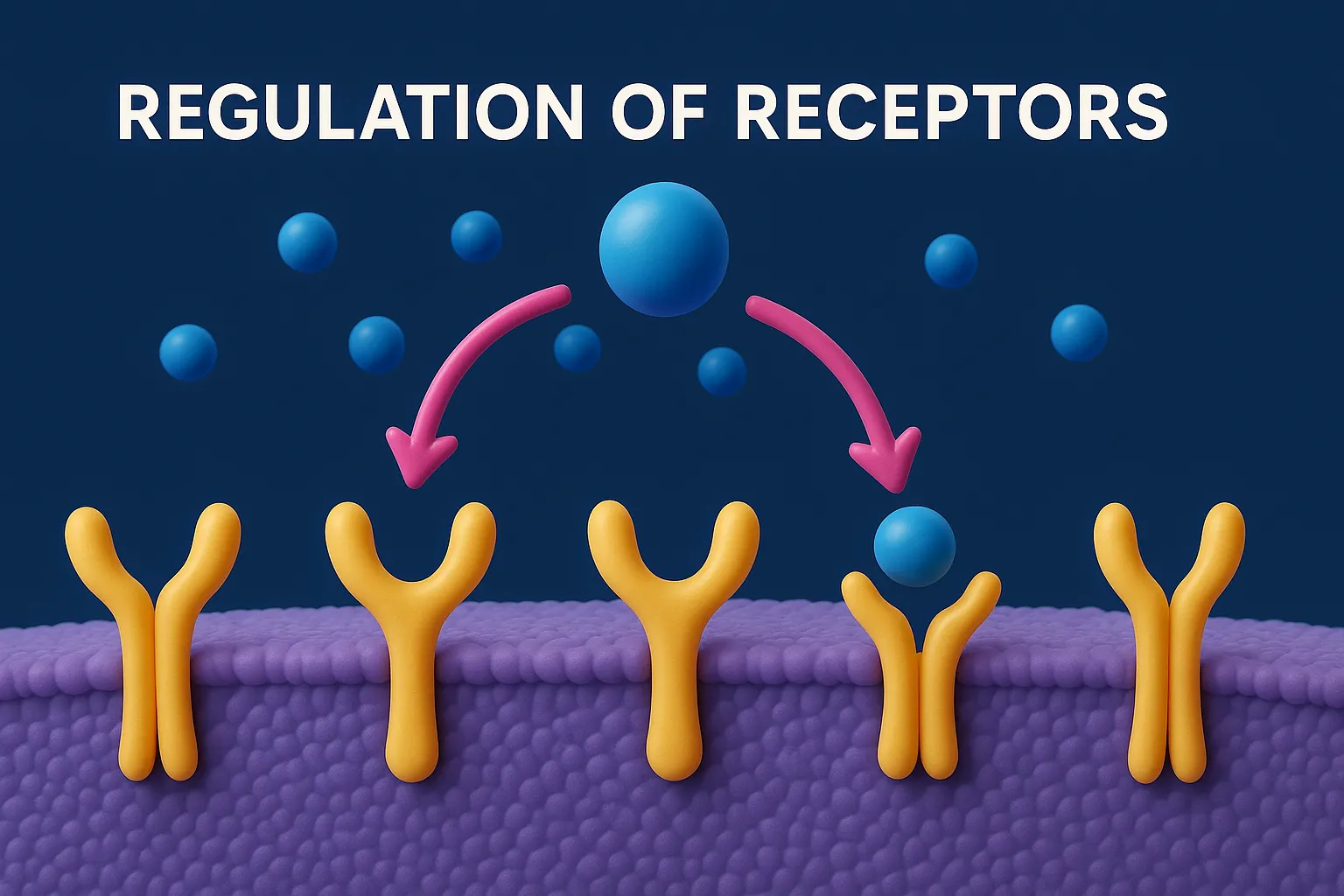
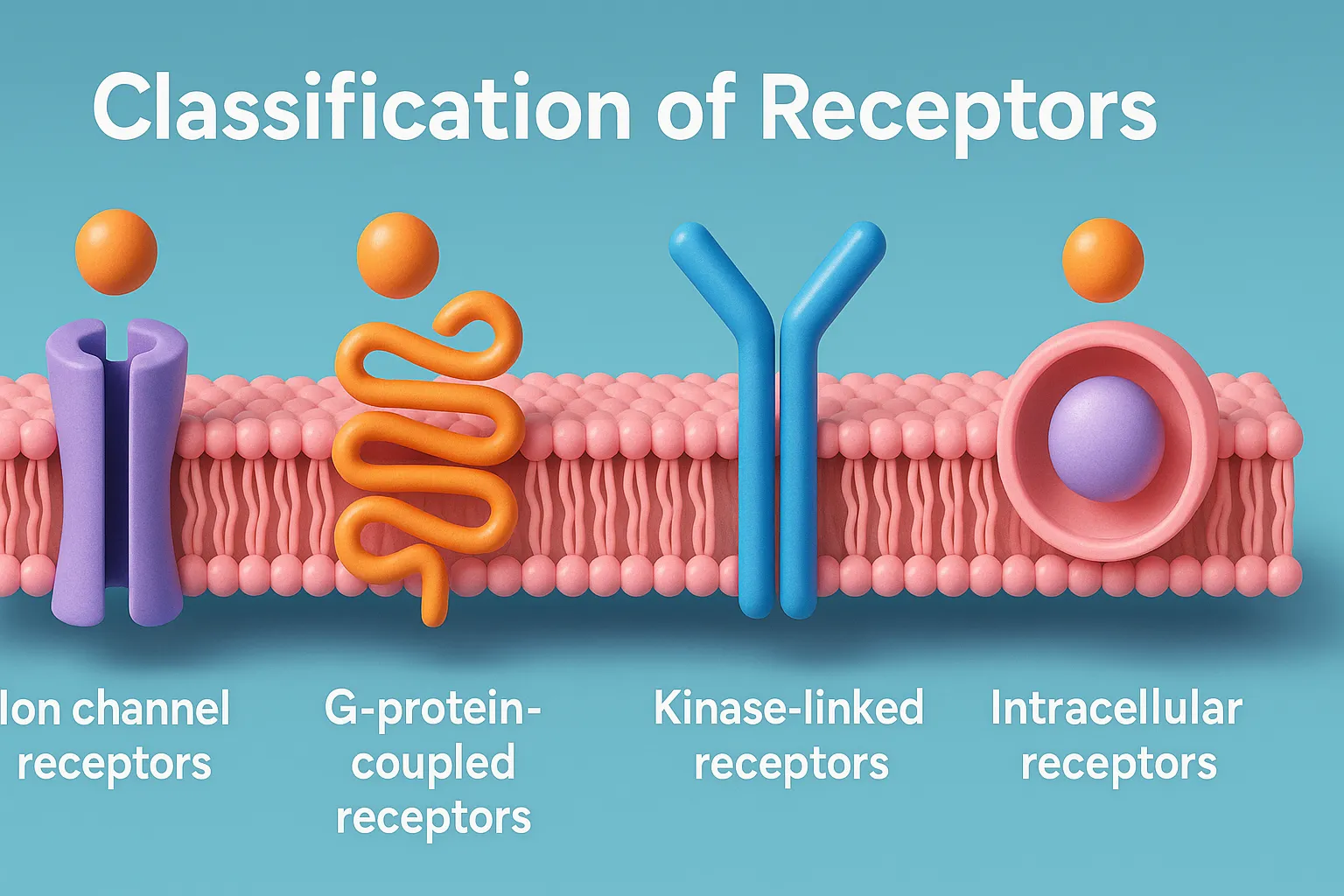
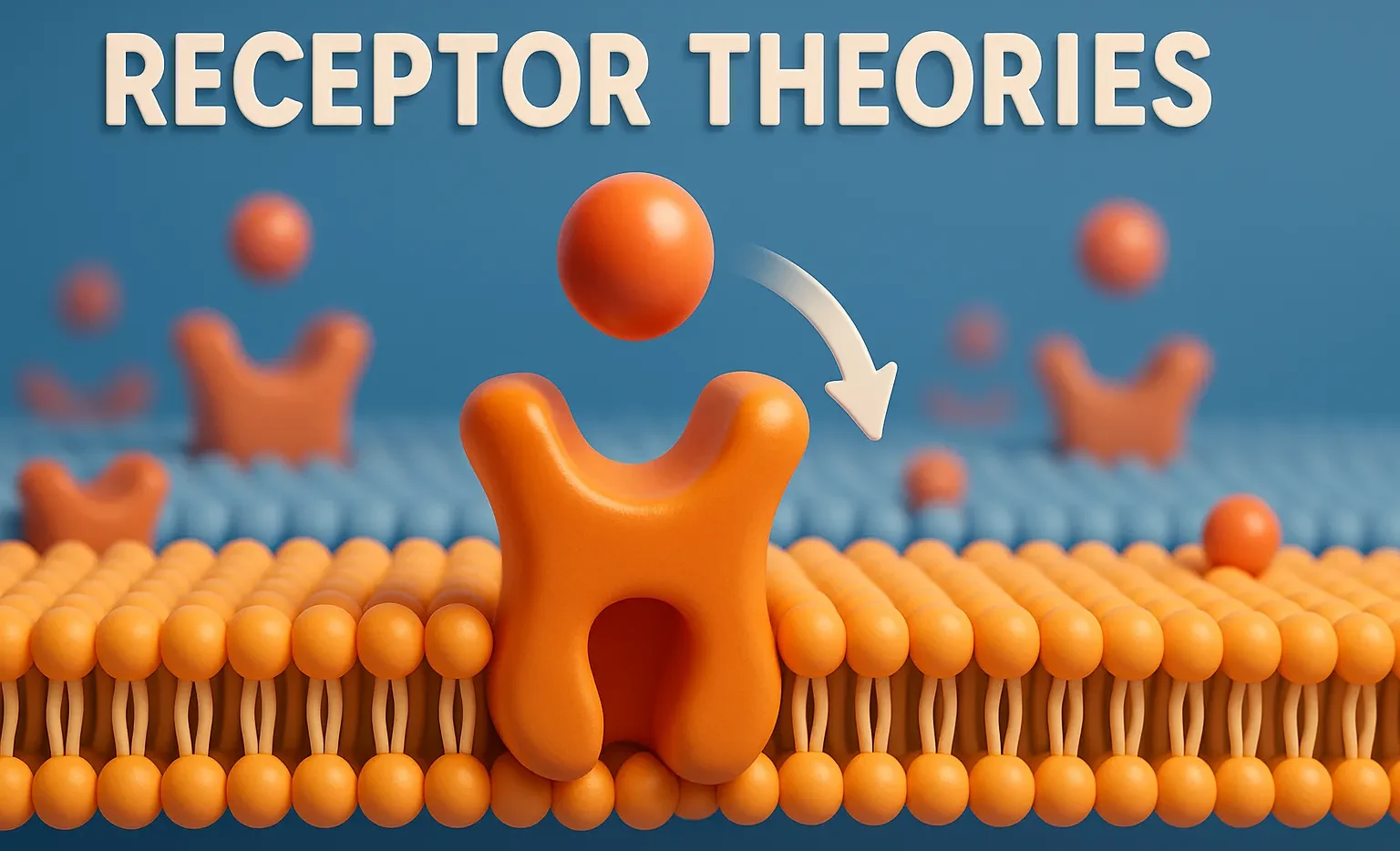
Regulation of Receptors
Regulation of receptors involves upregulation or downregulation, affecting drug sensitivity and therapeutic response. Regulation of Receptors Cells dynamically regulate receptors in response to various stimuli to maintain homeostasis. Key mechanisms include: Receptors can change in number or sensitivity in response to drug exposure: Upregulation Increase in receptor number or sensitivity. Occurs after prolonged use of … Read more