- Mediators Inflammation is regulated by various chemical mediators that orchestrate the inflammatory response.
- The Mediators can be derived from cells or plasma and have different roles in initiating and sustaining inflammation. Top of Form
- Its inflammation are substances that play key roles in initiating and regulating inflammatory responses.
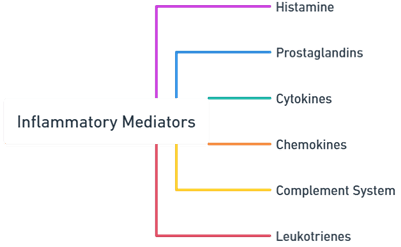
Main Types of Inflammatory Mediators
This is a sample ad placement!
-
Histamine
- Source: Released by mast cells and basophils.
- Function: Increases vascular permeability and causes vasodilation, leading to redness and swelling.
-
Prostaglandins
- Type: Lipid compounds.
- Function: Intensify inflammation by promoting vasodilation, fever, and pain.
-
Cytokines
- Examples: Interleukins and Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF).
- Function: Proteins that modulate the immune response and regulate inflammation.
-
Chemokines
- Type: A subset of cytokines.
- Function: Attract white blood cells to sites of infection or injury (chemotaxis).
-
Complement System
- Description: A series of plasma proteins.
- Function: Enhances the ability of antibodies and phagocytic cells to clear microbes and damaged cells.
-
Leukotrienes
- Type: Lipid compounds.
- Function: Mediate allergic and inflammatory responses by increasing vascular permeability and attracting leukocytes
Thank you for reading from Firsthope's notes, don't forget to check YouTube videos!
This is a sample ad placement!