- Alkenes Preparation, characterized by the presence of at least one carbon-carbon double bond, play a crucial role in organic synthesis and industrial chemistry.
- Their reactivity due to the double bond allows for a wide range of chemical transformations.
Here, we explore both the general methods for preparing alkenes and their significant chemical reactions.
Preparation of Alkenes

-
Dehydrohalogenation of Alkyl Halides:
- Process: An elimination reaction where a hydrogen atom and a halogen atom are removed from an alkyl halide, in the presence of a strong base.
- General Reaction: R-CH2-CH2-X + B- → R-CH=CH2 + BX + HB
- Example: Dehydrohalogenation of 2-chloropropane to propene.
- Reaction: (CH3)2CH-Cl + KOH → CH3-CH=CH2 + KCl + H2O
-
Dehydration of Alcohols:
- Process: Water molecule is removed from an alcohol, typically requiring an acid catalyst like sulfuric or phosphoric acid.
- General Reaction: R-CH2-CH2-OH + H+ → R-CH=CH2 + H2O
- Example: Dehydration of ethanol to ethene.
- Reaction: CH3-CH2-OH + H2SO4 → CH2=CH2 + H2O
-
Catalytic Cracking of Alkanes:
- Process: Large alkane molecules are broken down into smaller alkanes and alkenes, using a catalyst under high temperatures and pressures.
- Example: Cracking of hexane to produce ethene and butane.
- Reaction: C6H14 → C2H4 + C4H10
-
Wittig Reaction:
- Process: Alkenes are prepared from aldehydes or ketones using a phosphonium ylide, yielding an alkene and phosphine oxide.
- General Reaction: R1-CH=O + R2P=CHR3 → R1-CH=CHR3 + R2P=O
- Example: Formation of styrene from benzaldehyde and methylenetriphenylphosphorane.
- Reaction: C6H5-CH=O + Ph3P=CH2 → C6H5-CH=CH2 + Ph3P=O
Advertisements
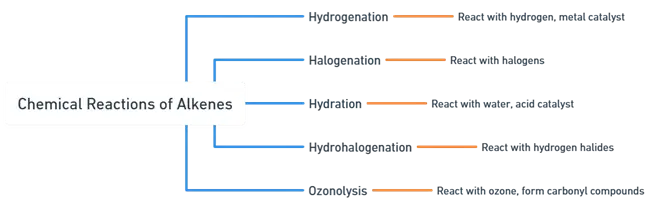
Chemical Reactions of Alkenes
-
Hydrogenation:
- Process: Alkenes react with hydrogen gas in the presence of a metal catalyst to form alkanes.
- Example: Hydrogenation of ethene to ethane.
- Reaction: CH2=CH2 + H2 → CH3-CH3
-
Halogenation:
- Process: Alkenes react with halogens to form dihaloalkanes.
- Example: Bromination of ethene to 1,2-dibromoethane.
- Reaction: CH2=CH2 + Br2 → CH2Br-CH2Br
-
Hydration:
- Process: Alkenes react with water in the presence of an acid catalyst to form alcohols.
- Example: Hydration of ethene to ethanol.
- Reaction: CH2=CH2 + H2O → CH3-CH2OH
-
Hydrohalogenation:
- Process: Alkenes react with hydrogen halides to form haloalkanes.
- Example: Addition of HBr to propene to form 2-bromopropane.
- Reaction: CH3-CH=CH2 + HBr → CH3-CHBr-CH3
-
Ozonolysis:
- Process: Alkenes react with ozone to form ozonides, which are then reduced to carbonyl compounds.
- Example: Ozonolysis of ethene to form formaldehyde.
- Reaction: CH2=CH2 + O3 → CH2O + H2O
