- Diencephalon is a region of the brain located between the cerebrum and the brainstem.
- It is composed of several important structures that play critical roles in sensory information processing, hormone regulation, and the maintenance of essential body functions.
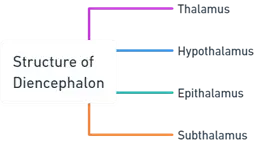
- The primary components of the diencephalon are the thalamus, hypothalamus, epithalamus, and subthalamus:
This is a sample ad placement!
1. Thalamus:
Structure:
- The thalamus is a large, paired structure made up of several nuclei. It is located at the center of the diencephalon and surrounded by the cerebral hemispheres.
Function:
- The thalamus serves as a relay center for sensory information, directing it to the appropriate regions of the cerebral cortex for processing. It plays a role in the processing of all sensory modalities, except olfaction (smell).
- The thalamus also contributes to the regulation of sleep, arousal, and consciousness.
This is a sample ad placement!
2. Hypothalamus:
Structure:
- The hypothalamus is a small but essential structure located below the thalamus. It is composed of various nuclei and is connected to the pituitary gland via a stalk called the infundibulum.
Function:
- The hypothalamus regulates essential functions such as body temperature, appetite, thirst, and sleep-wake cycles.
- It plays a crucial role in the endocrine system by producing and releasing hormones, controlling the release of hormones from the pituitary gland, and maintaining homeostasis.
This is a sample ad placement!
3. Epithalamus:
Structure:
- The epithalamus is a small region located dorsal to the thalamus. Its most prominent structure is the pineal gland, a small, pinecone-shaped gland that plays a role in the regulation of sleep and circadian rhythms.
Function:
- The pineal gland produces and secretes melatonin, a hormone that helps regulate sleep-wake cycles and circadian rhythms.
- The epithalamus also contains the habenula, a structure involved in the regulation of pain, mood, and the sleep-wake cycle.
4. Subthalamus:
Structure:
- The subthalamus is a small region located ventral to the thalamus. Its main structure is the subthalamic nucleus, which is functionally connected to the basal ganglia.
This is a sample ad placement!
Function:
- The subthalamic nucleus plays a role in the regulation of movement, primarily by modulating the activity of the basal ganglia, a group of nuclei involved in motor control and learning.
Thank you for reading from Firsthope's notes, don't forget to check YouTube videos!