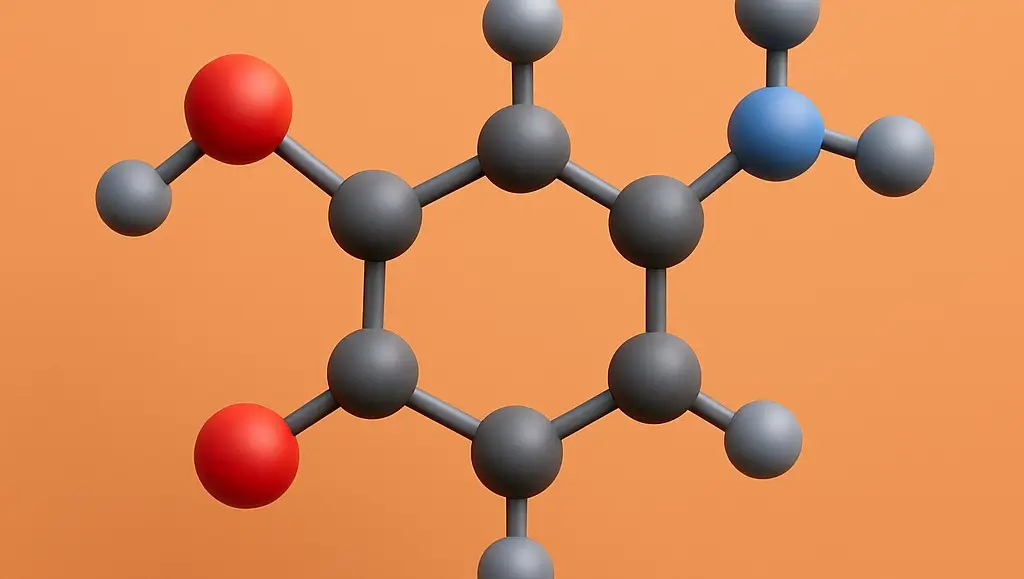
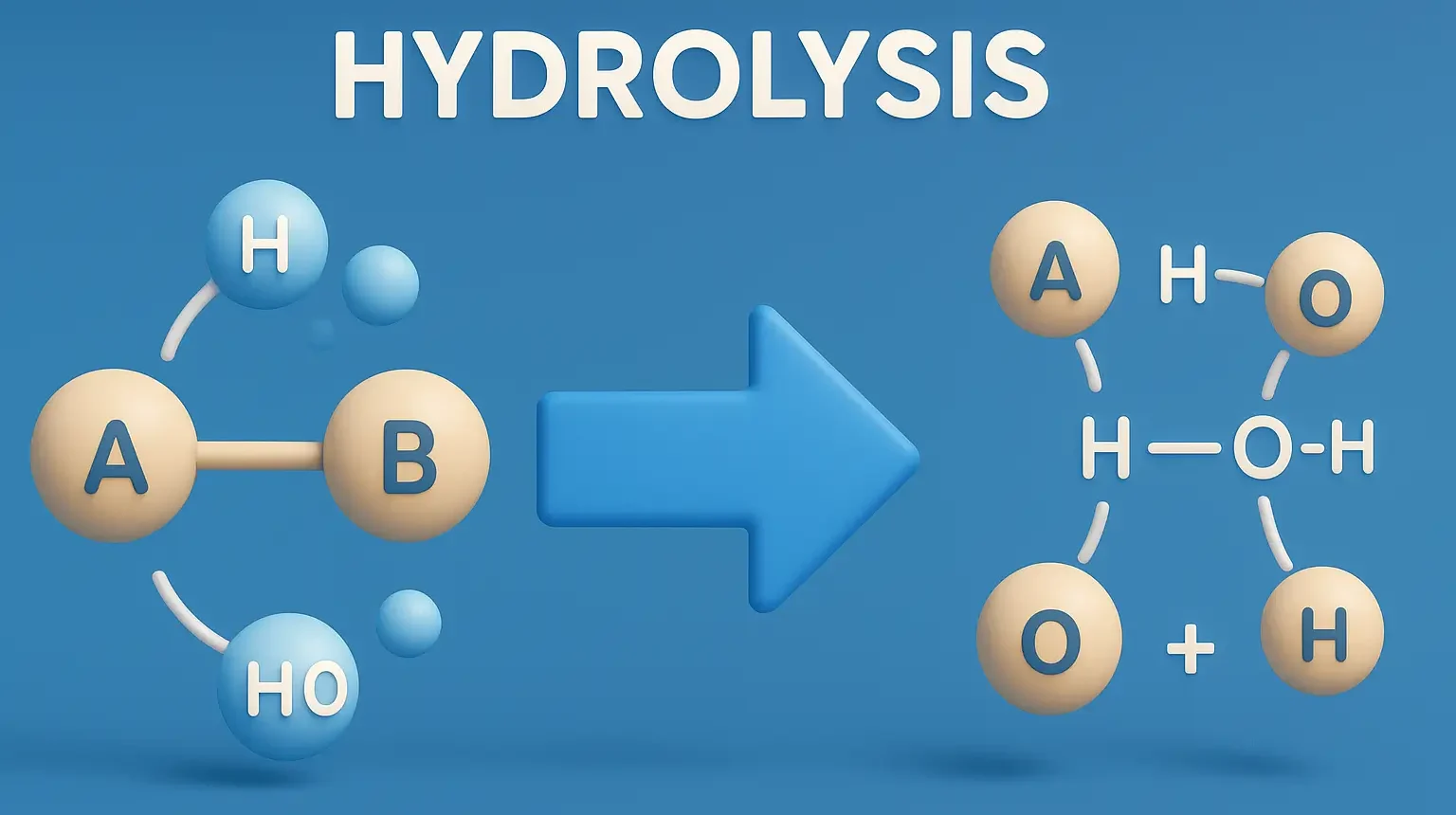
Noradrenaline (Norepinephrine)
Noradrenaline, also known as norepinephrine, is a neurotransmitter and hormone involved in the body’s “fight or flight” response. It is produced primarily in the adrenal medulla and nerve endings of the sympathetic nervous system. Synthesis: Conversion from Dopamine of Noradrenaline: Enzyme: Dopamine β-hydroxylase. Process: Dopamine is hydroxylated to (norepinephrine). Cofactor Required: Ascorbic acid (vitamin C). … Read more