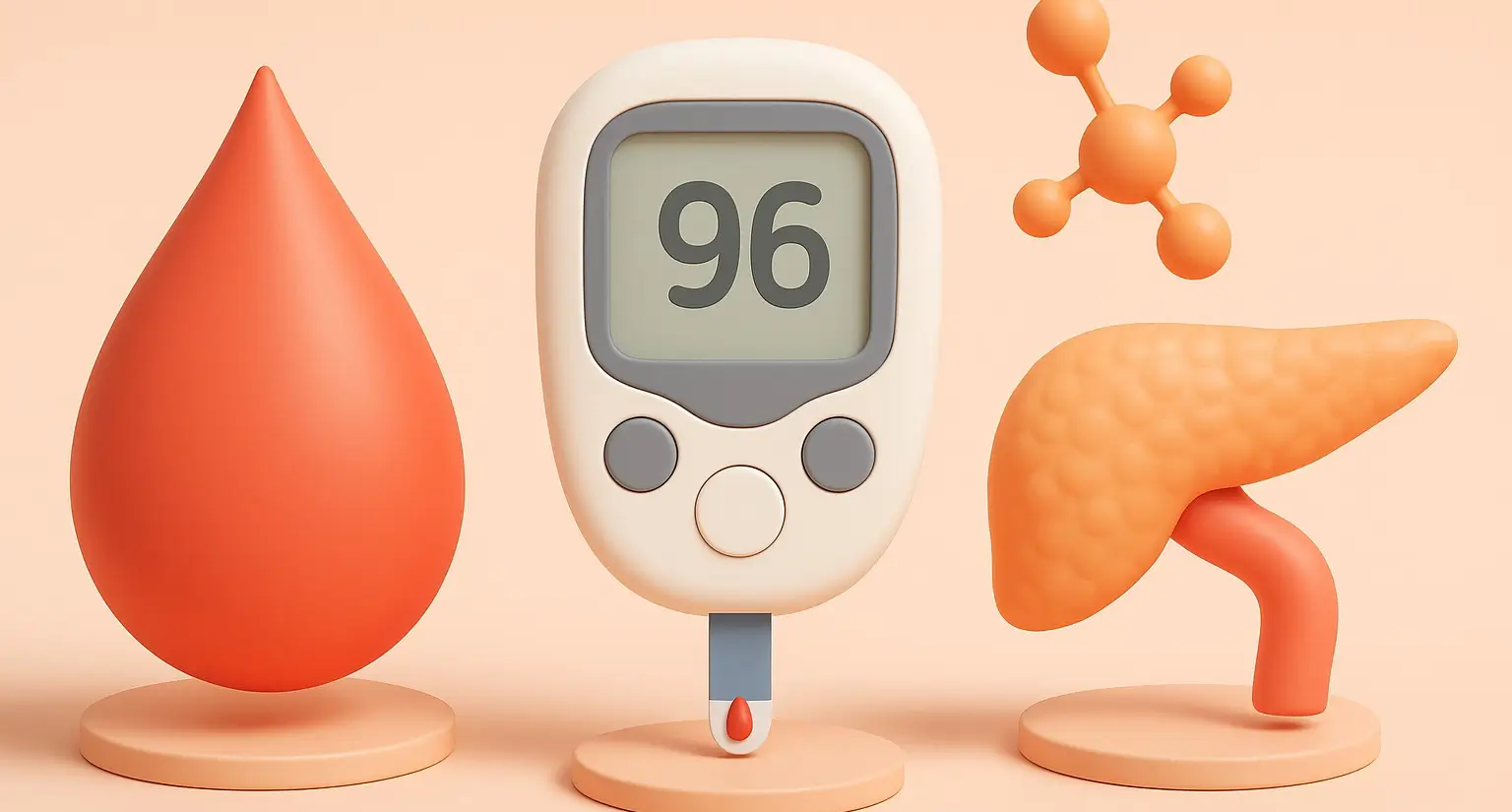
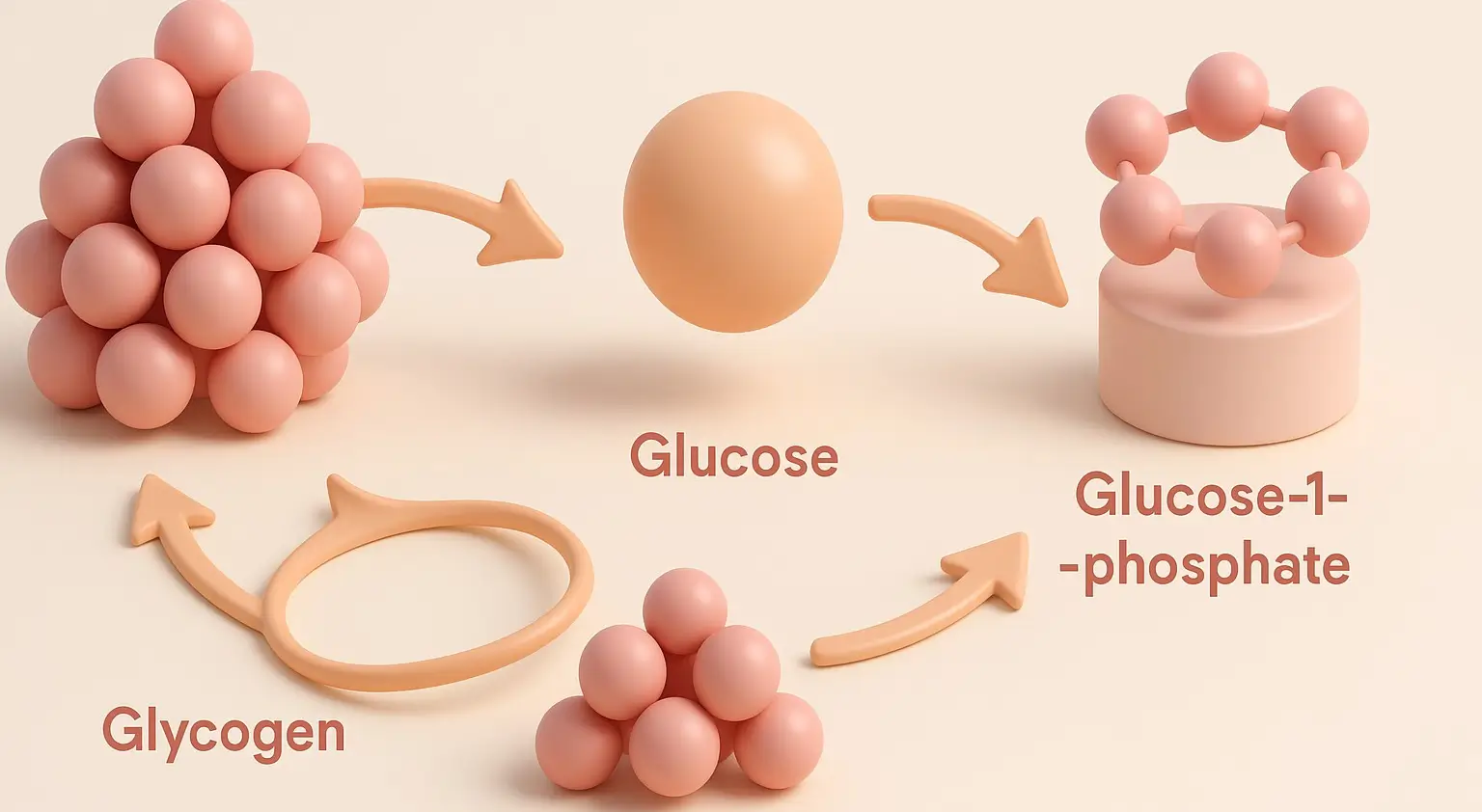
Concept of Reduction
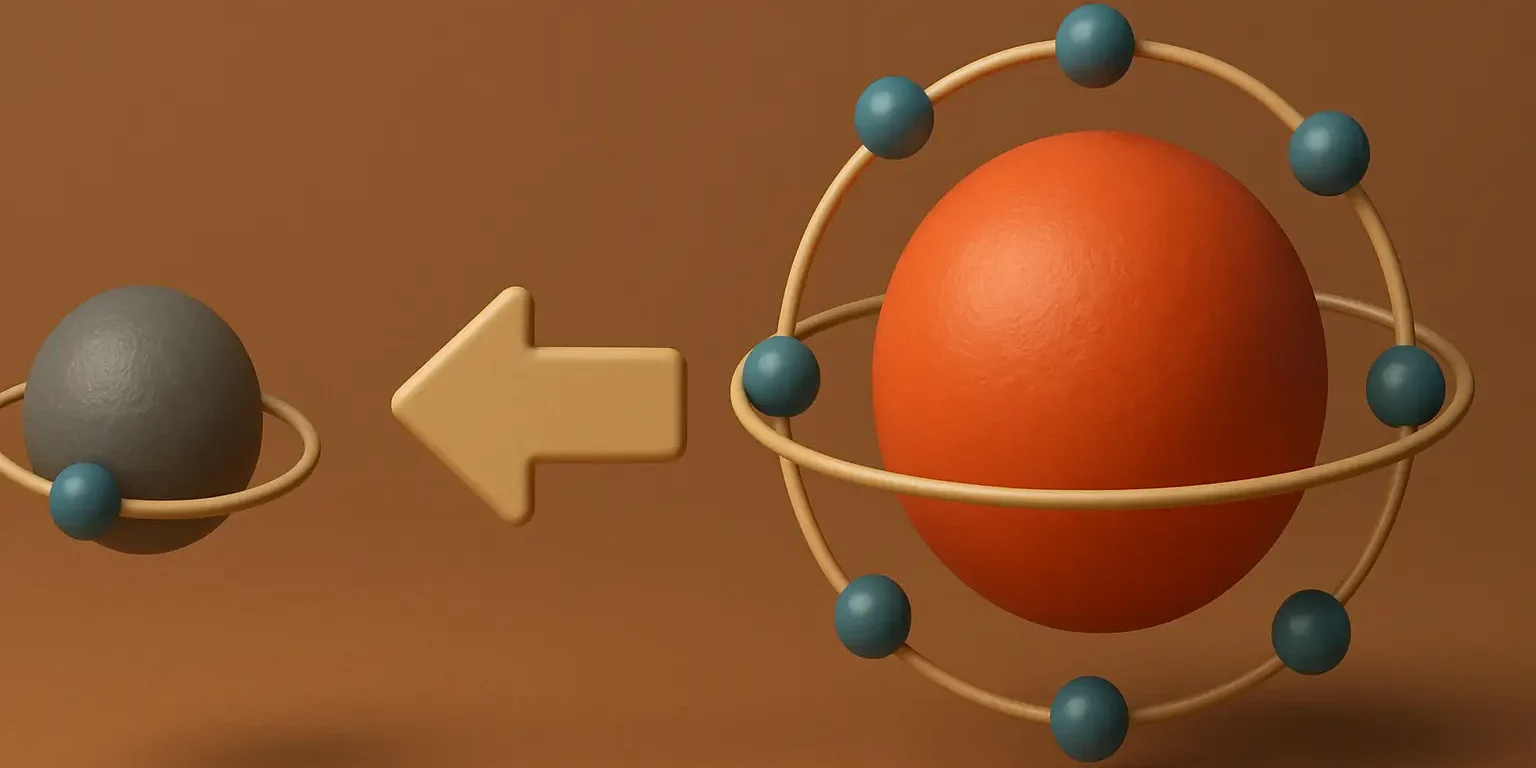
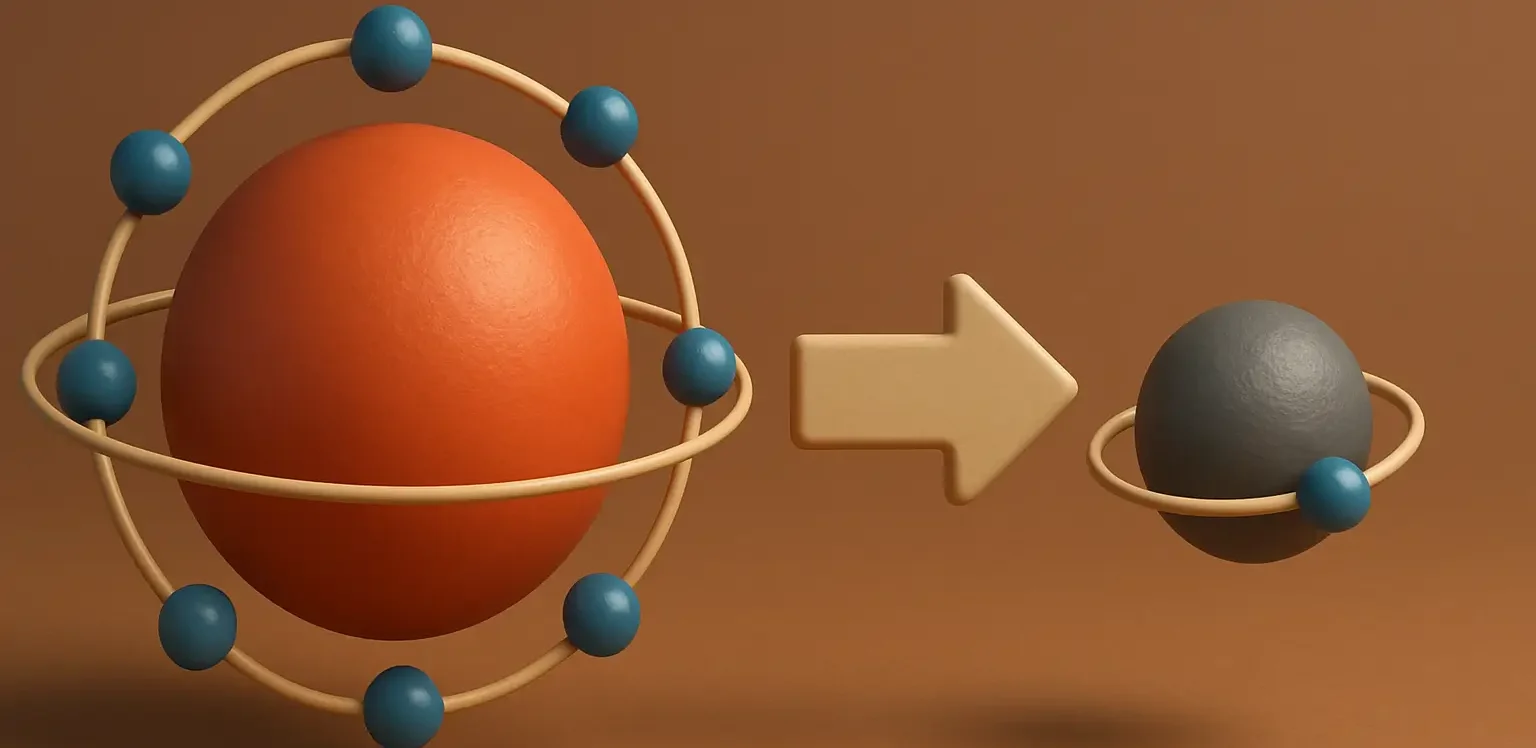
Concept of Reduction is a process in which a chemical species gains one or more electrons, leading to a decrease in its oxidation state. In other words, the species becomes less positively charged or more negatively charged. Reduction is often associated with the addition of hydrogen to a substance or the removal of oxygen from it, … Read more