Overview of Acetate Pathway (Polyketide Pathways):
- The Acetate pathway, often referred to as the polyketide pathway, involves the polymerization of acetyl-CoA or malonyl-CoA units.
- It is crucial not only for primary metabolites like fatty acids but also for numerous plant secondary metabolites (e.g., flavonoids, certain antibiotics in microorganisms, and various phenolics in plants).
Key Steps:
-
Acetyl-CoA Generation
- Acetyl-CoA is produced from:
- Glycolysis: Through the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex.
- Fatty acid β-oxidation.
- Malonyl-CoA is formed from acetyl-CoA by the enzyme acetyl-CoA carboxylase.
- Acetyl-CoA is produced from:
-
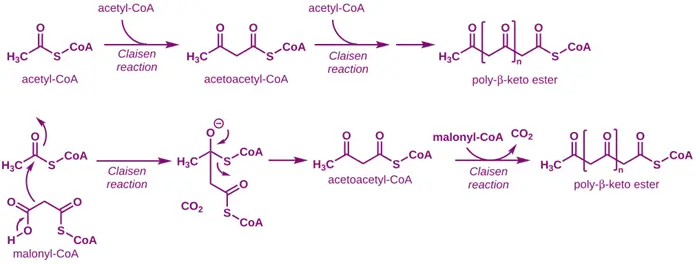
Polyketide Chain Elongation
- The acetate (acetyl-CoA) or malonate (malonyl-CoA) units undergo condensation reactions to form polyketide chains.
- Malonyl-CoA donates two-carbon units to elongate the chain.
- These steps are catalyzed by polyketide synthases (PKSs).
-
Cyclization and Modification
- The linear polyketide chains undergo various modifications, including:
- Cyclization: Formation of phenolic or aromatic ring structures.
- Reduction, Oxidation, Methylation: Generate diverse molecular scaffolds.
- These modifications create the structural diversity seen in polyketide-derived compounds.
- The linear polyketide chains undergo various modifications, including:
Major Secondary Metabolites from the Acetate/Polyketide Pathway:
- Fatty Acids: Membrane components (primary metabolism).
- Flavonoids: Pigments, antioxidants (linked to Shikimic pathway).
- Quinones: E.g., anthraquinones.
- Tannins: Derived from gallic acid.
- Phenolics: Polyketide-based compounds.
Biological Significance:
- Structural Protection: Waxes and cutin from fatty acids form protective barriers on leaves and fruits.
- Defense: Polyketide-derived phytoalexins, tannins, and flavonoids deter herbivores and pathogens.
- Pigmentation: Flavonoids and anthraquinones enhance flower and fruit coloration, attracting pollinators.
Applications:
- Agriculture: Waxes and cutin for protective coatings.
- Pharmaceuticals: Polyketides as precursors for antibiotics (e.g., erythromycin) and anticancer drugs.
- Biotechnology: Engineering polyketide pathways for industrial use.