Neurohumoral Transmission in the CNS
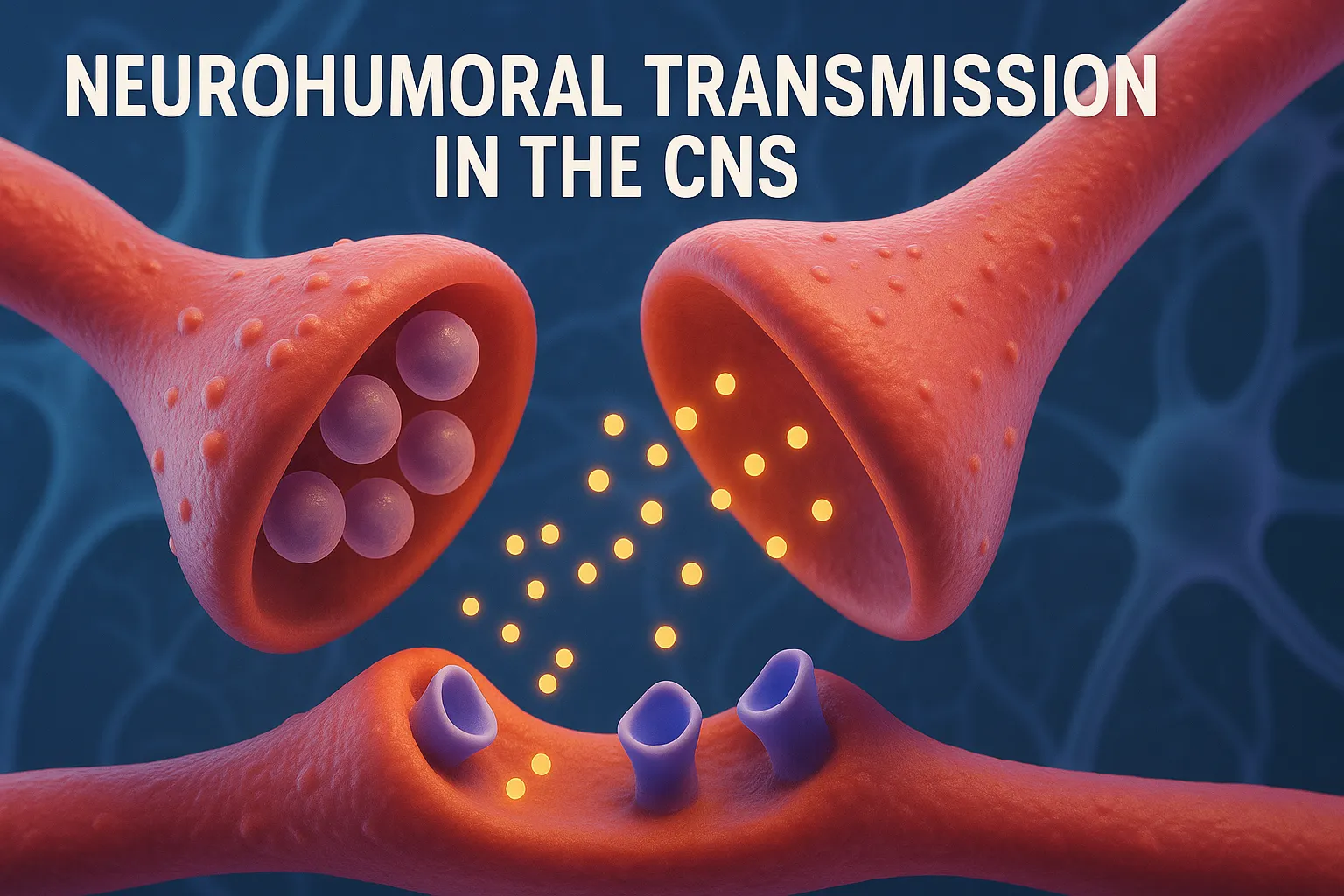
Neurohumoral Transmission in the CNS Neurohumoral transmission refers to the chemical communication between neurons via neurotransmitters across synapses. Neurohumoral transmission in the CNS involves chemical messengers like neurotransmitters regulating brain signaling. Steps in CNS Neurotransmission: Synthesis of neurotransmitter in the presynaptic neuron. Storage in synaptic vesicles. Release into synaptic cleft via exocytosis (triggered by Ca²⁺ … Read more