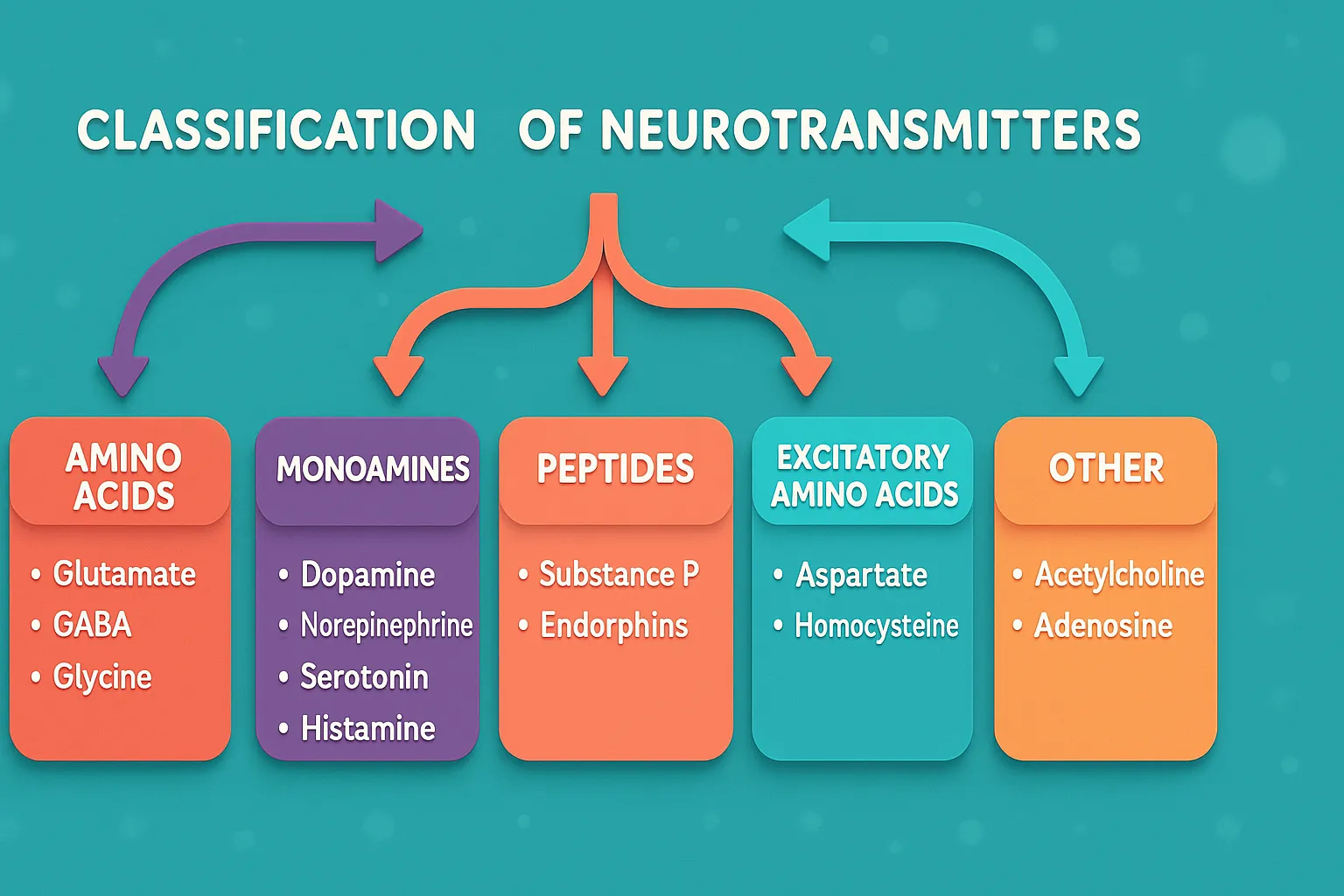
Benztropine Mesylate
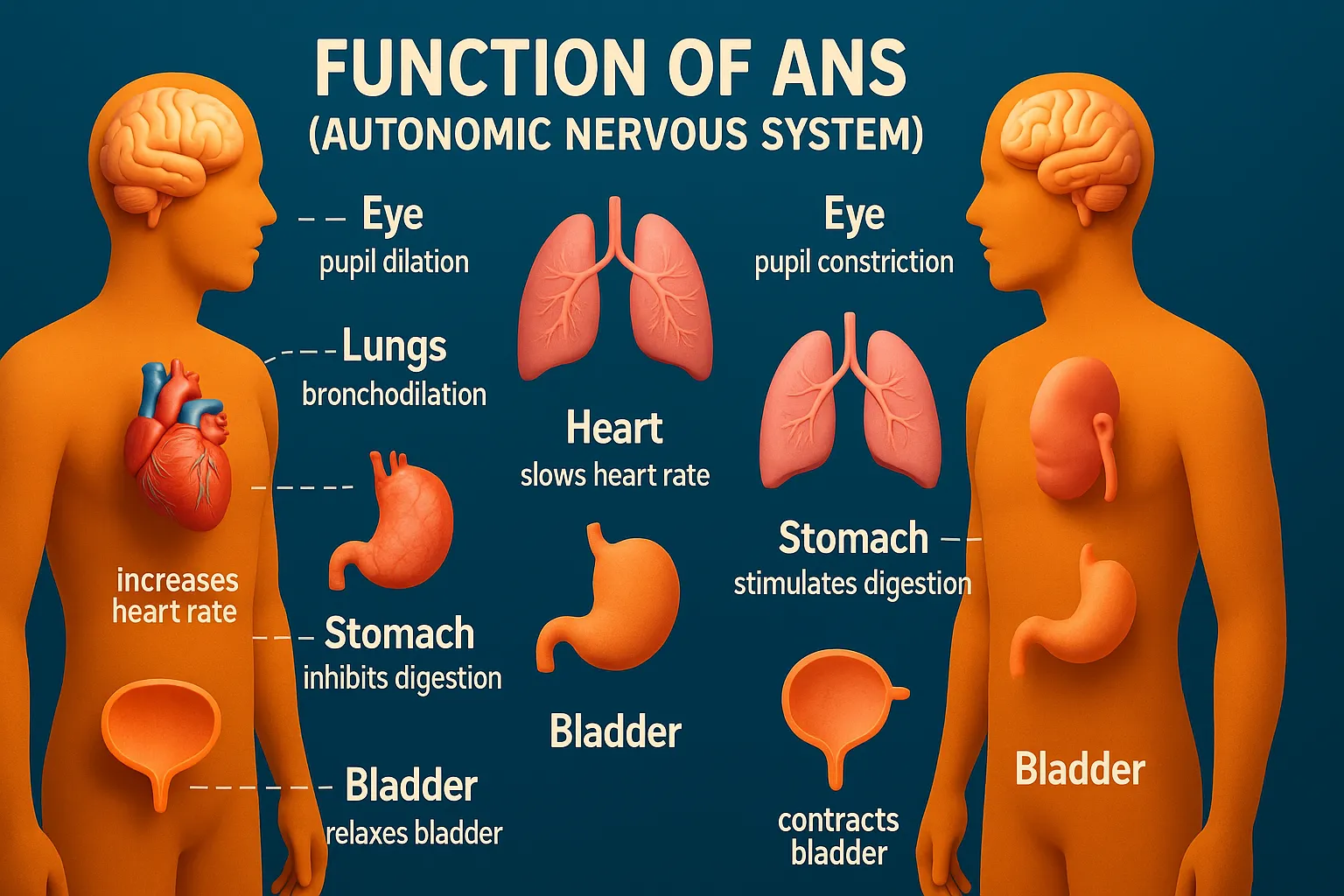
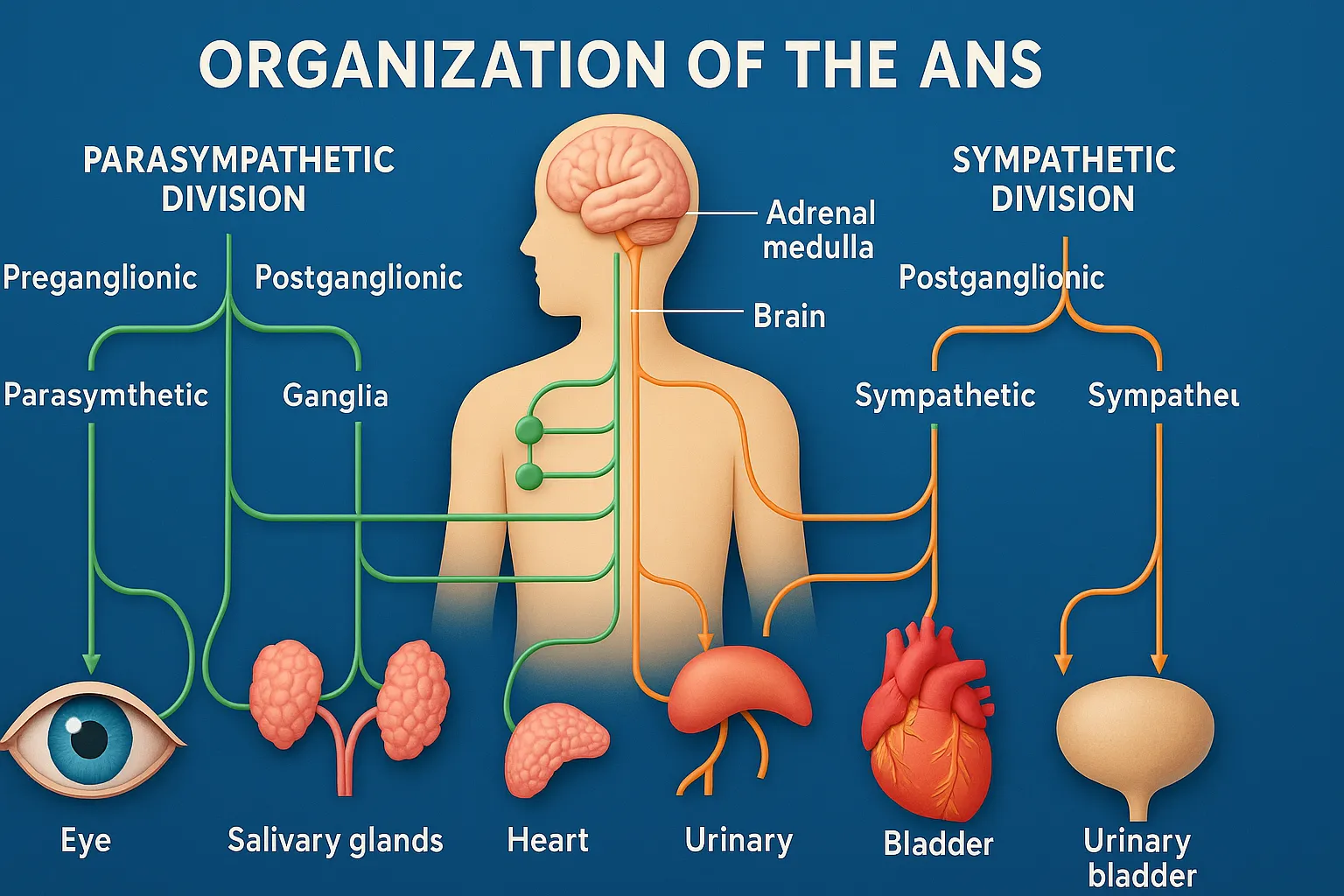
Benztropine Mesylate treats Parkinson’s disease and drug-induced extrapyramidal symptoms. Benztropine Mesylate works as an anticholinergic, balancing dopamine and acetylcholine activity. Chemical Formula: C₂₁H₂₅NO·CH₄O₃S Mechanism of Action: Centrally acting M1 antagonist Also has weak dopamine reuptake inhibition (antiparkinsonian effect) Therapeutic Uses of Benztropine Mesylate: Parkinson’s disease (adjunct) Drug-induced extrapyramidal symptoms (EPS) Side Effects of Benztropine Mesylate: … Read more