- Sperm, or spermatozoa, are male reproductive cells that fertilize the female egg (ovum) to create an embryo, leading to the development of a fetus.
This is a sample ad placement!
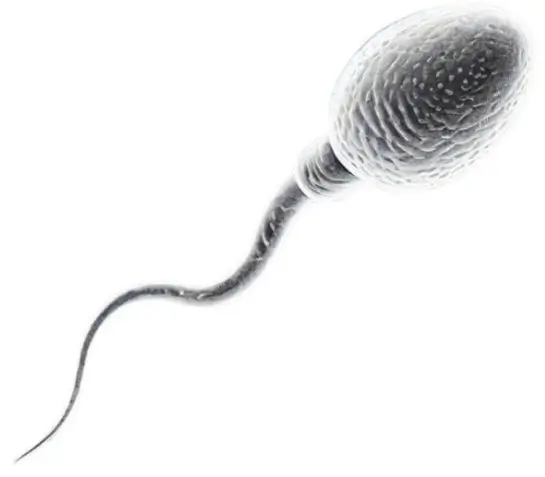
Structure of Sperm (Spermatozoa)
- Sperm cells have a specialized structure consisting of three main parts:
-
Head:
- Contains the nucleus with genetic material (DNA) passed to the offspring.
- Covered by the acrosome, a cap-like structure with enzymes to help the sperm penetrate the egg.
-
Midpiece:
- Connects the head to the tail and houses mitochondria, providing energy for sperm movement.
-
Tail (Flagellum):
- A whip-like structure that propels the sperm, allowing it to swim through the female reproductive tract.
This is a sample ad placement!
Sperm Production
- Sperm are produced in the seminiferous tubules within the testes through spermatogenesis:
- Spermatogonia (precursor cells) undergo mitosis and meiosis to form mature sperm with half the chromosomes of normal body cells, ensuring correct chromosomal count after fertilization.
Maturation and Storage
- After spermatogenesis, sperm move to the epididymis, a coiled tube where they mature and are stored until ejaculation.
This is a sample ad placement!
Ejaculation and Fertilization
- During ejaculation, sperm mix with fluids from the seminal vesicles, prostate, and bulbourethral glands to form semen.
- The sperm travel through the female reproductive tract, and if they reach the fallopian tubes where an ovum is present, they use acrosomal enzymes to penetrate the egg.
- One sperm fuses with the ovum, combining their genetic material in a process called fertilization, resulting in a zygote that can develop into an embryo.
Thank you for reading from Firsthope's notes, don't forget to check YouTube videos!