Substrate level phosphorylation
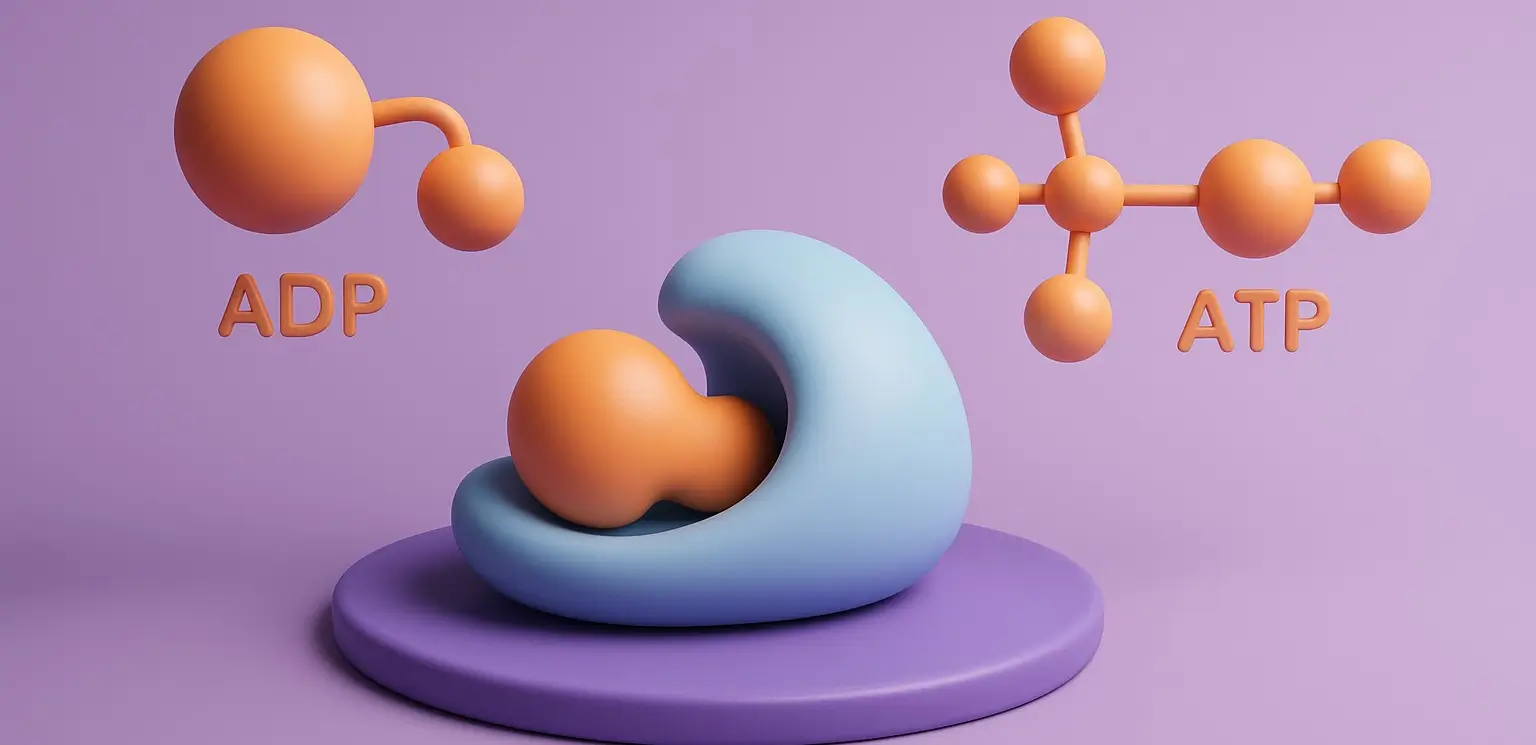
Substrate-level phosphorylation is a type of metabolic reaction in which a phosphate group is directly transferred from a phosphorylated intermediate (a substrate) to ADP (or GDP) to form ATP (or GTP) Substrate-Level Phosphorylation It is a direct method of ATP production, where a phosphate group is transferred from a high-energy substrate molecule to ADP. Unlike … Read more