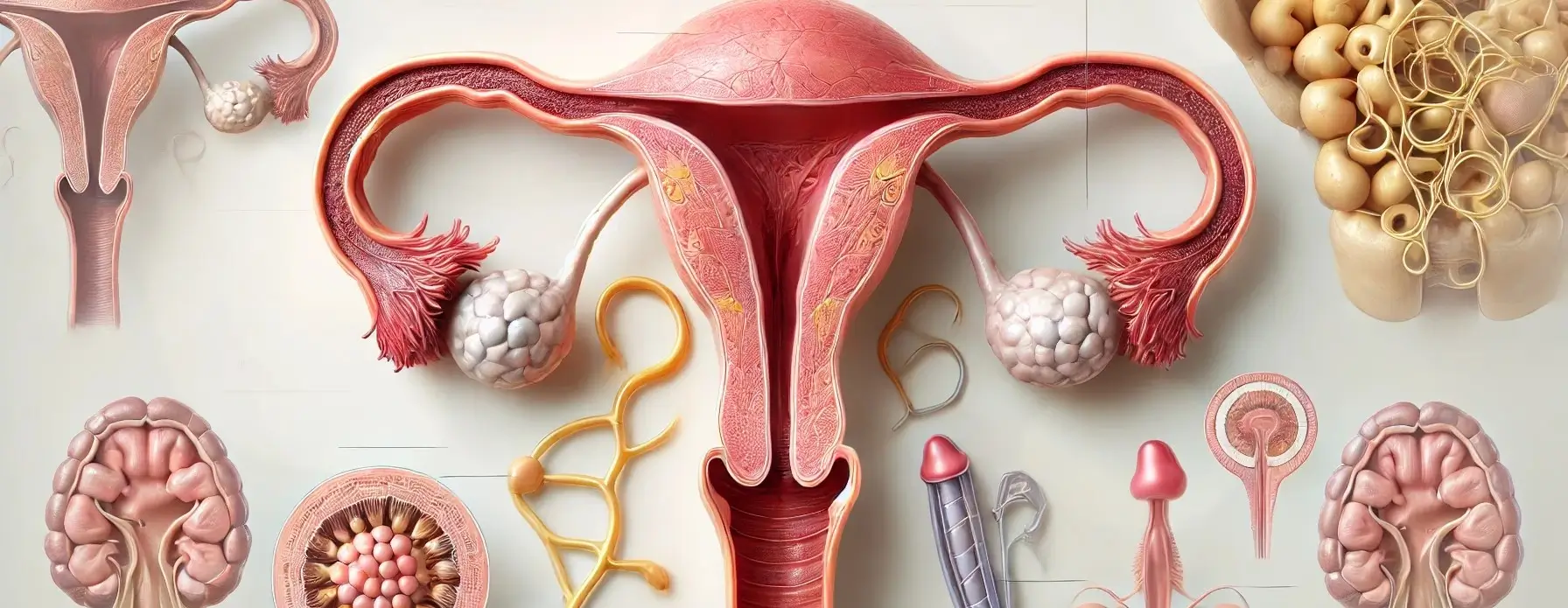
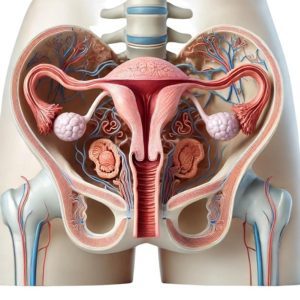
- The female reproductive system consists of internal and external organs that function together for reproduction, hormone regulation, and the menstrual cycle.
This is a sample ad placement!
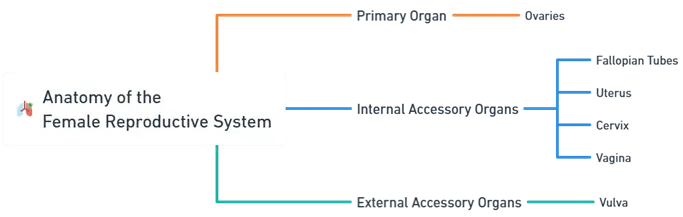
Primary Organ:
Ovaries:
-
- The primary reproductive organs in female reproductive system responsible for producing ova (eggs) and secreting the hormones estrogen and progesterone.
- Each ovary contains thousands of follicles, which are small sacs containing immature eggs. During each menstrual cycle, one or more follicles mature, and one egg is released during ovulation.
- Position:
- Located on either side of the lower abdomen, adjacent to the lateral pelvic wall.
- Structure:
- Almond-shaped organs containing numerous follicles (small sacs that contain immature eggs).
- Ovarian stroma, the connective tissue, contains blood vessels, nerves, and hormone-producing cells.
- Function:
This is a sample ad placement!
Accessory Organs:
Internal Accessory Organs
1. Fallopian Tubes (Oviducts):
- Two narrow tubes that extend from the ovaries to the uterus.
- Each tube has finger-like projections called fimbriae that guide the egg from the ovary into the tube.
- Fertilization typically occurs here.
- Position:
- Extending from the ovaries to the uterus.
- Structure:
- Lined with ciliated epithelial cells and smooth muscle.
- The fimbriae are at the end near the ovary to help capture the egg.
- Function:
- To transport the egg from the ovary to the uterus.
- To provide a suitable environment for fertilization.
- Position:
2. Uterus (Womb):
- A muscular, pear-shaped organ that houses and nourishes a developing foetus during pregnancy.
- The endometrium (inner lining of the uterus) thickens during the menstrual cycle to prepare for pregnancy, and if fertilization does not occur, the endometrium is shed during menstruation.
- Position:
- Located in the lower abdomen between the bladder and rectum.
- Structure:
- Composed of three layers:
- Endometrium (inner lining)
- Myometrium (middle muscular layer)
- Perimetrium (outer serous layer)
- Composed of three layers:
- Function:
- To house and nourish a developing foetus during pregnancy.
- To shed its inner lining during menstruation if fertilization does not occur.
- Position:
This is a sample ad placement!
3. Cervix:
- The lower, narrow part of the uterus that connects it to the vagina.
- Contains a small opening called the os that allows for the passage of sperm into the uterus and the exit of menstrual blood.
- During childbirth, the cervix dilates to allow the baby to pass through the birth canal.
4. Vagina:
- A muscular, elastic canal that extends from the cervix to the vulva.
- Serves multiple functions: it is the receptacle for the penis during sexual intercourse, the passage for menstrual blood to exit the body, and the birth canal during childbirth.
- Position:
- Extends from the cervix (lower part of the uterus) to the vulva.
- Structure:
- Composed of three layers:
- Mucosal layer (inner)
- Muscular layer (middle)
- Fibrous layer (outer)
- The vaginal walls can expand and contract to aid in childbirth.
- Composed of three layers:
- Function:
- Receptacle for the penis during sexual intercourse.
- Passage for menstrual blood to exit the body.
- Birth canal during childbirth.
- Position:
External Accessory Organs
Vulva:
- The external female genitalia, including:
- Mons pubis: A fatty, rounded area over the pubic bone, covered with pubic hair.
- Labia majora: Large, fleshy folds that surround the vaginal opening.
- Labia minora: Smaller inner folds that protect the clitoris and urethra.
- Clitoris: A small, sensitive organ involved in sexual arousal and pleasure.
- Vaginal opening: Allows for the entrance of the penis during intercourse, the exit of menstrual blood, and childbirth.
This is a sample ad placement!
Thank you for reading from Firsthope's notes, don't forget to check YouTube videos!