Drugs Used in Myasthenia Gravis (MG)
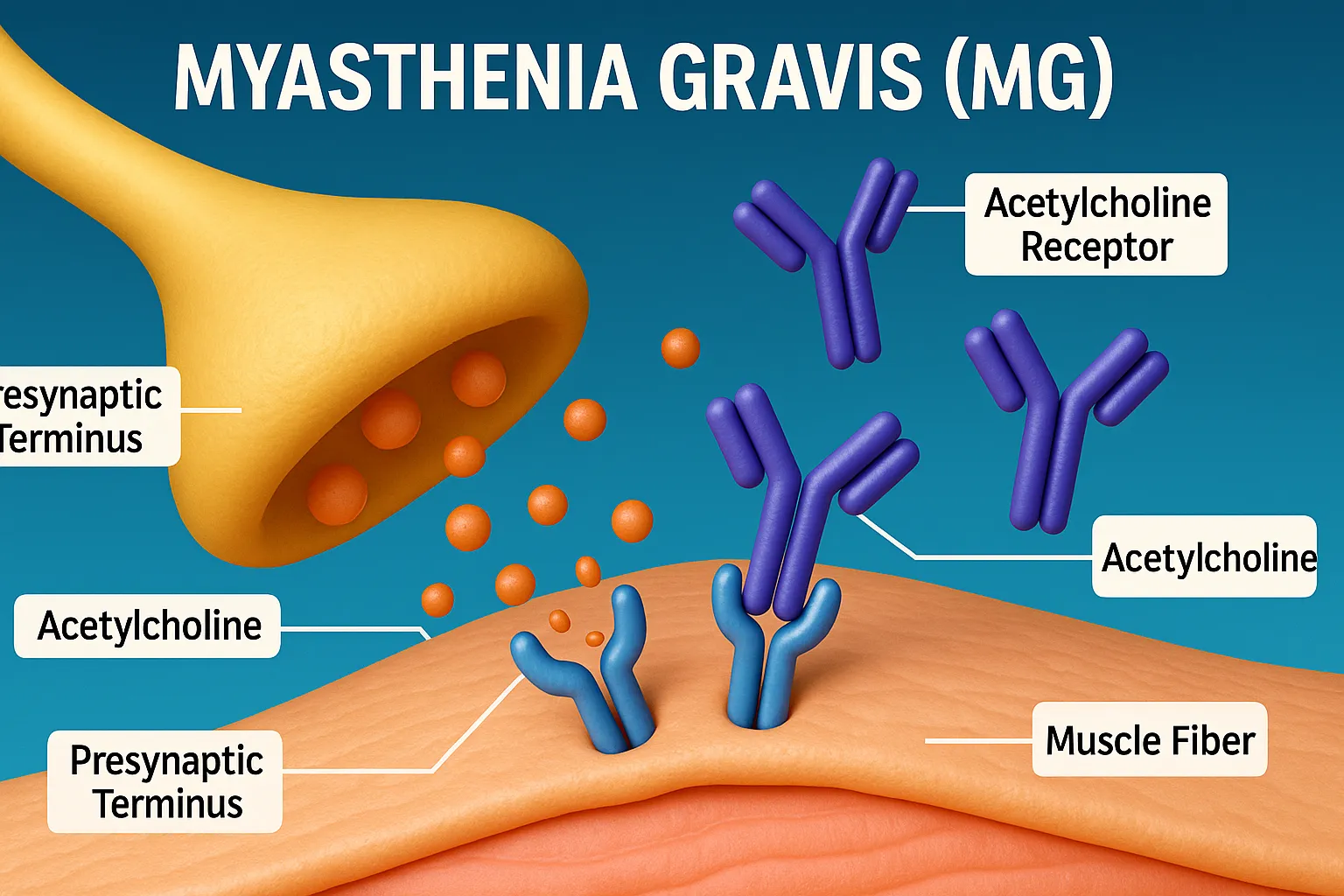
Drugs for Myasthenia Gravis include cholinesterase inhibitors, immunosuppressants, and corticosteroids to improve muscle strength. Pharmacological Goal: To increase acetylcholine availability at the neuromuscular junction and/or suppress the autoimmune response. Main Classes of Drugs: Cholinesterase Inhibitors (First-line therapy): Mechanism: Inhibit the enzyme acetylcholinesterase, increasing ACh levels at the neuromuscular junction. Examples: Pyridostigmine (preferred) Neostigmine Adverse Effects: … Read more