Principles of Paddles:
- This mixers operate on the principle of convective mixing.
- It move through the material, pushing and folding it to achieve thorough mixing.
- This type of mixing is gentle and suitable for materials that are sensitive to shear.
Construction of Paddles:
This is a sample ad placement!
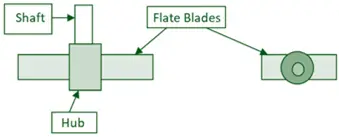
- Paddles: Large flat or curved blades mounted on a central shaft.
- Shaft: Central shaft that holds the paddles.
- Drive System: Motor and gearbox to rotate the shaft and paddles.
- Vessel: U-shaped or cylindrical container that holds the material to be mixed.
- Support Frame: Sturdy frame to hold the vessel and drive system.
Working:
- Materials are loaded into the vessel.
- The paddles rotate, moving through the materials and creating a mixing action.
- This rotation lifts and folds the materials, ensuring thorough mixing.
- Mixing continues until the desired homogeneity is achieved.
- The mixed product is discharged through a bottom valve or port.
This is a sample ad placement!
Uses:
- Food Industry: Mixing dough, cereals, and dry powders.
- Pharmaceuticals: Blending powders and granules.
- Chemical Industry: Mixing fine chemicals and dry materials.
Merits:
- Gentle mixing action, suitable for delicate materials.
- Simple design and operation.
- Can handle a wide range of viscosities.
- Low energy consumption.
This is a sample ad placement!
Demerits:
- Less efficient for very fine powders or materials with significant density differences.
- May not provide adequate mixing for high-shear applications.
- Limited to batch processing.
Thank you for reading from Firsthope's notes, don't forget to check YouTube videos!

