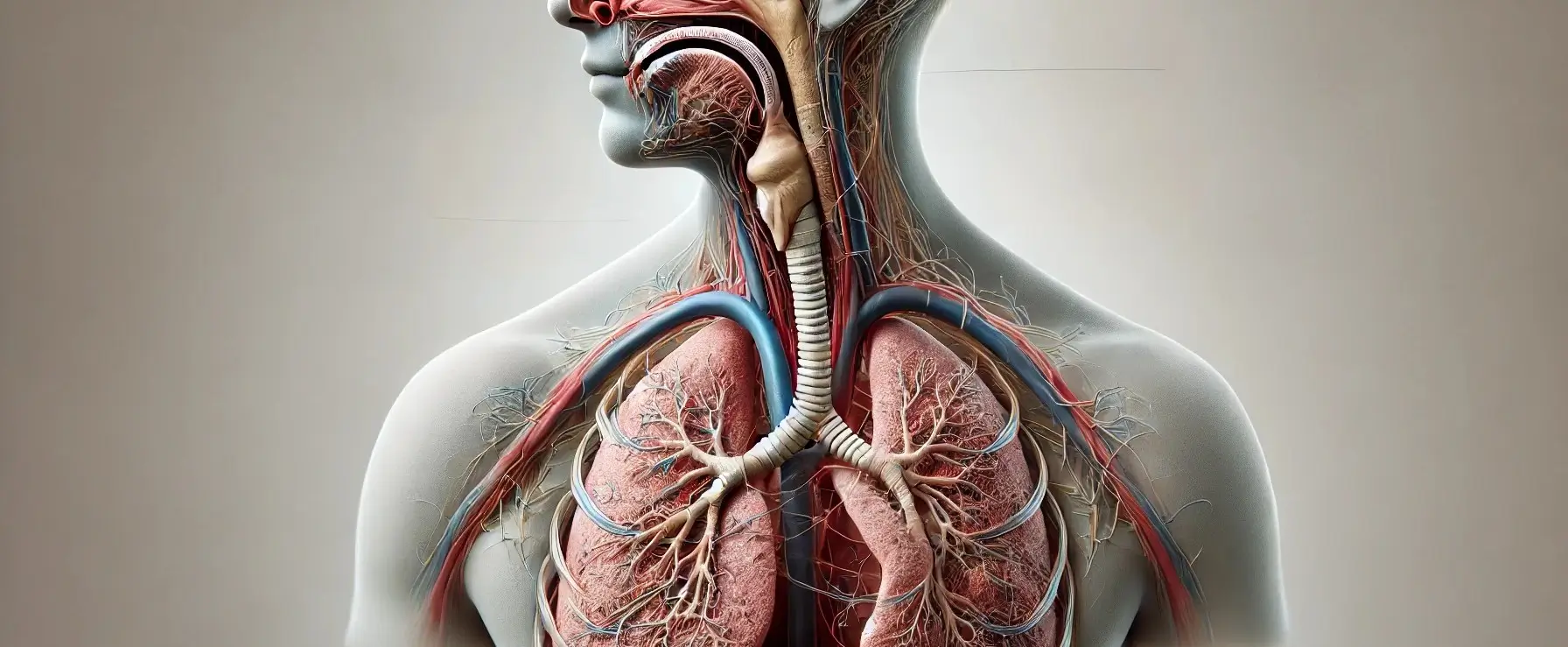
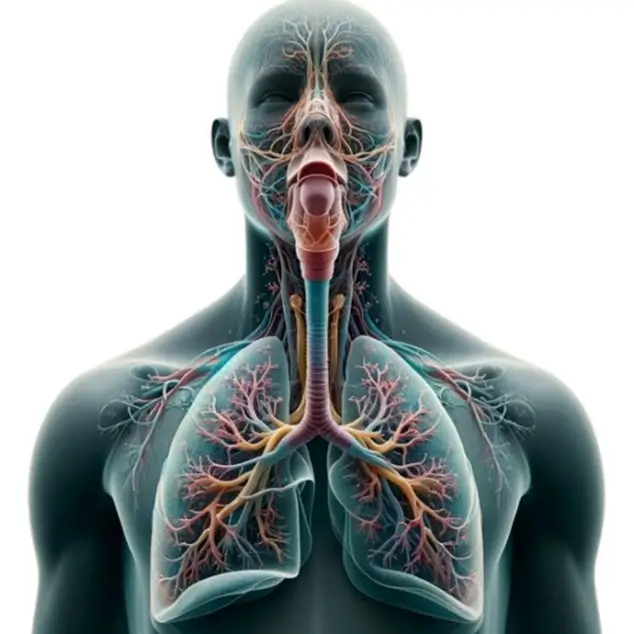
- Respiratory system is a vital organ system responsible for gas exchange, supplying oxygen to the body and removing carbon dioxide.
This is a sample ad placement!
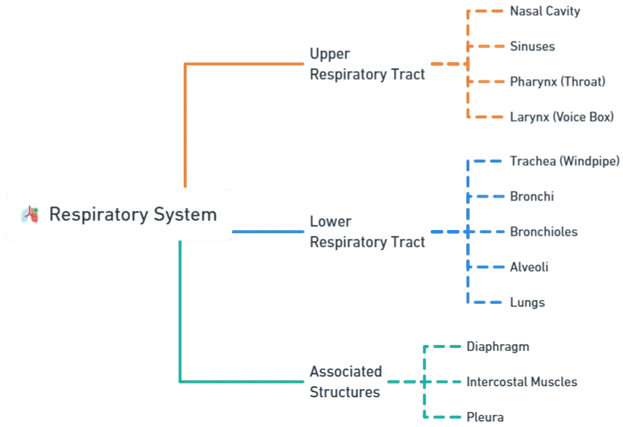
- Here’s an overview of its anatomy, divided into the upper respiratory tract and the lower respiratory tract:
This is a sample ad placement!
Upper Respiratory Tract
Nasal Cavity:
- Structure: Divided by the nasal septum; contains turbinates (conchae) to increase surface area.
- Function: Filters, warms, and moistens incoming air; houses olfactory receptors for smell.
Sinuses:
- Structure: Air-filled cavities in the skull (e.g., frontal, maxillary, sphenoid, and ethmoid sinuses).
- Function: Lighten the skull, enhance voice resonance, and aid in warming/moistening air.
This is a sample ad placement!
Pharynx (Throat):
- Sections:
- Nasopharynx: Connects to the nasal cavity; contains the adenoids and openings of the Eustachian tubes.
- Oropharynx: Shared passageway for air and food.
- Laryngopharynx: Leads to the larynx and esophagus.
- Function: Directs air to the larynx.
Larynx (Voice Box):
- Structure: Composed of cartilage (e.g., thyroid cartilage, cricoid cartilage, and epiglottis).
- Function: Protects the airway during swallowing (via the epiglottis) and facilitates sound production.
Lower Respiratory Tract
Trachea (Windpipe):
- Structure: A tube supported by C-shaped cartilage rings, lined with ciliated epithelium and mucus-producing goblet cells.
- Function: Provides a clear airway to the lungs and filters debris.
This is a sample ad placement!
Bronchi:
- Structure: Two main bronchi (left and right), branching into smaller secondary and tertiary bronchi.
- Function: Distribute air to each lung.
Bronchioles:
- Structure: Smaller branches of bronchi without cartilage, ending in alveolar ducts.
- Function: Control airflow resistance and air distribution within the lungs.
Alveoli:
- Structure: Tiny air sacs surrounded by capillaries, with thin walls for efficient gas exchange.
- Function: Site of oxygen and carbon dioxide exchange.
This is a sample ad placement!
Lungs:
- Structure: Paired organs divided into lobes (3 on the right, 2 on the left due to the heart’s position).
- Function: Expand and contract during breathing to facilitate gas exchange.
Associated Structures of Respiratory system
Diaphragm:
- Structure: A dome-shaped muscle located below the lungs.
- Function: Primary muscle for respiration; contracts to draw air into the lungs.
Intercostal Muscles:
- Structure: Located between ribs.
- Function: Assist in expanding and compressing the thoracic cavity during breathing.
This is a sample ad placement!
Pleura:
- Structure: Double-layered membrane surrounding each lung.
- Visceral pleura: Covers the lungs.
- Parietal pleura: Lines the chest wall.
- Function: Reduces friction during breathing and creates a pressure gradient for lung expansion.
Thank you for reading from Firsthope's notes, don't forget to check YouTube videos!