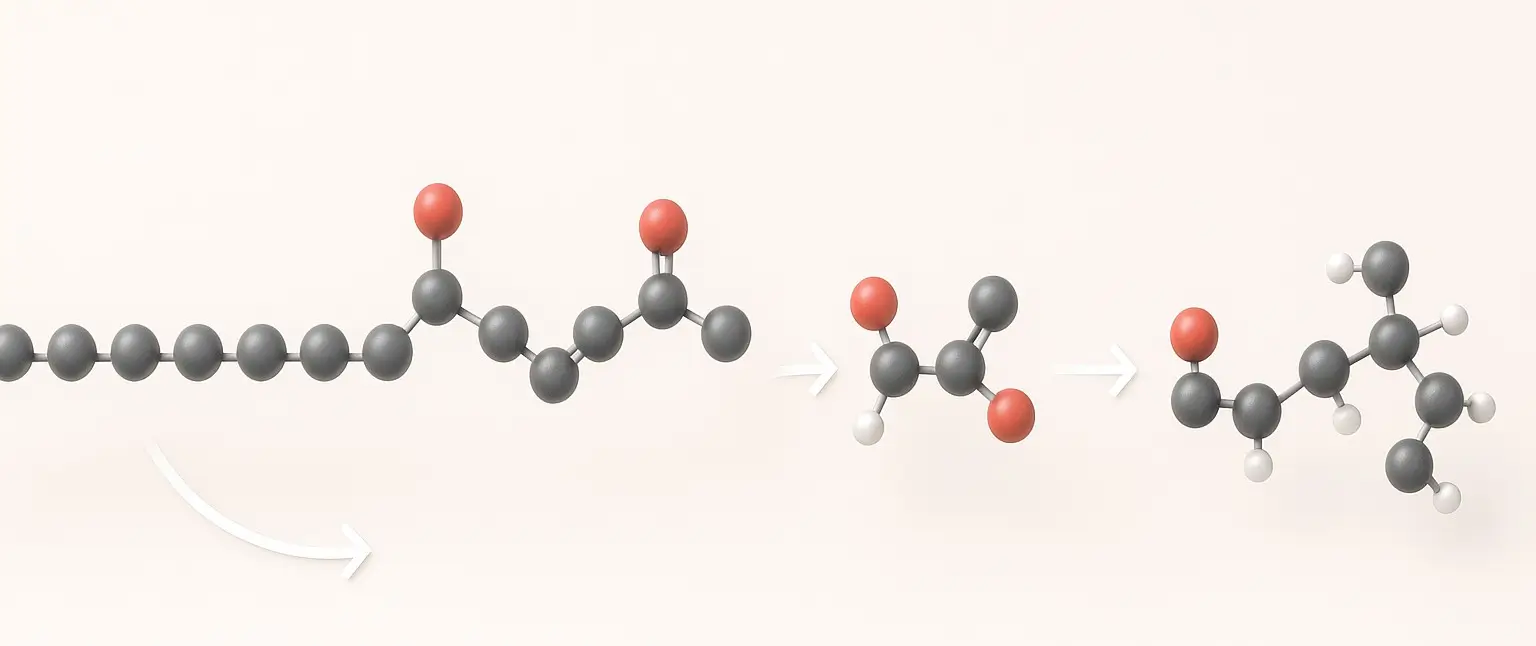
β-Oxidation of saturated fatty acid (Palmitic acid)
β-Oxidation is the primary pathway for breaking down fatty acids to generate energy. In this process, fatty acids are converted into acetyl-CoA, which enters the citric acid cycle (TCA cycle) to produce ATP. Here’s a detailed explanation of the beta-oxidation of palmitic acid, a saturated fatty acid with 16 carbons (C16:0). 1. Activation and Transport into … Read more