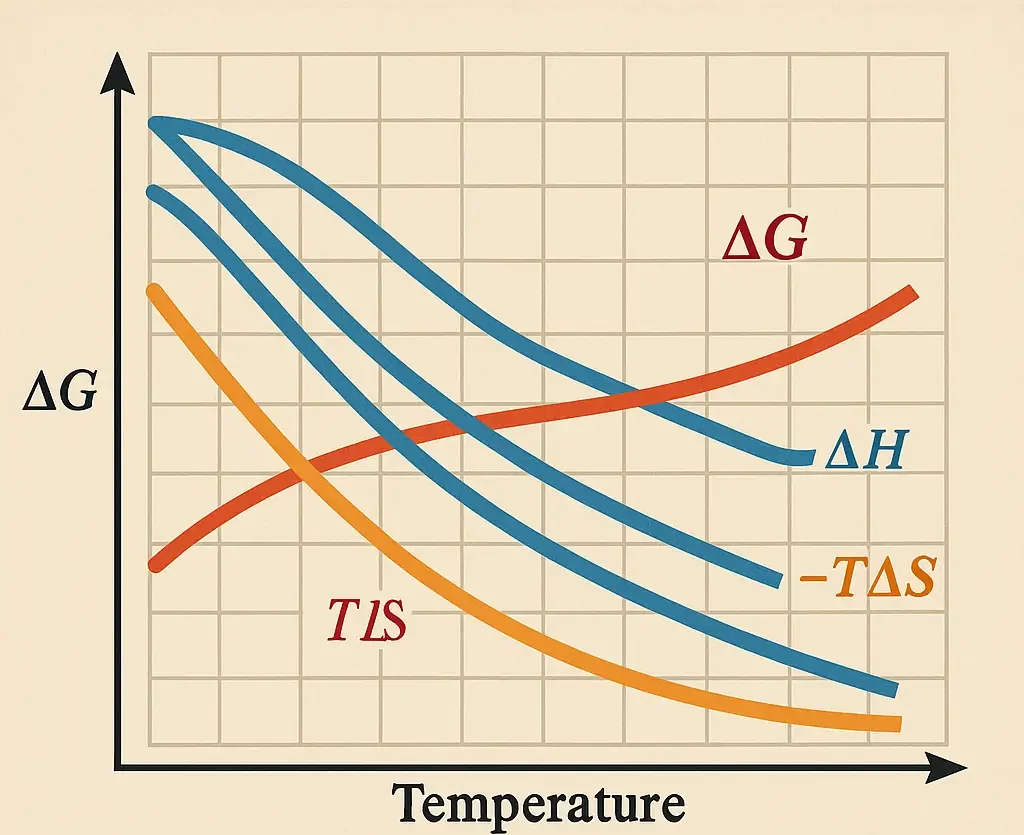
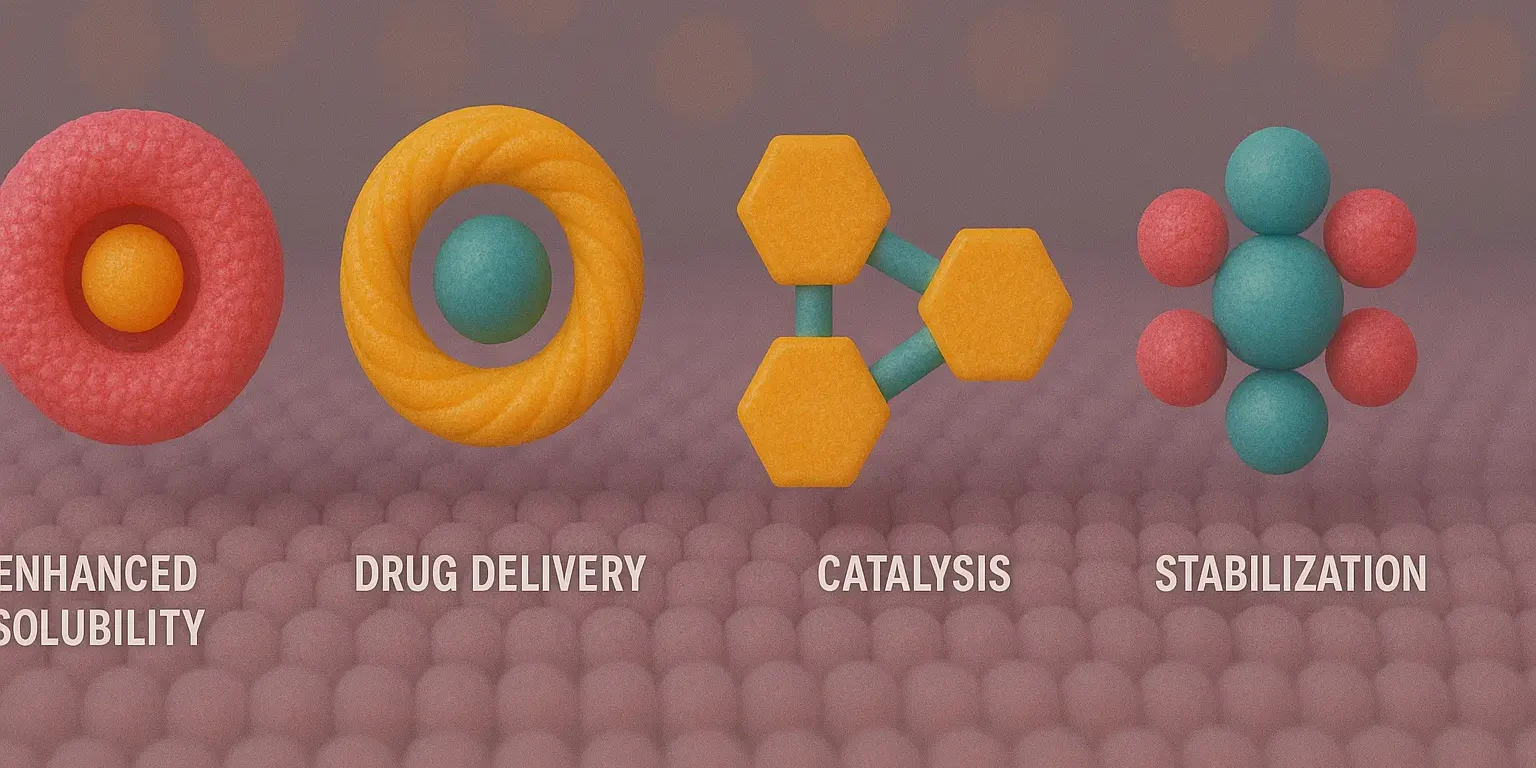
Carbohydrate
Carbohydrate are vital organic molecules composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms, typically in a ratio of 1:2:1. These molecules play a pivotal role as an essential nutrient and primary energy source for most living organisms, besides serving structural functions in some instances. Classification of Carbohydrate Carbohydrate are categorized based on their complexity into: Monosaccharides … Read more