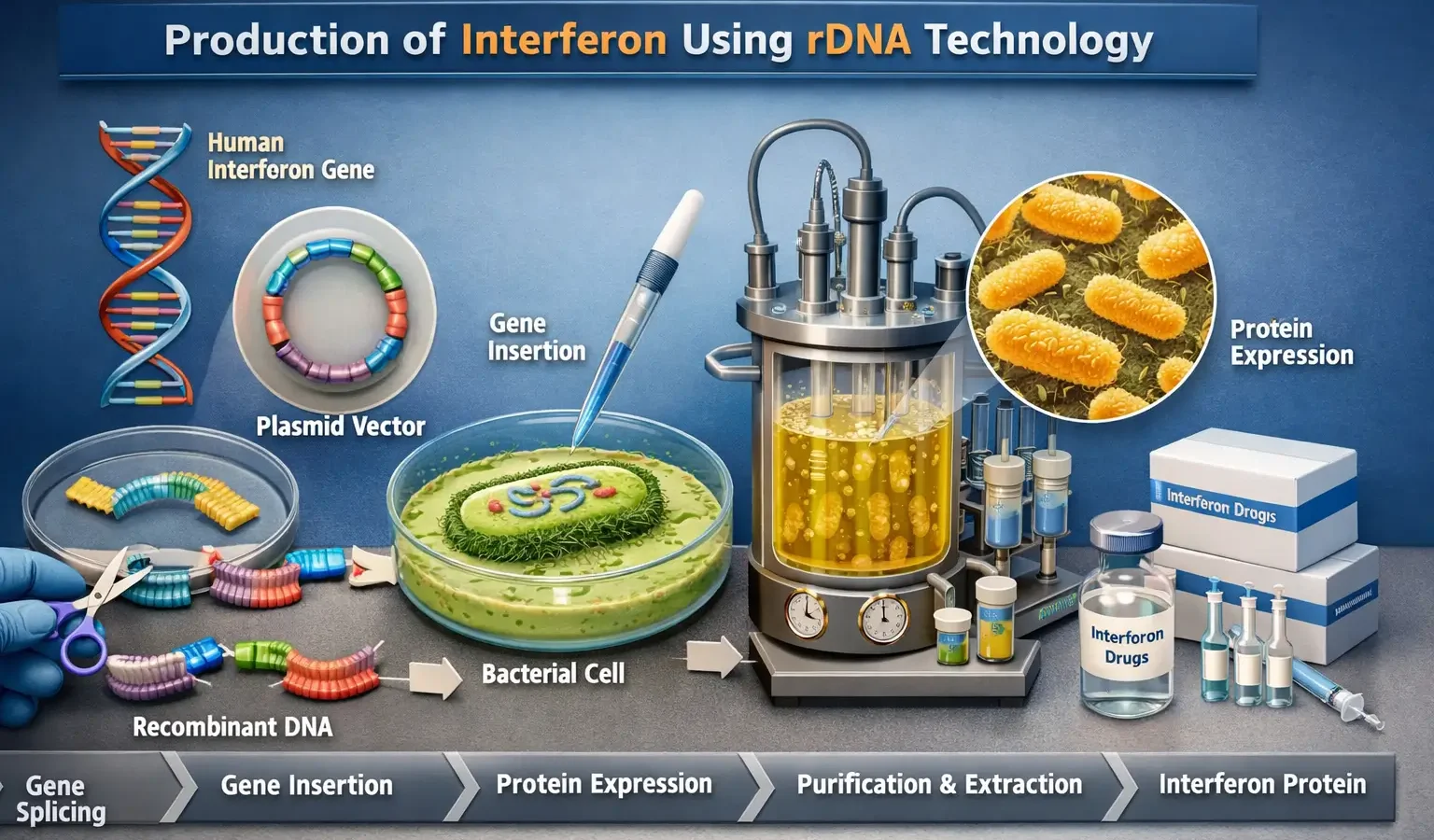
Production of Interferon Using rDNA Technology
What is Interferon? Interferons (IFNs) are a group of antiviral and immune-modulating proteins produced naturally by cells in response to viral infections. They are used to treat viral infections, cancer, and immune disorders. Types of Interferons Interferon-α (IFN-α) → Used for treating hepatitis B, hepatitis C, and leukemia. Interferon-β (IFN-β) → Used for treating multiple … Read more