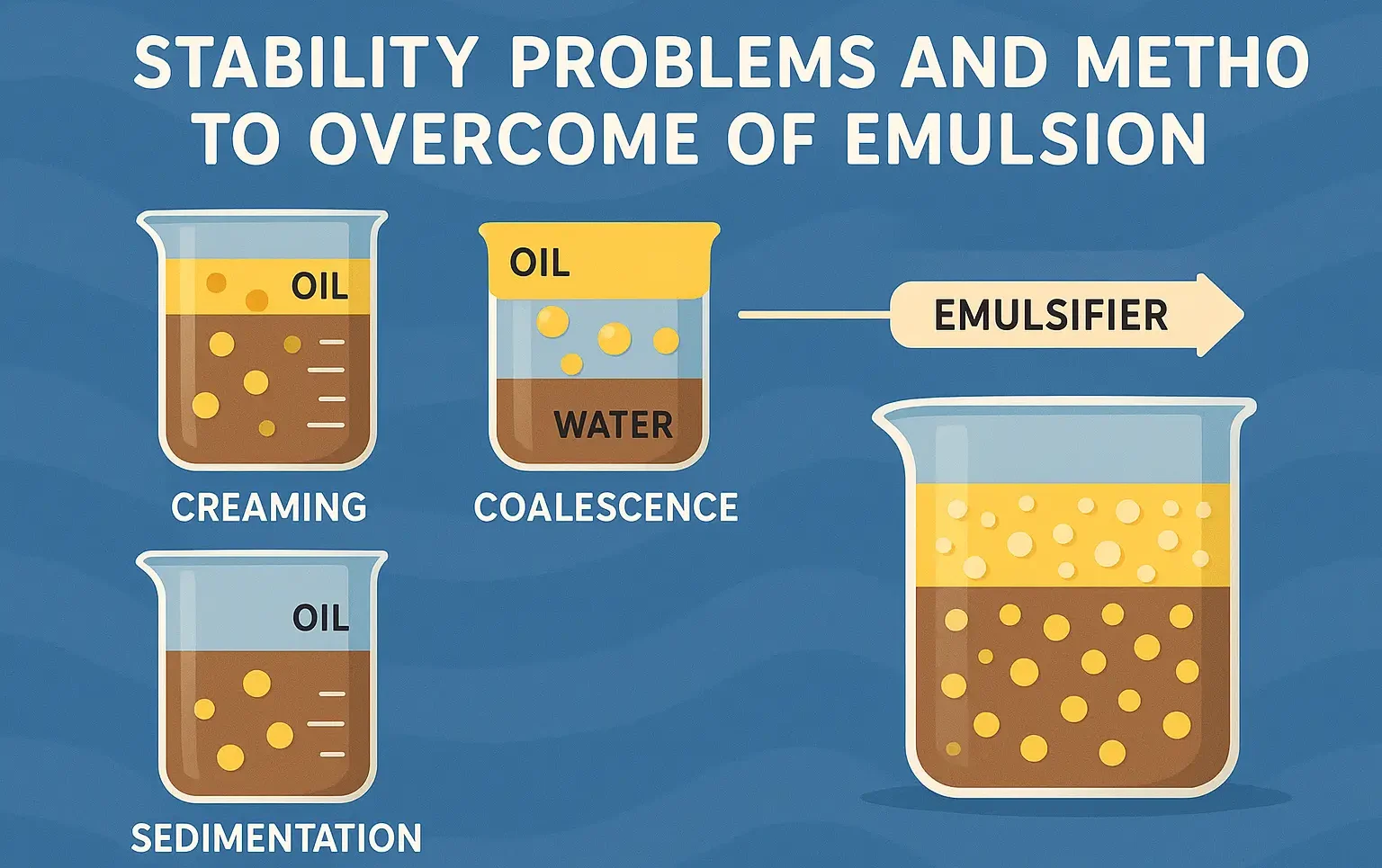
Strategies to overcome incompatibilities
Effective strategies can help mitigate physical, chemical, and therapeutic incompatibilities in pharmaceutical formulations, ensuring the safety, stability, and efficacy of the final product. 1. Physical Incompatibilities Alteration of Base Composition Changing the base (e.g., using cocoa butter, glycerinated gelatin, or PEG) can help manage incompatibilities. Use of Surfactants Adding surfactants improves the dispersion of active … Read more