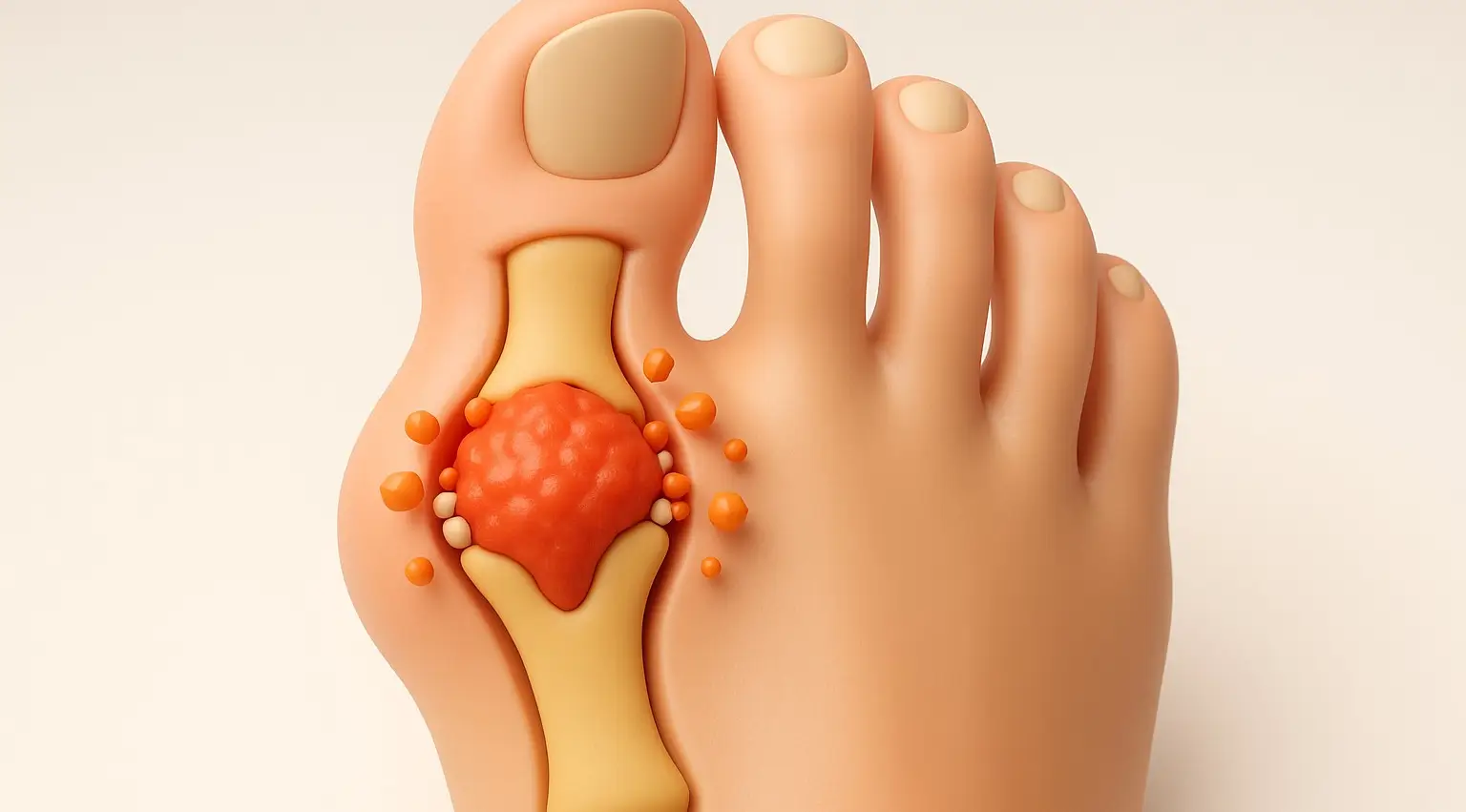
Licensing Authorities
Purpose of Licensing Authorities: Responsible for issuing, renewing, and revoking licenses required for manufacturing, wholesale, and retail of drugs and cosmetics. Functions: Application Processing: Reviewing and approving applications for various licenses as per the Act and rules. Compliance Verification: Ensuring that applicants meet all the necessary criteria, including infrastructure, qualifications, and financial stability. Inspections: Conducting … Read more