- Organic Compounds Classification is a fundamental aspect of organic chemistry, facilitating the organization, study, and understanding of the vast array of organic molecules.
- Organic compounds classification are primarily made up of carbon atoms along with hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, sulfur, and halogens.
- The classification is based on the structure, functional groups, and the type of bonding and molecular interactions present.
This is a sample ad placement!
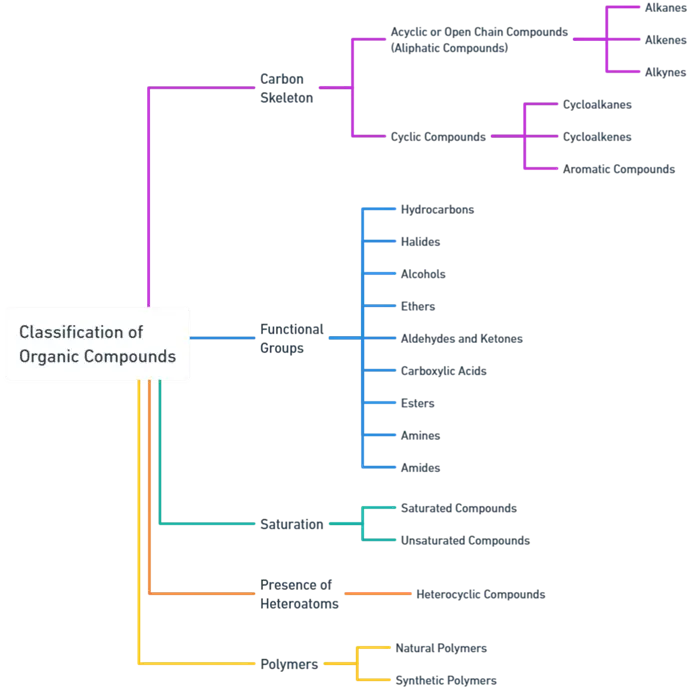
1. Organic Compounds Classification Based on Carbon Skeleton
- Organic compounds can be categorized based on the arrangement of carbon atoms in their molecular structure.
-
Acyclic or Open Chain Compounds
- These compounds consist of carbon atoms arranged in straight or branched chains and are known as aliphatic compounds. They can be further classified into:
-
Cyclic Compounds
- These compounds contain carbon atoms arranged in a closed ring structure. They are further divided into:
- Cycloalkanes – Saturated cyclic hydrocarbons with single bonds.
- Cycloalkenes – Unsaturated cyclic hydrocarbons containing one or more double bonds.
- Aromatic Compounds – Planar ring structures that exhibit resonance and follow Hückel’s rule. Benzene is the simplest example.
- These compounds contain carbon atoms arranged in a closed ring structure. They are further divided into:
This is a sample ad placement!
2. Organic Compounds Classification Based on Functional Groups
- Functional groups are specific atoms or groups of atoms within molecules that determine their characteristic chemical properties.
- Organic compounds are classified based on the functional groups they contain:
-
Hydrocarbons
- Compounds containing only carbon and hydrogen.
- The foundation of more complex organic compounds.
-
Halides
- Organic compounds where one or more hydrogen atoms are replaced by halogens (F, Cl, Br, I).
-
Alcohols
- Compounds with one or more hydroxyl (-OH) groups attached to a carbon atom.
-
Ethers
- Compounds containing an oxygen atom bonded to two alkyl or aryl groups.
-
Aldehydes and Ketones
- Contain a carbonyl group (C=O).
- Aldehydes: At least one hydrogen atom is attached to the carbonyl carbon.
- Ketones: Two alkyl or aryl groups are attached to the carbonyl carbon.
-
Carboxylic Acids
- Contain a carboxyl (-COOH) group, consisting of a hydroxyl group bonded to a carbonyl group.
-
Esters
- Derived from carboxylic acids, where the hydrogen in the hydroxyl group is replaced by an alkyl or aryl group.
-
Amines
- Contain a nitrogen atom bonded to one or more alkyl or aryl groups.
-
Amides
- Contain a carbonyl group bonded to a nitrogen atom from an amine.
-
3. Organic Compounds Classification on Saturation
- Organic compounds can also be classified based on the presence or absence of multiple bonds.
-
Saturated Compounds
- Contain only single bonds.
- Examples: Alkanes and Cycloalkanes.
-
Unsaturated Compounds
- Contain double or triple bonds.
- Examples: Alkenes, Alkynes, and Aromatic Compounds.
-
This is a sample ad placement!
Thank you for reading from Firsthope's notes, don't forget to check YouTube videos!