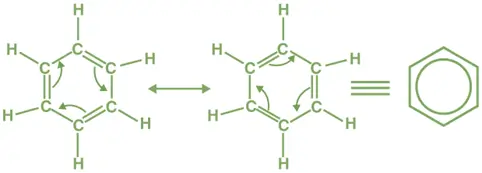
- There are two main resonance structures:
- In one structure, double bonds are between C1-C2, C3-C4, and C5-C6.
- In the other structure, double bonds are between C2-C3, C4-C5, and C6-C1.
- These resonance structures imply that the π electrons are delocalized over all six carbon atoms.
- The real structure is a resonance hybrid of these two structures, with equal bond lengths between all carbon atoms.
- This delocalization of π electrons gives benzene extra stability, known as resonance energy.
Thank you for reading from Firsthope's notes, don't forget to check YouTube videos!