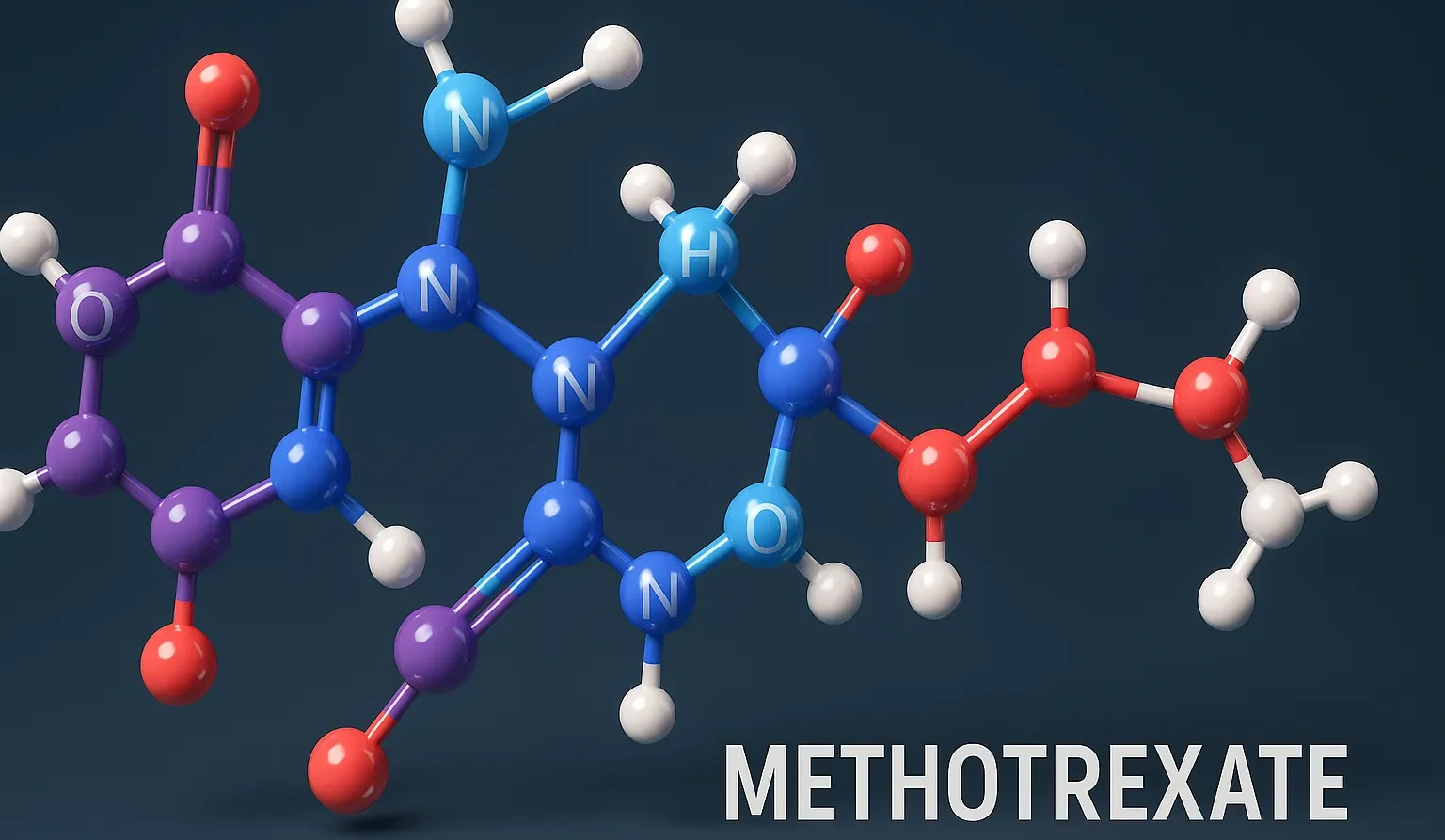
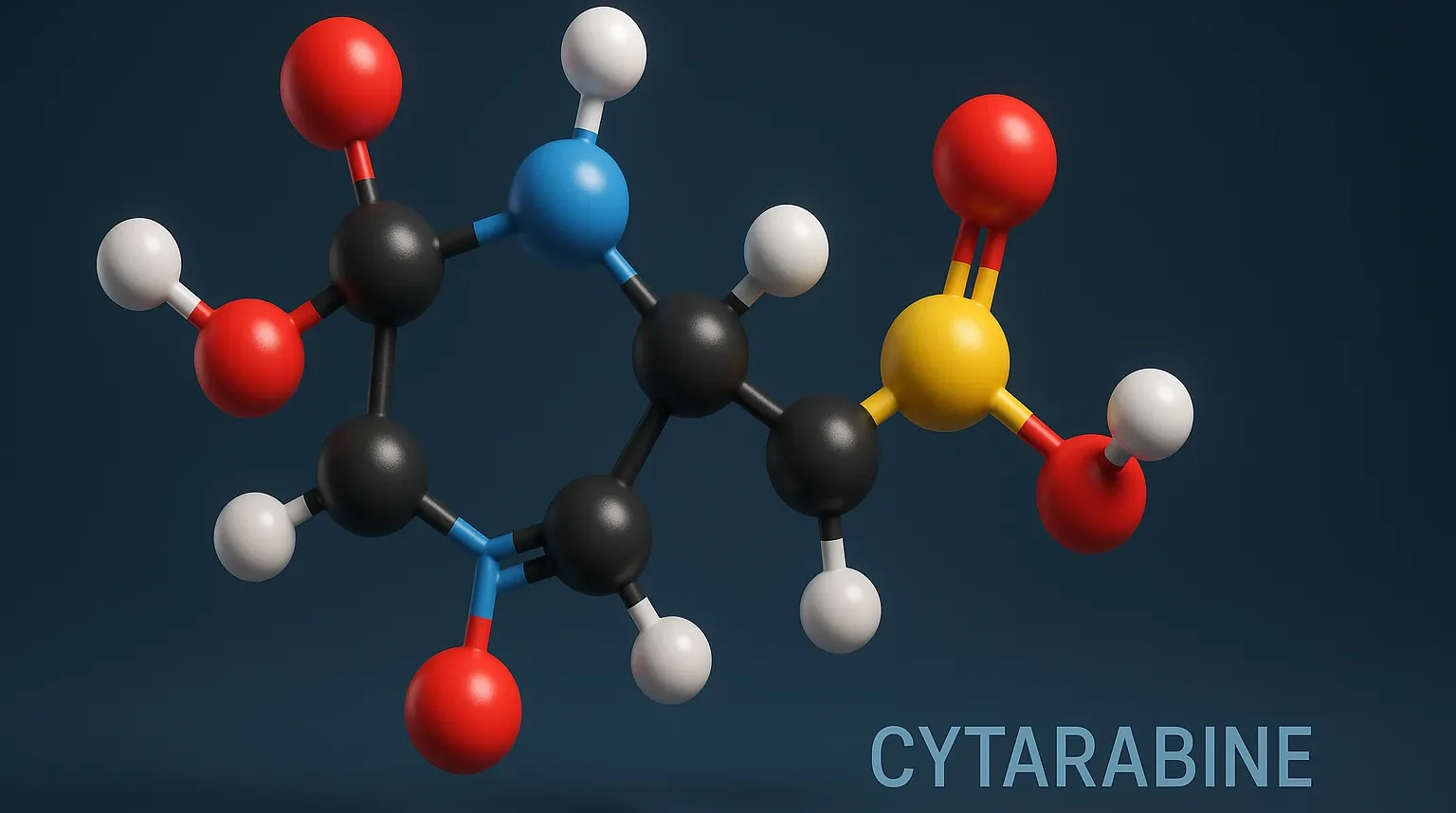
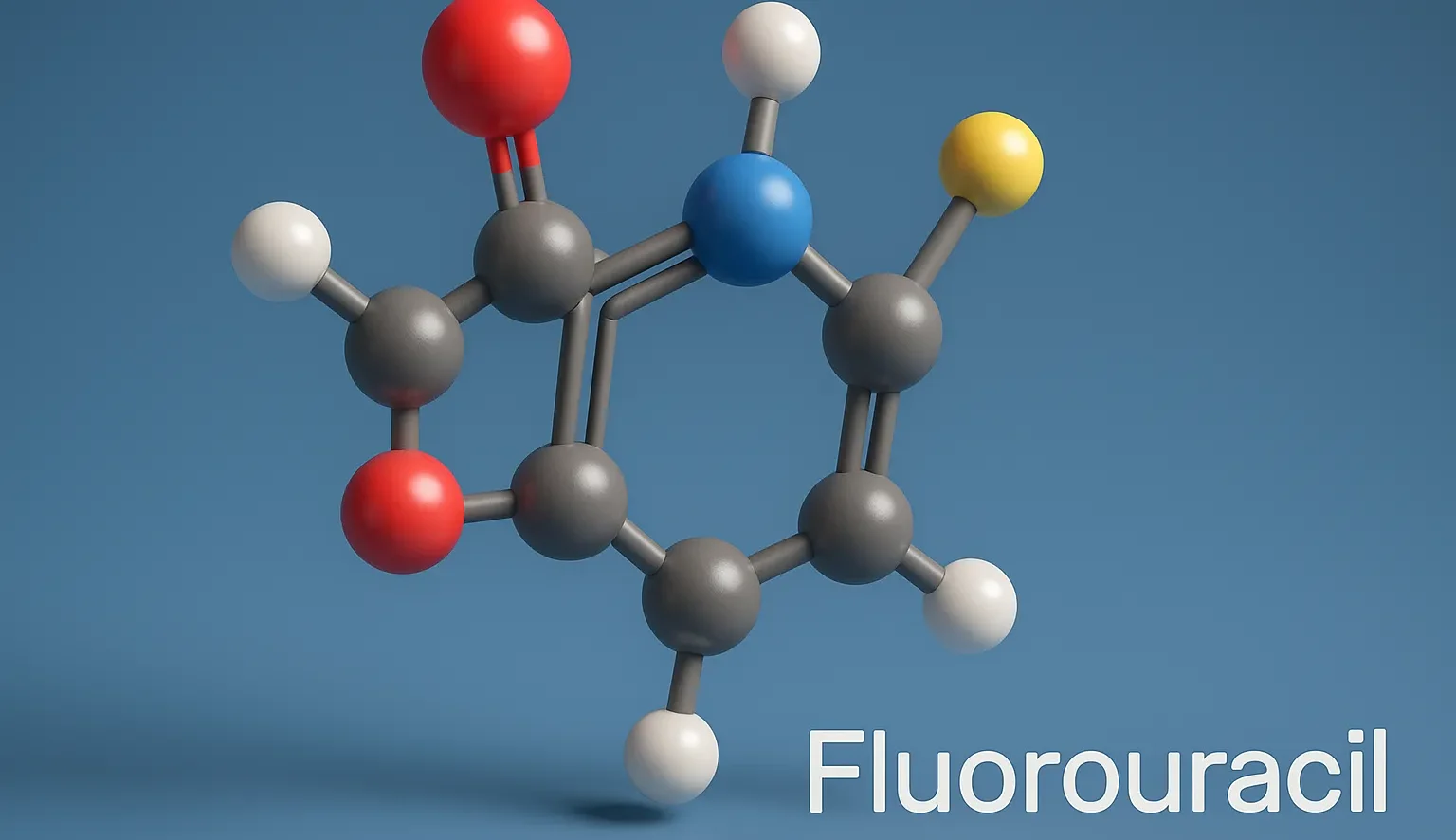
Menthol
Source and Occurrence of Menthol: Menthol is predominantly found in the essential oils of the peppermint plant (Mentha × piperita), but it is also present in other mint species such as spearmint (Mentha spicata). It is widely used in pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and food industries for its cooling sensation and minty flavor. Isolation of Menthol: Extraction: … Read more