Introduction to Gastrointestinal Agents
- Introduction to Gastrointestinal agents include are medications or substances used to treat various conditions and symptoms affecting the gastrointestinal (GI) tract.
- They target different parts of the digestive system, from the esophagus to the colon, addressing issues such as indigestion, acid reflux, constipation, and diarrhea.
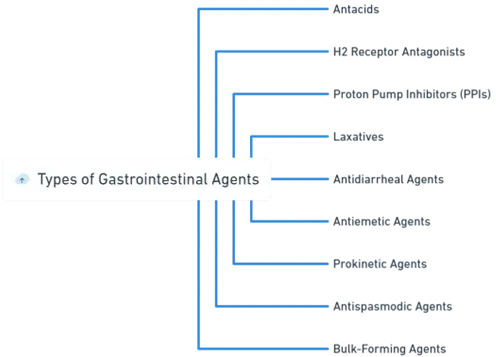
Types of Gastrointestinal Agents
This is a sample ad placement!
Antacids
-
- Function: Neutralize stomach acid and provide relief from heartburn, acid reflux, and indigestion.
- Common Examples: Calcium carbonate, aluminum hydroxide, magnesium hydroxide.
H2 Receptor Antagonists
-
- Function: Decrease the production of stomach acid by blocking histamine H2 receptors on the acid-producing cells in the stomach lining.
- Common Examples: Ranitidine, cimetidine, famotidine.
This is a sample ad placement!
Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs)
-
- Function: Reduce stomach acid production by inhibiting the proton pump in the stomach’s acid-producing cells.
- Common Examples: Omeprazole, lansoprazole, pantoprazole.
Laxatives
-
- Function: Treat constipation by softening the stool, increasing stool volume, or stimulating bowel movements.
- Types:
- Bulk-forming: Psyllium
- Osmotic: Polyethylene glycol
- Stimulant: Bisacodyl
- Stool Softeners: Docusate
This is a sample ad placement!
Antidiarrheal Agents
-
- Function: Manage diarrhea by reducing stool frequency or consistency.
- Common Examples: Loperamide, diphenoxylate with atropine, bismuth subsalicylate.
Antiemetic Agents
-
- Function: Prevent and treat nausea and vomiting.
- Types:
- Serotonin 5-HT3 Receptor Antagonists: Ondansetron
- Dopamine D2 Receptor Antagonists: Metoclopramide
- Antihistamines: Dimenhydrinate
Prokinetic Agents
- Function: Improve gastrointestinal motility by enhancing the coordinated contractions of the GI tract.
- Common Examples: Metoclopramide, erythromycin.
This is a sample ad placement!
Antispasmodic Agents
- Function: Relieve abdominal pain and cramping by relaxing the smooth muscles of the GI tract.
- Common Examples: Dicyclomine, hyoscyamine.
Bulk-forming Agents
- Function: Normalize bowel movements by adding bulk and water to the stool, making it easier to pass.
- Common Examples: Psyllium, methylcellulose.
Thank you for reading from Firsthope's notes, don't forget to check YouTube videos!
This is a sample ad placement!