- Equipments employed in large scale sterilization processes: various types of equipment are employed depending on the nature of the materials being sterilized and the required sterility assurance level.
- The choice of sterilization equipment depends on factors such as the type of material, the heat sensitivity of the product, and the level of microbial inactivation needed.
Autoclave
-
Operating Principle:
- Autoclaves use moist heat (steam) under high pressure, typically 121°C at 15 psi for 15-30 minutes. Pressurized steam disrupts proteins and nucleic acids, killing microorganisms.
-

Equipment’s employed in large scale sterilization
-
- Autoclaves use moist heat (steam) under high pressure, typically 121°C at 15 psi for 15-30 minutes. Pressurized steam disrupts proteins and nucleic acids, killing microorganisms.
-
Applications:
- Sterilizes surgical instruments, glassware, culture media, pharmaceutical products, and canned goods.
-
Advantages:
- Highly effective for most microorganisms, including spores.
- Suitable for heat-resistant materials like metal, glass, and some plastics.
- Consistent and reliable.
-
Limitations:
- Unsuitable for heat-sensitive materials (e.g., electronics, certain plastics).
- Requires regular maintenance and validation.
This is a sample ad placement!
Hot Air Oven
-
Operating Principle:
- Uses dry heat (160°C-180°C for 2-4 hours) to kill microorganisms by oxidative damage.
- Uses dry heat (160°C-180°C for 2-4 hours) to kill microorganisms by oxidative damage.
-
Applications:
- Sterilizes glassware, metal tools, powders, oils, and moisture-sensitive items.
-
Advantages:
- Ideal for moisture-sensitive materials.
- Effective for heat-resistant materials that cannot be autoclaved.
-
Limitations:
- Requires longer cycles than moist heat.
- High temperatures may not suit all materials.
- High energy consumption.
Microwave Sterilization
-
Operating Principle:
- Uses microwave radiation to generate heat within materials, with added steam enhancing effectiveness.
-
Applications:
- Sterilizes small medical devices, medical waste, and some food products.
-
Advantages:
- Rapid, energy-efficient sterilization.
- Suitable for small items or complex geometries.
-
Limitations:
- Limited penetration depth; ineffective for bulk materials.
- Not suitable for metallic or microwave-sensitive items.
- Risk of uneven heating.
This is a sample ad placement!
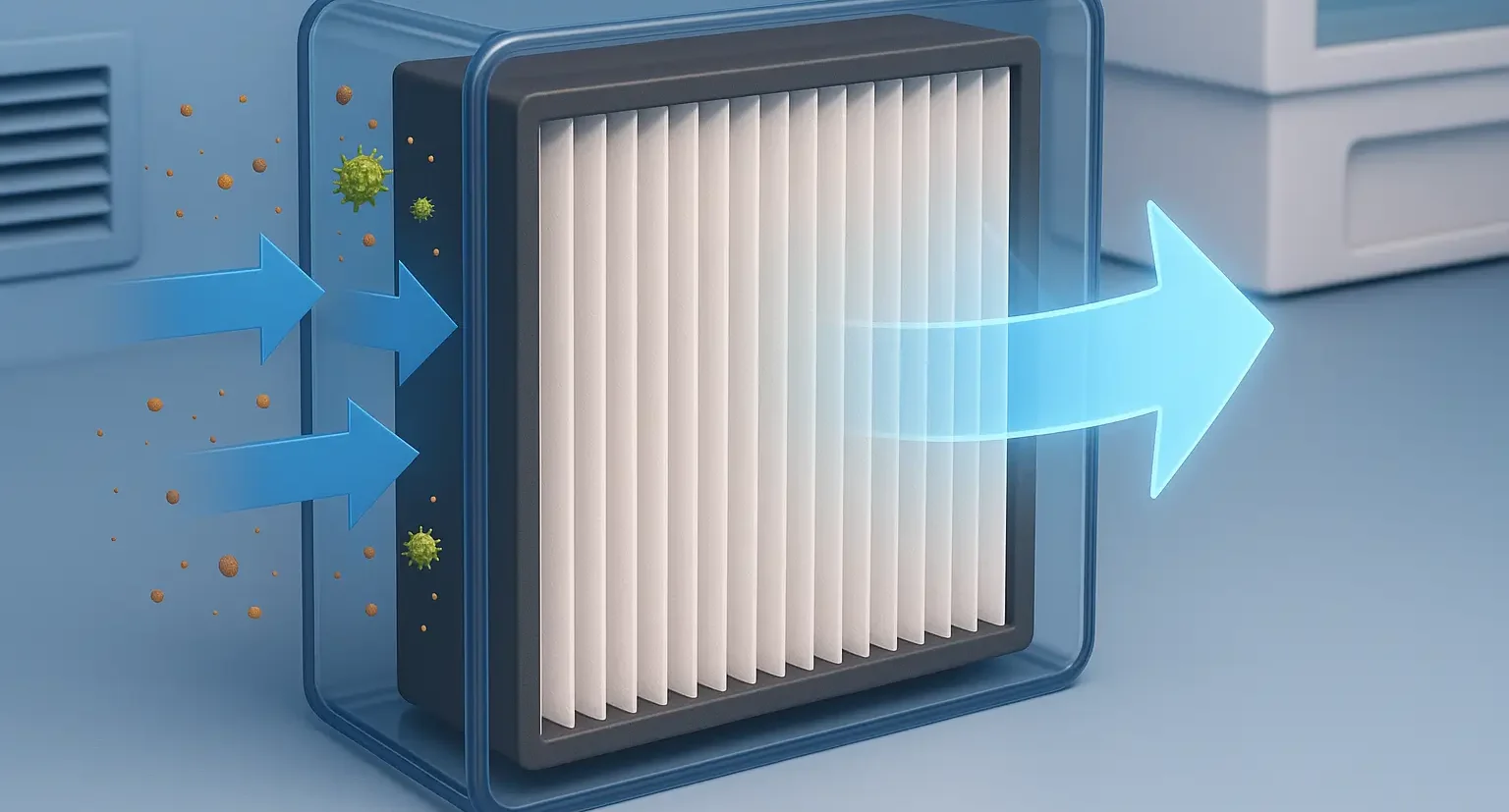
HEPA Filter
-
Operating Principle:
- Filters air through fine fibers, trapping particles as small as 0.3 microns using impaction, interception, and diffusion.

-
Applications:
- Used in cleanrooms, biological safety cabinets, hospital HVAC systems, air purifiers, and laboratories.
-
Advantages:
- Highly effective at filtering airborne microorganisms.
- Maintains sterile environments.
- Versatile, integrates into HVAC and other systems.
-
Limitations:
- Does not sterilize surfaces or materials, only air.
- Filters require regular cleaning or replacement.
- Must be properly maintained to prevent contamination buildup.
Thank you for reading from Firsthope's notes, don't forget to check YouTube videos!
This is a sample ad placement!