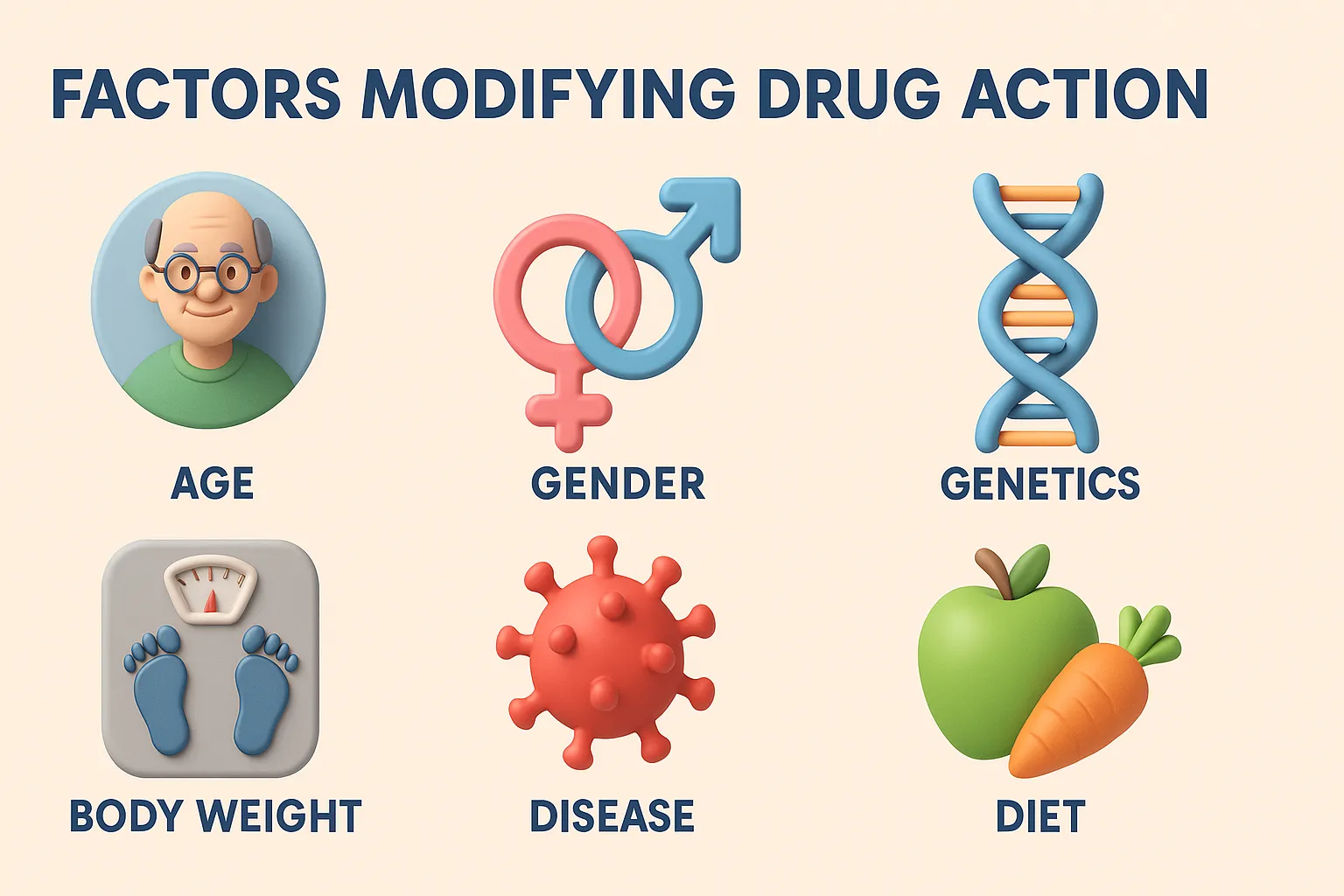
Factors Modifying Drug Action
Factors Modifying Drug Action include age, body weight, genetics, sex, disease, diet, and drug interactions that influence a drug’s effects. Factors Modifying Drug Action Several factors can influence how a drug acts in the body: Age Neonates: Immature liver/kidneys → slower metabolism and excretion. Elderly: Reduced organ function → altered drug response. Body Weight & … Read more