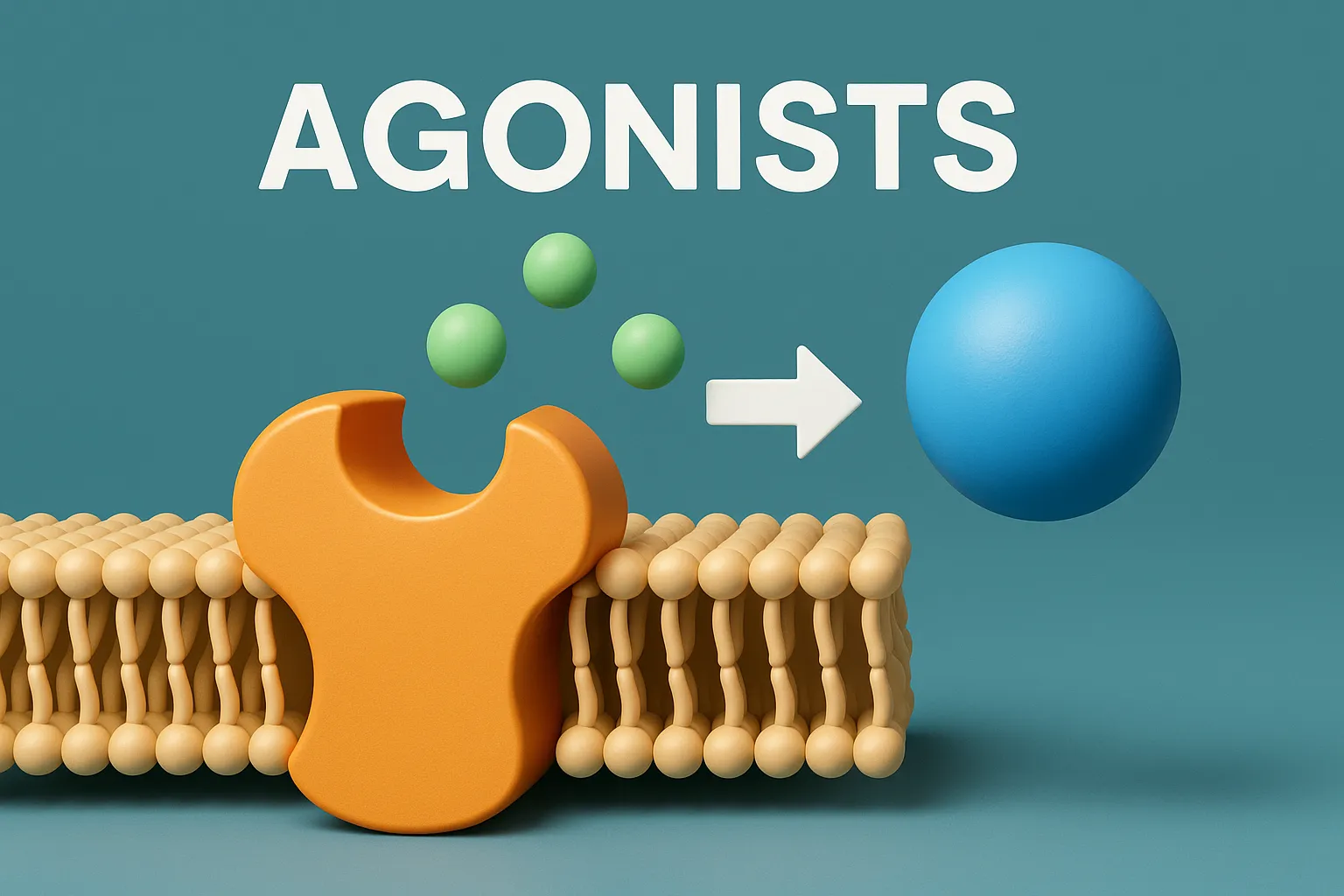
Agonists are drugs that bind to receptors and activate them to produce a biological response.
Definition:
- An agonist is a drug (or any chemical) that binds to a receptor and activates it, producing a biological response.
- Agonists mimic the action of endogenous (natural) ligands like hormones or neurotransmitters.
Types of Agonists:
-
Full Agonist:
- Produces maximum possible response when it binds to the receptor.
- Example: Morphine (a full opioid receptor agonist).
-
Partial Agonist:
- Produces a less than maximal response even if all receptors are occupied.
- Example: Buprenorphine (partial agonist at opioid receptors).
-
Inverse Agonist:
- Binds to the same receptor as an agonist but produces the opposite effect.
- Example: Beta-carbolines at GABA-A receptors.
Click Here to Watch the Best Pharma Videos