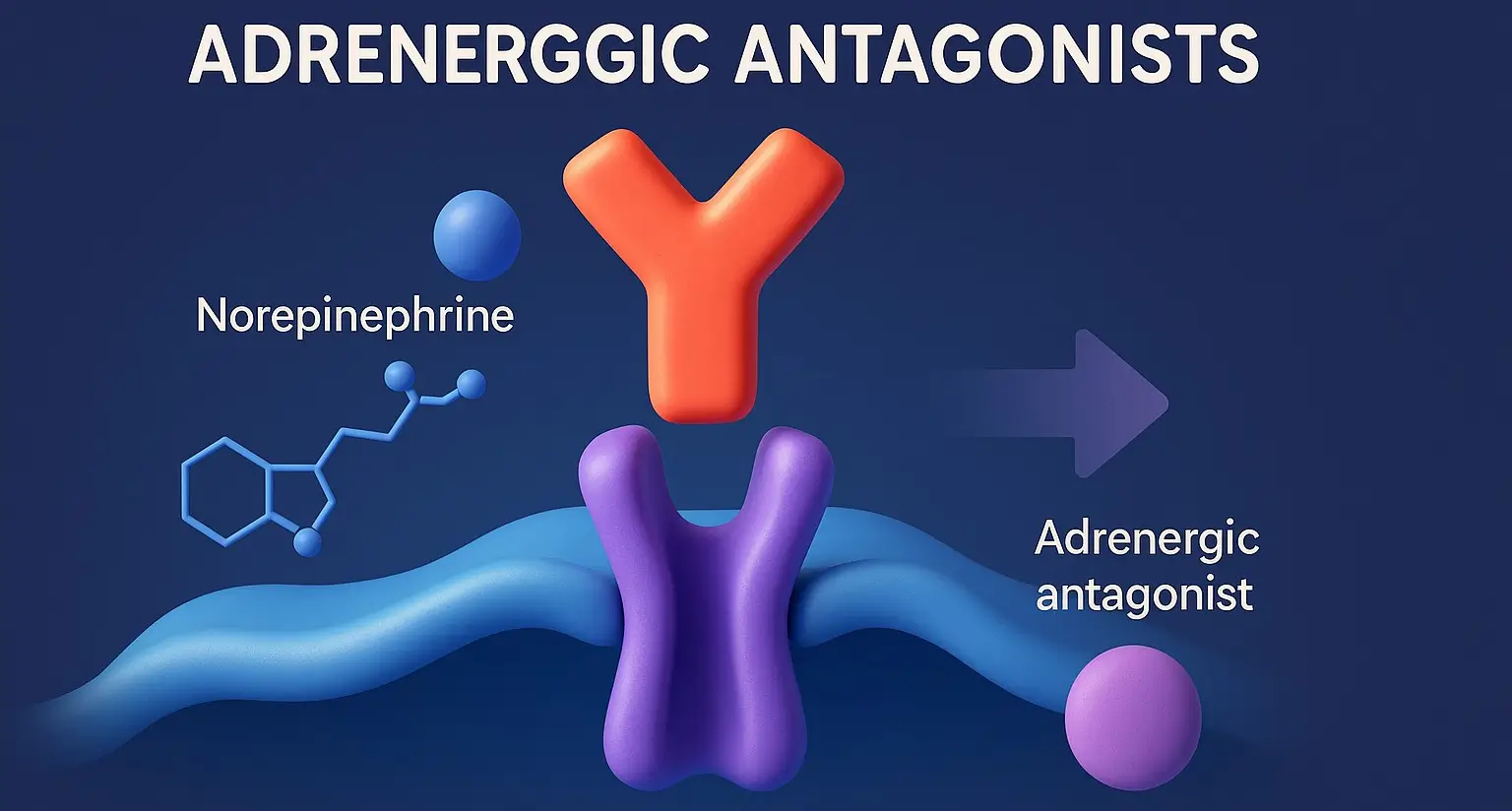
- Adrenergic antagonists (also called adrenergic blockers or adrenolytics) are agents that bind to adrenergic (adrenaline/noradrenaline) receptors but do not activate them.
- By blocking these receptors, they inhibit the sympathetic (adrenergic) nervous system’s actions.
Classification of Adrenergic Antagonists
- They are broadly divided based on the types of adrenergic receptors they block:
- Alpha-adrenergic blockers (or α-blockers)
- Beta-adrenergic blockers (or β-blockers)
- Some agents can block both alpha and beta receptors (mixed blockers).
General Mechanisms of Action
-
Prevention of receptor activation:
- Adrenergic compete with endogenous catecholamines (e.g., norepinephrine, epinephrine) for receptor binding sites, preventing those endogenous substances from exerting their effect.
-
Reduction in sympathetic tone:
- By blocking alpha or beta receptors, these drugs reduce various sympathetic effects such as vasoconstriction, increased heart rate, and increased cardiac contractility.
Click Here to Watch the Best Pharma Videos