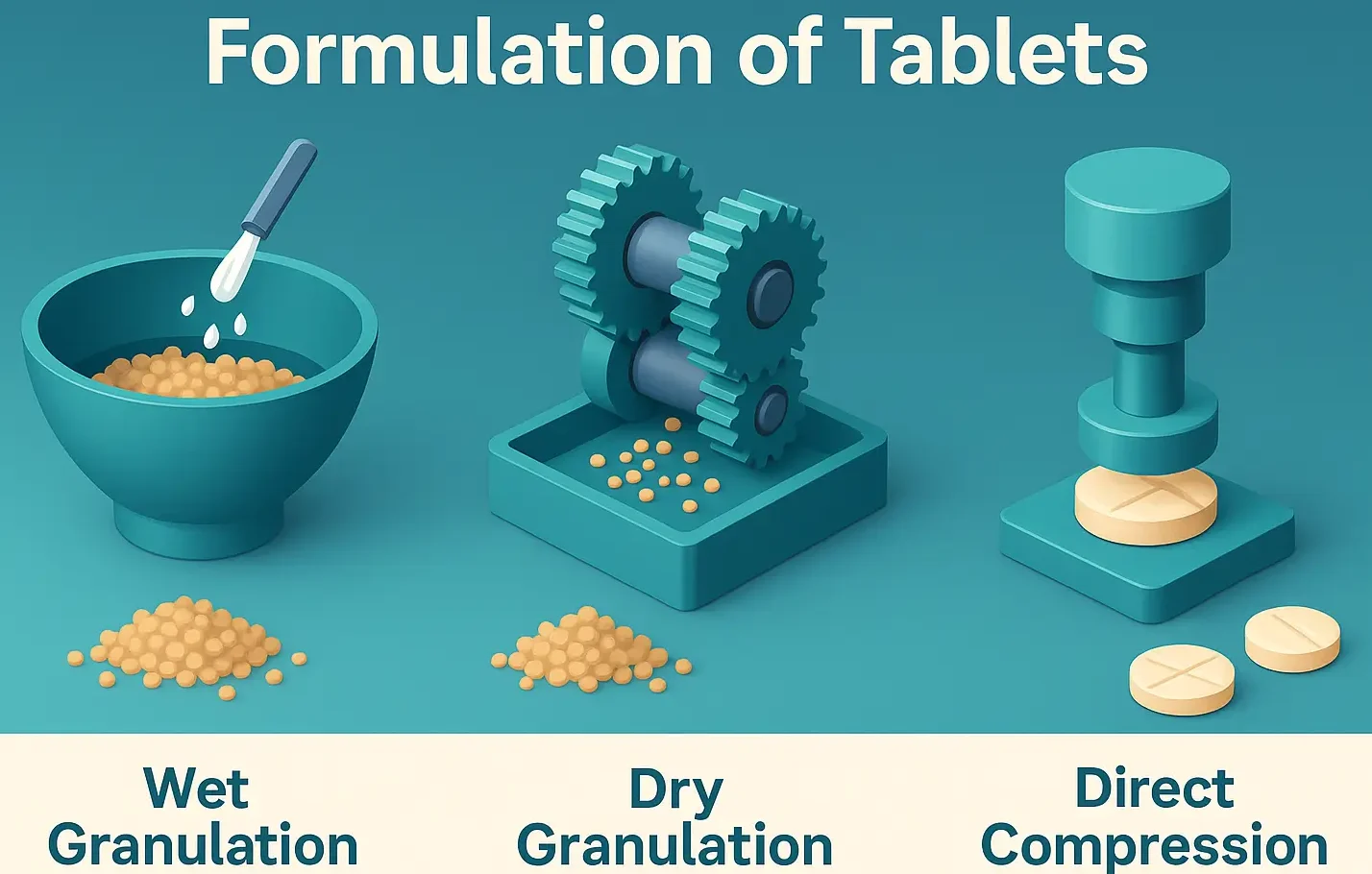
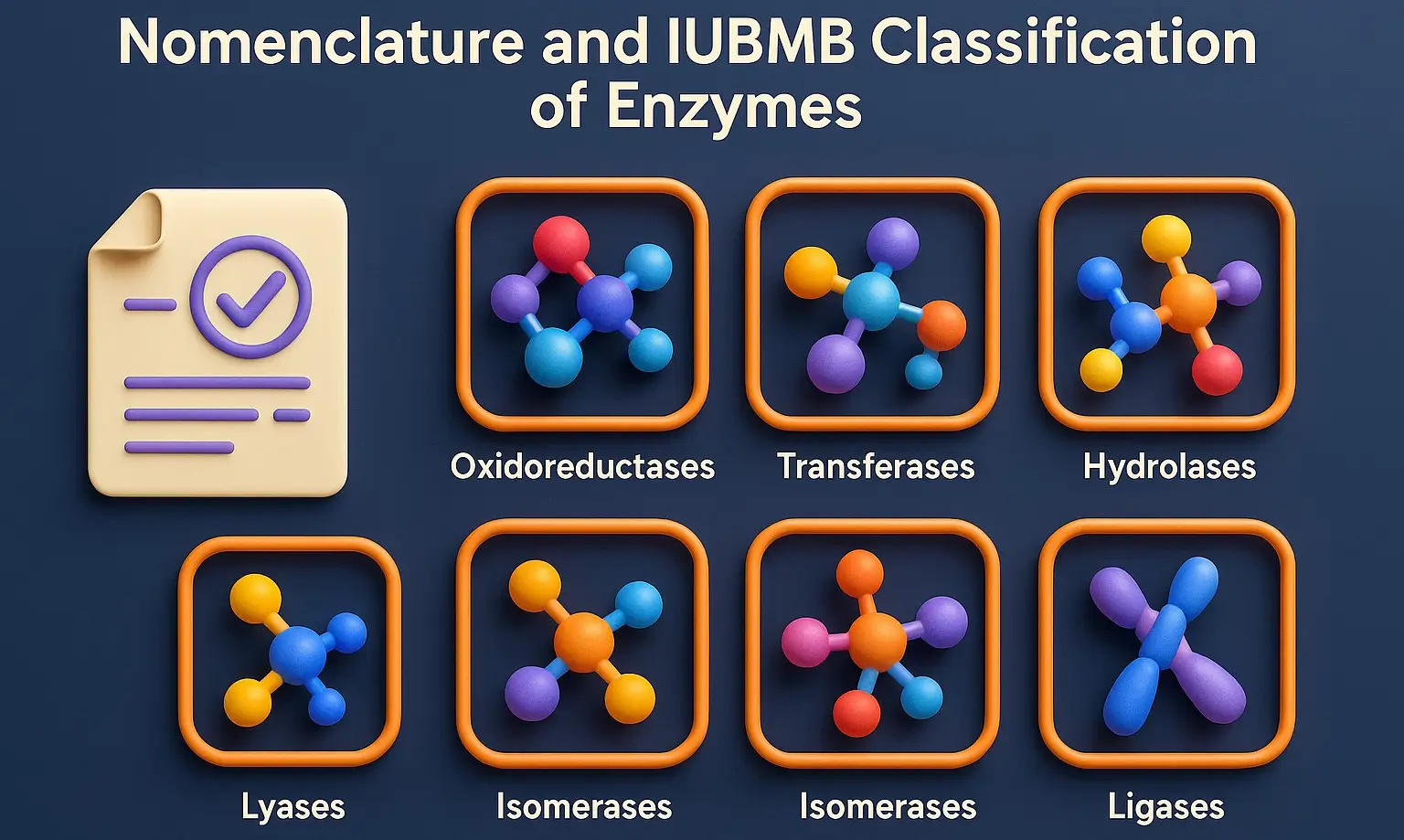
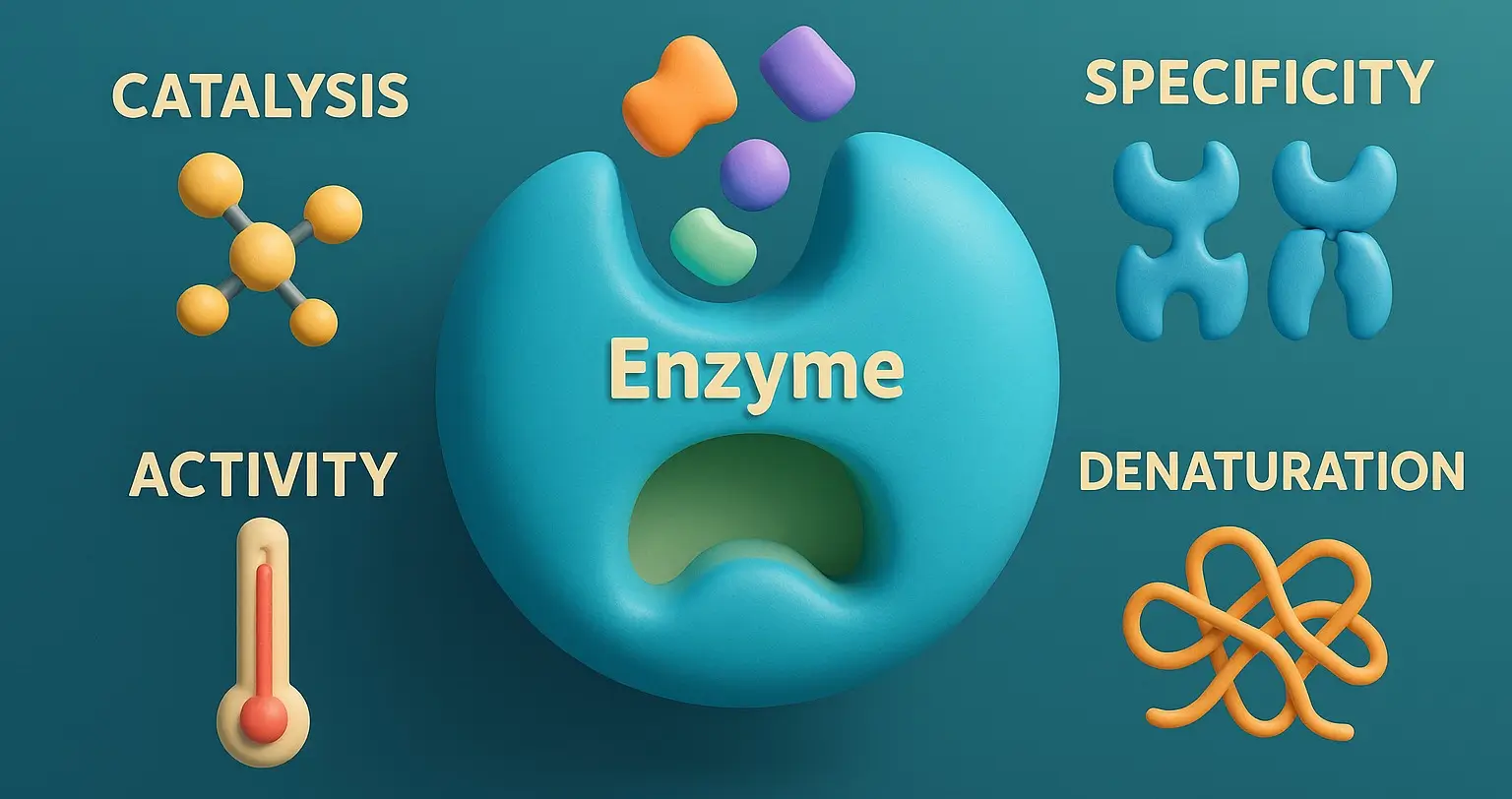
Opium Poppy Cultivation
Definition of Opium Poppy Cultivation The cultivation of Papaver somniferum (opium poppy) for producing opium and its derivatives. Licensing and Regulation Cultivation License: Required for legally growing opium poppy. Issued by the Central Bureau of Narcotics (CBN) or relevant state authorities. Criteria for Licensing: Land suitability and security measures. Compliance with agricultural and safety standards. … Read more