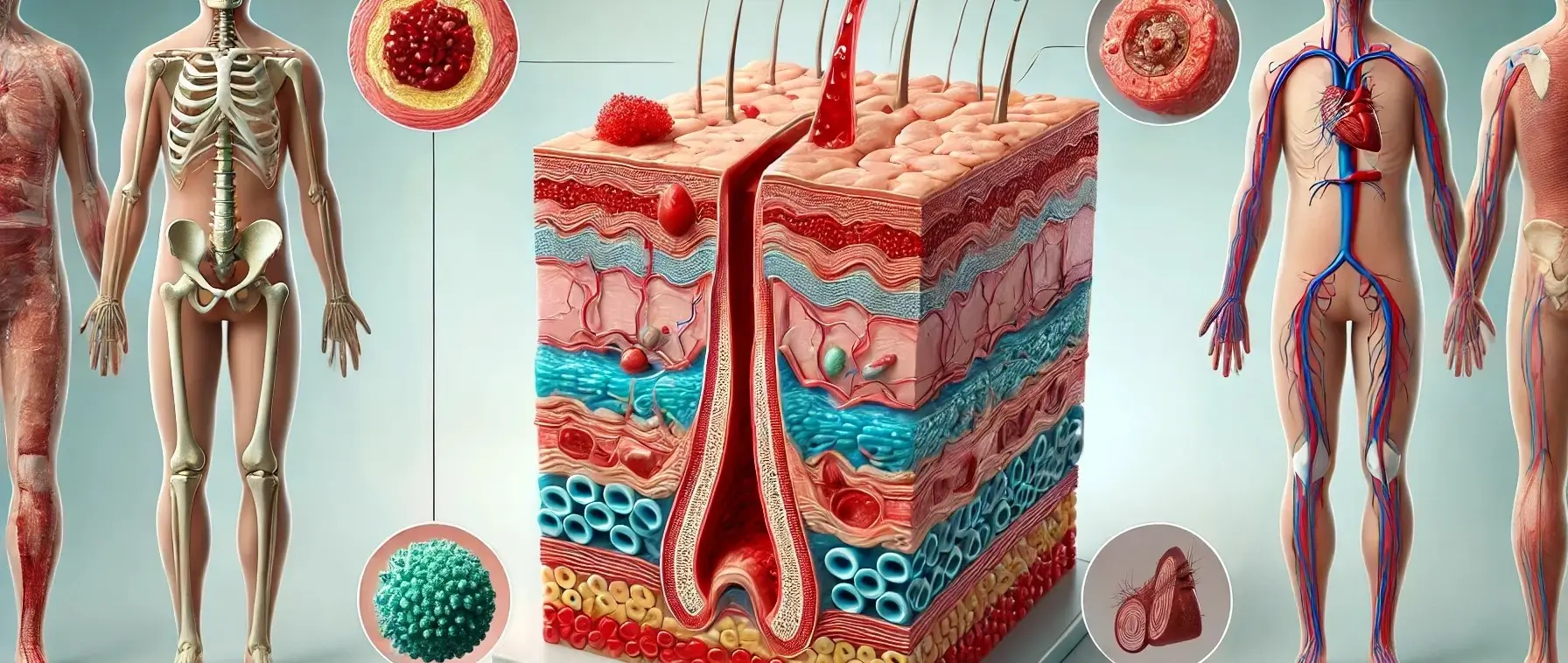
- The basic principles of wound healing in the skin involve a series of biological events aimed at repairing damaged tissue and restoring skin integrity.
This is a sample ad placement!
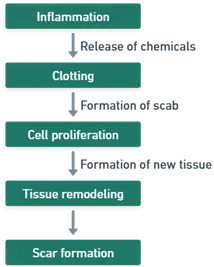
These can be divided into four overlapping phases:
-
Hemostasis:
- Immediate Response: Occurs immediately after injury to stop bleeding.
- Clot Formation: Blood vessels constrict, platelets aggregate to form a platelet plug, and fibrin stabilizes the clot to prevent further blood loss.
-
Inflammation:
- Early Phase: Begins shortly after injury and lasts for several days.
- Immune Response: Blood vessels dilate, increasing blood flow and attracting neutrophils and macrophages to the wound site. These cells remove debris, release growth factors, and help prevent infection.
-
Proliferation:
- Tissue Formation: Lasts for several days to weeks.
- Key Events:
- Angiogenesis: New blood vessels form to supply nutrients and oxygen.
- Fibroblast Proliferation: Fibroblasts produce collagen and elastin, strengthening new tissue.
- Epithelialization: Epithelial cells migrate and cover the wound, restoring the skin barrier.
- Contraction: Myofibroblasts pull wound edges together, reducing wound size.
-
Remodeling:
- Long-term Phase: Can last for months to years.
- Tissue Maturation: Collagen fibers realign, excess cells and vessels are removed, and the scar tissue strengthens, though it never fully regains original skin strength and elasticity.
- These Basic principles of wound healing in the skin phases ensure effective wound repair, maintaining skin function and protection.
This is a sample ad placement!
Thank you for reading from Firsthope's notes, don't forget to check YouTube videos!