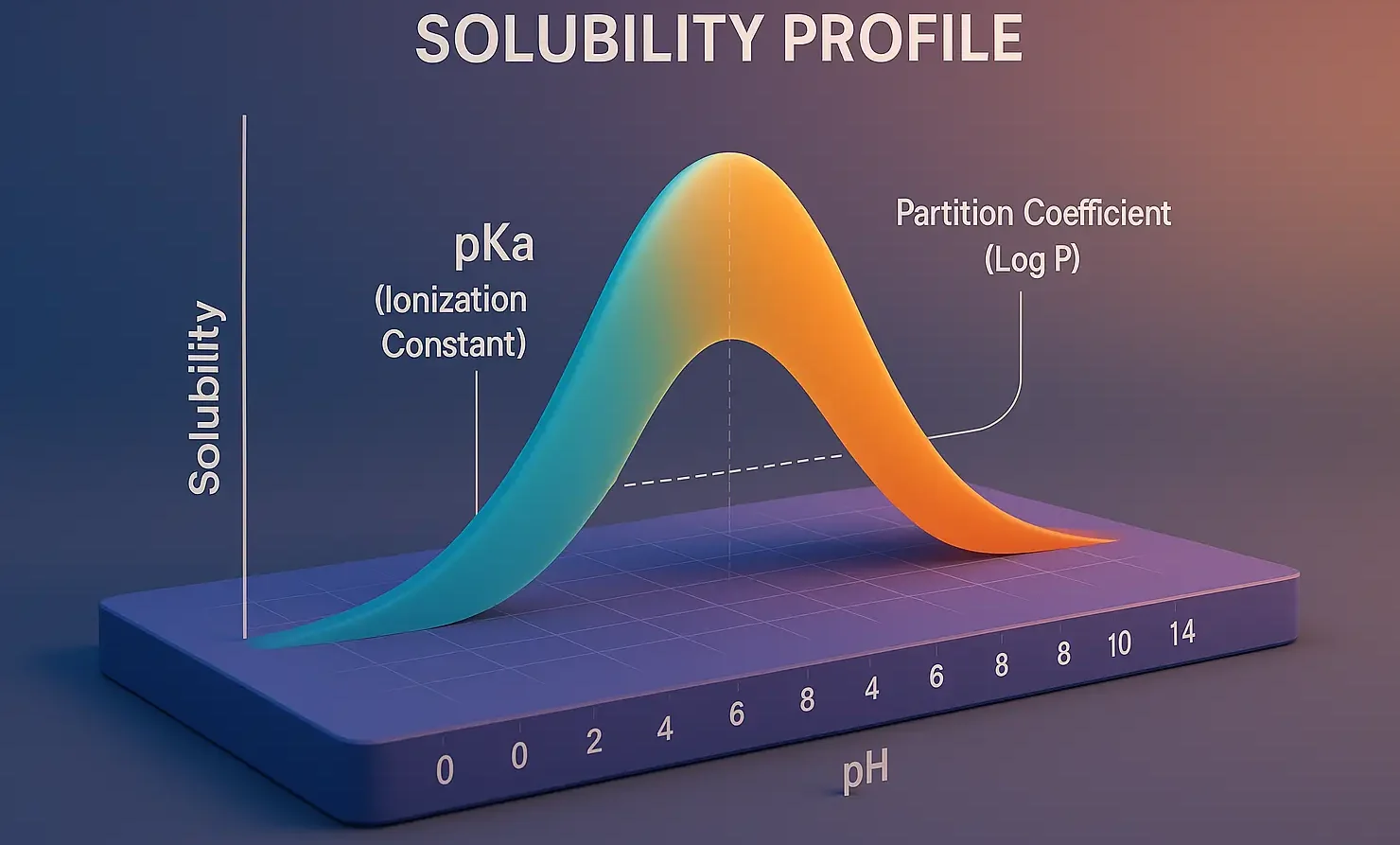
Solubility Profile
The solubility profile helps determine how a drug dissolves in bodily fluids, influencing its absorption and bioavailability. pKa, pH, and Log P are key parameters that affect a compound’s solubility profile and its formulation. pKa (Ionization Constant): Definition: The pH at which 50 Importance: Ionized drugs are more soluble in water, while unionized drugs have … Read more