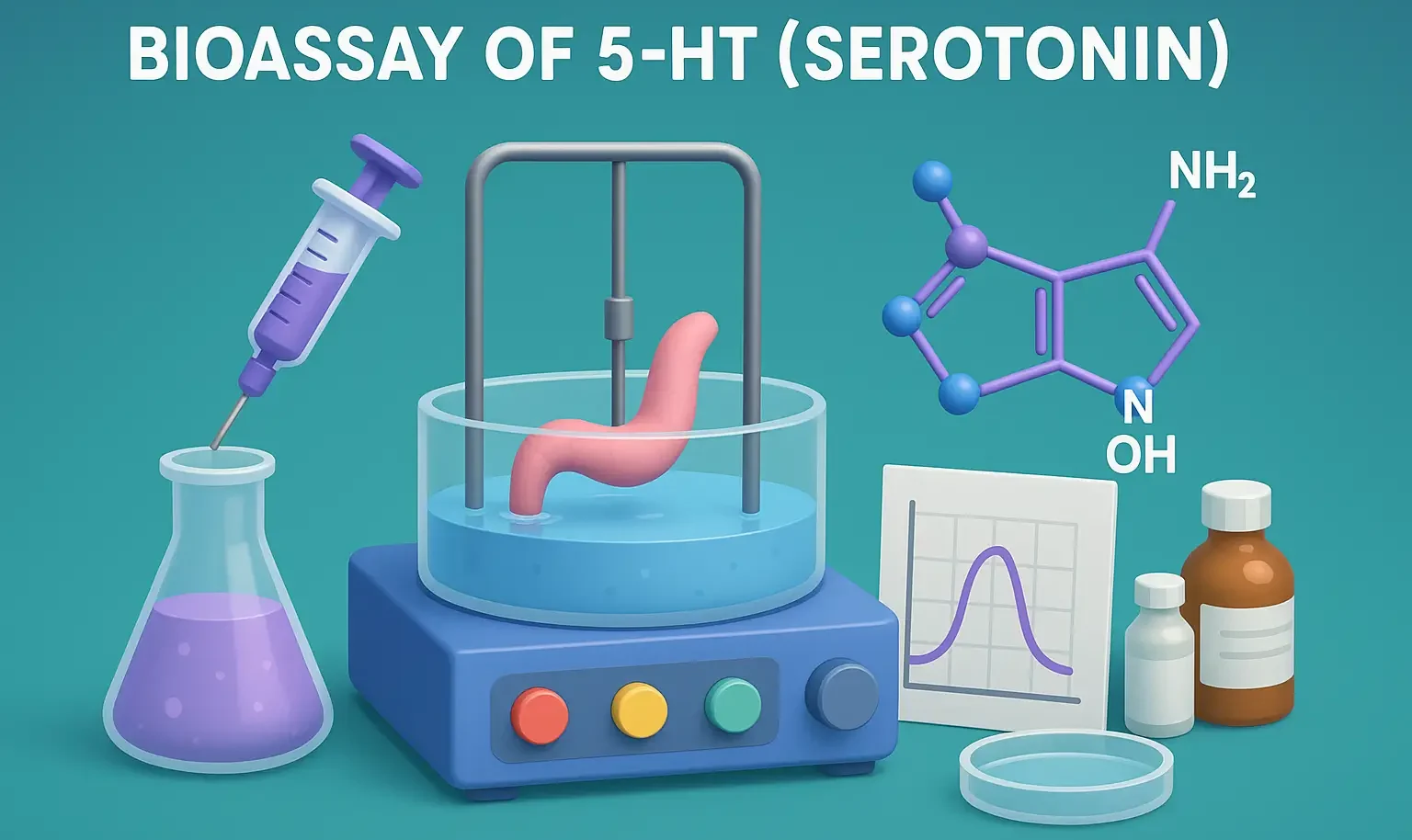
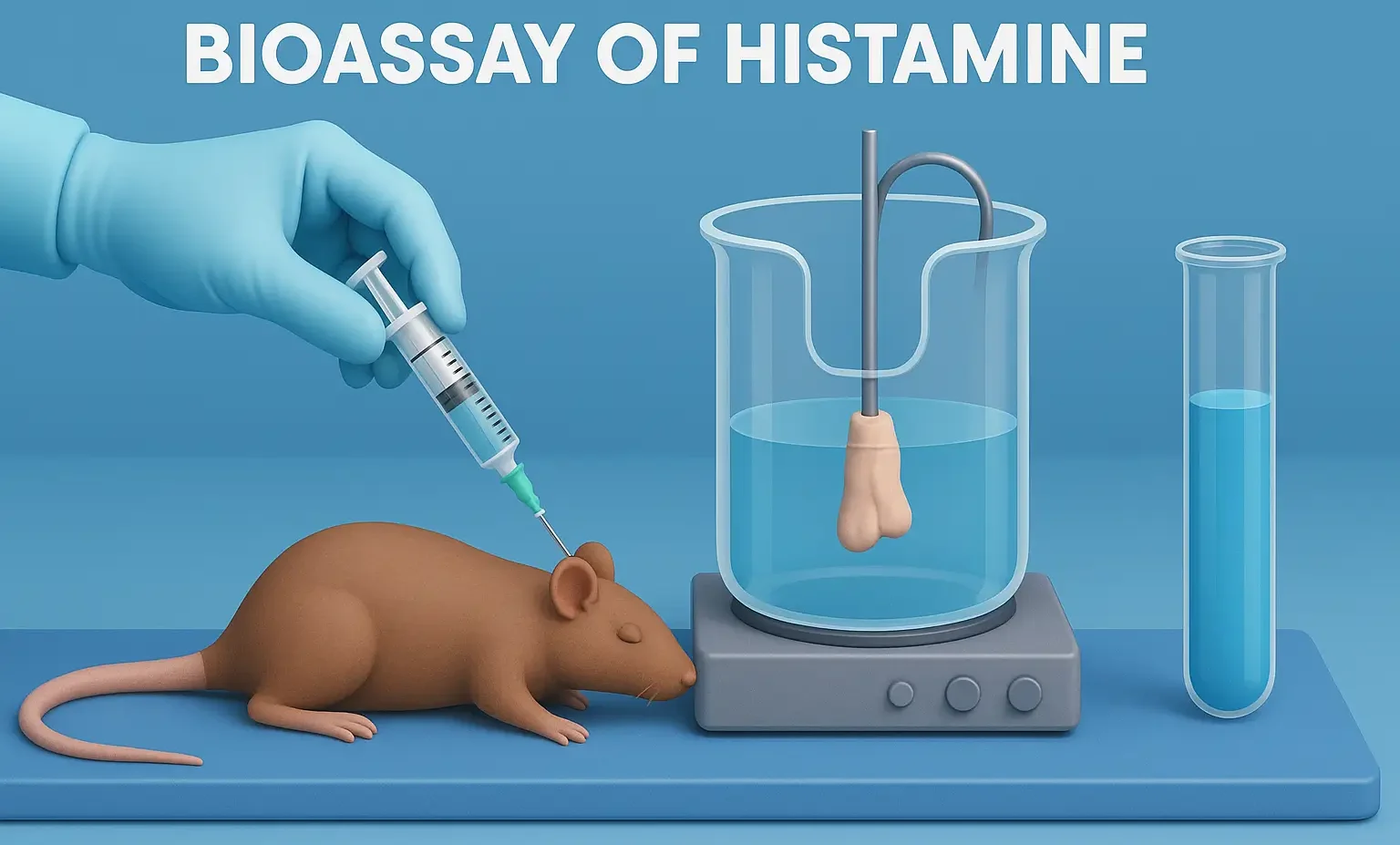
Introduction to Pharmacognosy
Introduction to Pharmacognosy: Study of drugs from natural sources, their origin, properties, and uses in medicine. Importance: Introduction to Pharmacognosy links nature with modern drug discovery for safe, effective treatments. Definition Pharmacognosy: The branch of pharmaceutical sciences that deals with the study of drugs of natural origin, encompassing their biological, chemical, biochemical, and physical properties. … Read more