- Infectious Diseases are illnesses caused by pathogens such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites.
- Infectious diseases can spread directly (e.g., person-to-person contact) or indirectly (e.g., through vectors like insects or contaminated surfaces).
This is a sample ad placement!
Types of Pathogens
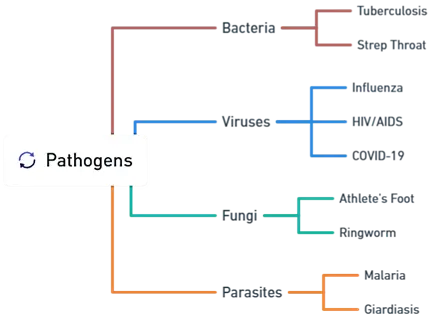
- Bacteria: Cause diseases like tuberculosis and strep throat.
- Viruses: Cause influenza, HIV/AIDS, and COVID-19.
- Fungi: Cause athlete’s foot and ringworm.
- Parasites: Cause malaria and giardiasis.
This is a sample ad placement!
Transmission Methods
- Direct Contact: Physical interactions (e.g., STIs).
- Indirect Contact: Contaminated surfaces or airborne particles.
- Vector-Borne: Insects like mosquitoes and ticks.
- Food and Water: Contaminated consumption (e.g., cholera).
Common Symptoms:
- Unexplained weight loss
- Persistent fatigue
- Unrelated pain
- Skin changes
- Unusual lumps or swelling
- Difficulty swallowing
- Changes in bowel/bladder habits
- Persistent cough or hoarseness
- Unexplained bleeding or bruising
This is a sample ad placement!
Diagnosis of Infectious diseases:
- Medical history and physical exams
- Laboratory tests: Blood tests, cultures, imaging, molecular diagnostics
Treatment Options:
-
Medications:
- Antibiotics for bacteria
- Antivirals for viruses
- Antifungals for fungi
- Antiparasitics for parasites
-
Supportive Care:
- Symptom management, hydration, nutrition
Prevention Strategies for Infectious diseases:
- Vaccination: Protects against diseases like measles and influenza
- Hygiene: Regular handwashing and safe food practices
- Protective Measures: Insect repellent, safe sex, mask-wearing
- Quarantine/Isolation: Contain outbreaks
This is a sample ad placement!
Public Health Measures
- Surveillance: Monitor disease spread
- Outbreak Control: Implement containment strategies
- Education: Inform the public on prevention and treatment
Thank you for reading from Firsthope's notes, don't forget to check YouTube videos!